Guest post by IDS Corporate Communications
Autonomously driving robotic assistance system for the automated placement of coil creels
Due to the industry standard 4.0, digitalisation, automation and networking of systems and facilities are becoming the predominant topics in production and thus also in logistics. Industry 4.0 pursues the increasing optimisation of processes and workflows in favour of productivity and flexibility and thus the saving of time and costs. Robotic systems have become the driving force for automating processes. Through the Internet of Things (IoT), robots are becoming increasingly sensitive, autonomous, mobile and easier to operate. More and more they are becoming an everyday helper in factories and warehouses. Intelligent imaging techniques are playing an increasingly important role in this.

To meet the growing demands in scaling and changing production environments towards fully automated and intelligently networked production, the company ONTEC Automation GmbH from Naila in Bavaria has developed an autonomously driving robotic assistance system. The „Smart Robot Assistant“ uses the synergies of mobility and automation: it consists of a powerful and efficient intralogistics platform, a flexible robot arm and a robust 3D stereo camera system from the Ensenso N series by IDS Imaging Development Systems GmbH.
The solution is versatile and takes over monotonous, weighty set-up and placement tasks, for example. The autonomous transport system is suitable for floor-level lifting of Euro pallets up to container or industrial format as well as mesh pallets in various sizes with a maximum load of up to 1,200 kilograms. For a customer in the textile industry, the AGV (Automated Guided Vehicle) is used for the automated loading of coil creels. For this purpose, it picks up pallets with yarn spools, transports them to the designated creel and loads it for further processing. Using a specially developed gripper system, up to 1000 yarn packages per 8-hour shift are picked up and pushed onto a mandrel of the creel. The sizing scheme and the position of the coils are captured by an Ensenso 3D camera (N45 series) installed on the gripper arm.
Application
Pallets loaded with industrial yarn spools are picked up from the floor of a predefined storage place and transported to the creel location. There, the gripper positions itself vertically above the pallet. An image trigger is sent to the Ensenso 3D camera from the N45 series, triggered by the in-house software ONTEC SPSComm. It networks with the vehicle’s PLC and can thus read out and pass on data. In the application, SPSComm controls the communication between the software parts of the vehicle, gripper and camera. This way, the camera knows when the vehicle and the grabber are in position to take a picture. This takes an image and passes on a point cloud to a software solution from ONTEC based on the standard HALCON software, which reports the coordinates of the coils on the pallet to the robot. The robot can then accurately pick up the coils and process them further. As soon as the gripper has cleared a layer of the yarn spools, the Ensenso camera takes a picture of the packaging material lying between the yarn spools and provides point clouds of this as well. These point clouds are processed similarly to provide the robot with the information with which a needle gripper removes the intermediate layers. „This approach means that the number of layers and finishing patterns of the pallets do not have to be defined in advance and even incomplete pallets can be processed without any problems,“ explains Tim Böckel, software developer at ONTEC. „The gripper does not have to be converted for the use of the needle gripper. For this application, it has a normal gripping component for the coils and a needle gripping component for the intermediate layers.“
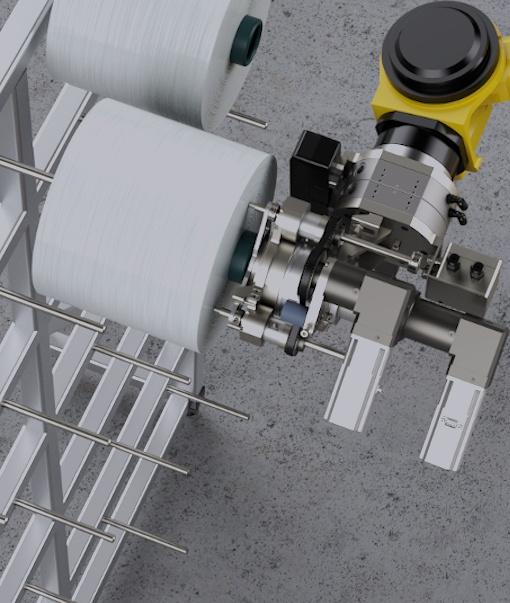
For this task, the mobile use for 3D acquisition of moving and static objects on the robot arm, the Ensenso 3D camera is suitable due to its compact design. The Ensenso N 45’s 3D stereo electronics are completely decoupled from the housing, allowing the use of a lightweight plastic composite as the housing material. The low weight facilitates the use on robot arms such as the Smart Robotic Asstistant. The camera can also cope with demanding environmental conditions. „Challenges with this application can be found primarily in the different lighting conditions that are evident in different rooms of the hall and at different times of the day,“ Tim Böckel describes the situation. Even in difficult lighting conditions, the integrated projector projects a high-contrast texture onto the object to be imaged by means of a pattern mask with a random dot pattern, thus supplementing the structures on featureless homogenous surfaces. This means that the integrated camera meets the requirements exactly. „By pre-configuring within NxView, the task was solved well.“ This sample programme with source code demonstrates the main functions of the NxLib library, which can be used to open one or more stereo and colour cameras whose image and depth data are visualised. Parameters such as exposure time, binning, AOI and depth measuring range can – as in this case – be adjusted live for the matching method used.
The matching process empowers the Ensenso 3D camera to recognise a very high number of pixels, including their position change, by means of the auxiliary structures projected onto the surface and to create complete, homogeneous depth information of the scene from this. This in turn ensures the necessary precision with which the Smart Robot Assistant proceeds. Other selection criteria for the camera were, among others, the standard vision interface Gigabit Ethernet and the global shutter 1.3 MP sensor. „The camera only takes one image pair of the entire pallet in favour of a faster throughput time, but it has to provide the coordinates from a relatively large distance with an accuracy in the millimetre range to enable the robot arm to grip precisely,“ explains Matthias Hofmann, IT specialist for application development at ONTEC. „We therefore need the high resolution of the camera to be able to safely record the edges of the coils with the 3D camera.“ The localisation of the edges is important in order to be able to pass on as accurate as possible the position from the centre of the spool to the gripper.
Furthermore, the camera is specially designed for use in harsh environmental conditions. It has a screwable GPIO connector for trigger and flash and is IP65/67 protected against dirt, dust, splash water or cleaning agents.
Software
The Ensenso SDK enables hand-eye calibration of the camera to the robot arm, allowing easy translation or displacement of coordinates using the robot pose. In addition, by using the internal camera settings, a „FileCam“ of the current situation is recorded at each pass, i.e. at each image trigger. This makes it possible to easily adjust any edge cases later on, in this application for example unexpected lighting conditions, obstacles in the image or also an unexpected positioning of the coils in the image. The Ensenso SDK also allows the internal camera LOG files to be stored and archived for possible evaluation.

ONTEC also uses these „FileCams“ to automatically check test cases and thus ensure the correct functioning of all arrangements when making adjustments to the vision software. In addition, various vehicles can be coordinated and logistical bottlenecks minimised on the basis of the control system specially developed by ONTEC. Different assistants can be navigated and act simultaneously in a very confined space. By using the industrial interface tool ONTEC SPSComm, even standard industrial robots can be safely integrated into the overall application and data can be exchanged between the different systems.
Outlook
Further development of the system is planned, among other things, in terms of navigation of the autonomous vehicle. „With regard to vehicle navigation for our AGV, the use of IDS cameras is very interesting. We are currently evaluating the use of the new Ensenso S series to enable the vehicle to react even more flexibly to obstacles, for example, classify them and possibly even drive around them,“ says Tim Böckel, software developer at ONTEC, outlining the next development step.
ONTEC’s own interface configuration already enables the system to be integrated into a wide variety of Industry 4.0 applications, while the modular structure of the autonomously moving robot solution leaves room for adaptation to a wide variety of tasks. In this way, it not only serves to increase efficiency and flexibility in production and logistics, but in many places also literally contributes to relieving the workload of employees.
More at: https://en.ids-imaging.com/casestudies-detail/picked-up-and-put-off-ensenso.html



