IFR presents World Robotics Report 2022 #WorldRobotics
Frankfurt, Oct 13, 2022 — The new World Robotics report shows an all-time high of 517,385 new industrial robots installed in 2021 in factories around the world. This represents a growth rate of 31% year-on-year and exceeds the pre-pandemic record of robot installation in 2018 by 22%. Today, the stock of operational robots around the globe hits a new record of about 3.5 million units.”
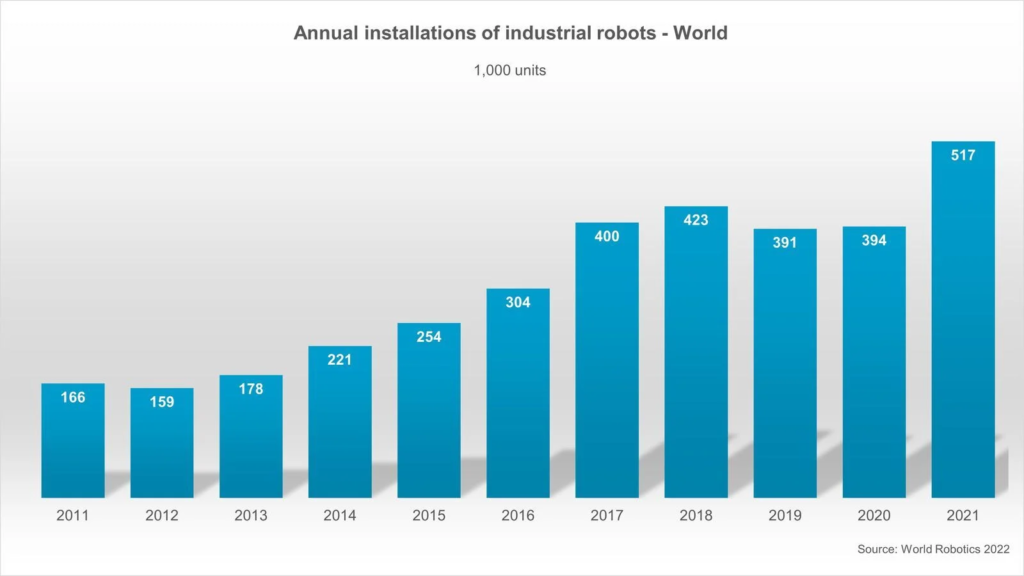
“The use of robotics and automation is growing at a breathtaking speed,” says Marina Bill, President of the International Federation of Robotics. “Within six years, annual robot installations more than doubled. According to our latest statistics, installations grew strongly in 2021 in all major customer industries, although supply chain disruptions as well as different local or regional headwinds hampered production.”
Asia, Europe and the Americas – overview
Asia remains the world’s largest market for industrial robots. 74% of all newly deployed robots in 2021 were installed in Asia (2020: 70%).
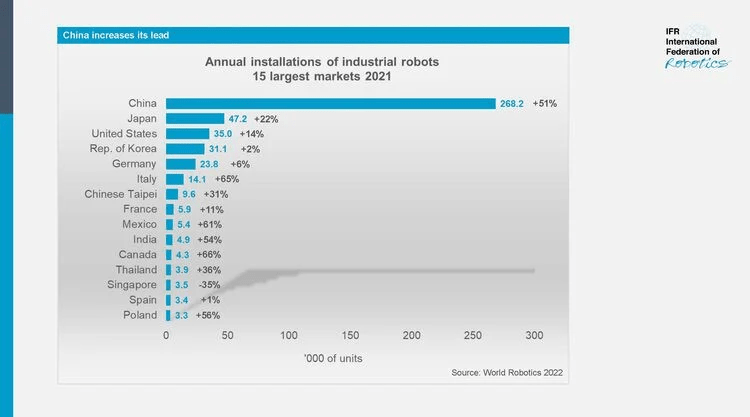
Installations for the region´s largest adopter China grew strongly by 51% with 268,195 units shipped. Every other robot installed globally in 2021 was deployed here. The operational stock broke the 1-million-unit mark (+27%). This high growth rate indicates the rapid speed of robotization in China.
Japan remained second to China as the largest market for industrial robots. Installations were up 22% in 2021 with 47,182 units. Japan’s operational stock was 393,326 units (+5%) in 2021.
After two years of declining robot installations in all major industries, numbers began growing again in 2021. Japan is the world´s predominant robot manufacturing country: Exports of Japanese industrial robots achieved a new peak level at 186,102 units in 2021.
The Republic of Korea was the fourth largest robot market in terms of annual installations, following the US, Japan and China. Robot installations increased by 2% to 31,083 units in 2021. This followed four years of declining installation figures. The operational stock of robots was computed at 366,227 units (+7%).
Europe
Robot installations in Europe were up 24% to 84,302 units in 2021. This represents a new peak. Demand from the automotive industry was steady, while demand from the general industry was up by 51%. Germany, which belongs to the five major robot markets in the world, had a share of 28% of total installations in Europe. Italy followed with 17% and France with 7%.
The number of installed robots in Germany grew by 6% to 23,777 units in 2021. This is the second highest installation count ever recorded, following the peak caused by massive investments from the automotive industry in 2018 (26,723 units). The operational stock of robots was calculated at 245,908 units (+7%) in 2021. Exports of industrial robots from Germany were up 41% to 22,870 units, exceeding the pre-pandemic level.
Italy is the second largest robot market in Europe after Germany. The main growth driver between 2016 and 2021 was the general industry with an annual average growth rate of 8%.
The operational stock of robots was computed at 89,330 units (+14%) in 2021. The 2021 results were driven by catch-up effects and earlier purchases due to a reduction of tax credits in 2022. This created a 65% increase of robot installations to a new record level of 14,083 units in 2021.
The robot market in France ranked third in Europe in 2021 regarding annual installations and operational stock, following Italy and Germany. In 2021, robot installations increased by 11% to 5,945 units. The operational stock of robots in France was calculated at 49,312 units, a 10% increase over the previous year.
In the United Kingdom, industrial robot installations were down by 7% to 2,054 units. The operational stock of robots was calculated at 24,445 units (+6%) in 2021. This is less than a tenth of Germany´s stock. The automotive industry reduced installations by 42% to 507 units in 2021.
The Americas
In 2021, 50,712 industrial robots were installed in the Americas, 31% more than in 2020. This is a remarkable recovery from the pandemic dip in 2020 and the second time that robot installations in the Americas exceeded the 50,000-unit mark, with 55,212 units in 2018 setting the benchmark.
New installations in the United States were up by 14% to 34,987 units in 2021. This exceeded the pre-pandemic level of 33,378 units in 2019 but was still considerably lower than the peak level of 40,373 units in 2018. The automotive industry is still by far the number one adopter with 9,782 units installed in 2021. However, demand had been continuously declining for five years (2016-2021). In 2021 installations were down 7% compared to 2020. Installations in the metal and machinery industry surged by 66% to 3,814 units in 2021, putting this industry into second place in terms of robot demand. The plastic and chemical products industry had 3,466 robots (+30%) newly installed in 2021. The food and beverage industry installed 25% more robots, reaching a new peak level of 3,402 units in 2021. The robotics industry offers hygienic solutions that experienced growing demand during the Covid-19 pandemic.
Outlook
Rising energy prices, intermediate product prices and scarcity of electronic components are challenging all branches of the global economy. But order books are full and demand for industrial robots has never been higher. In total, global robot installations are expected to grow by 10% to almost 570,000 units in 2022. The post-pandemic boom experienced in 2021 is expected to fade out in 2022. From 2022 to 2025, average annual growth rates in the medium to upper single-digit range are forecast.
Orders for World Robotics 2022 Industrial Robots and Service Robots reports can be placed online. Further downloads on the content are available here.