The mBot2 programming robot replaces the globally successful mBot1 after 8 years and inspires with state-of-the-art sensor technology, new motors and a brand new AI control board in a familiar design. For children, teachers and tinkerers who want to learn more about computer science, STEM, IoT, AI and block-based coding through play

Ubstadt-Weiher, 29.04.2021 – Over the past eight years, the educational robot mBot from MAKEBLOCK has not only taught millions of children, students, teachers and aspiring programmers complex STEM (science, technology, engineering, mathematics) relationships in a playful way, but also put a smile on their faces after completing successful missions. And the success story continues with the new mBot2: Under the carefully modified shell, which is now made of robust aluminum, concentrated state-of-the-art technology is packed that enables countless new programming and application possibilities. The most striking thing at first glance are the next-generation ultrasonic sensors, which look at you in bright blue. Who can resist this seductive look? The blue „eyes“ are not only suitable for precise distance measurement, they also convey emotions with the help of the controllable ambient lighting. The mBot2 almost seeks eye contact with the little programmers, because AI image recognition can be used to control speed via facial expressions, for example.
The „brain“ of the mBot2 is the powerful CyberPi microcontroller with integrated color display, speaker, microphone, light sensor, gyroscope, RGB display and more. The built-in WiFi and Bluetooth module allows you to connect to the Internet for smart functions such as speech recognition, speech synthesis, LAN broadcast and uploading data to Google Sheets. The mBot2 is currently the most exciting toy robot to build yourself (only a screwdriver required), versatile expandable and with great design freedom in programming, which also makes the inner workings of a robot tangible: Available now for an RRP of 139 EUR (incl. VAT) in the Solectric online shop.
mBot2 communicates with its environment – powered by CyberPi
One of the most important innovations of the mBot2 compared to the previous version is its network capability with the help of the CyberPi microcomputer. The programmable powerhouse, in combination with the mBlock coding editor, is a practical learning aid for computer science and AI education and sets hardly any limits to children’s play instinct. Teachers have the option of using Google Classroom, for example, to conduct interactive and advanced lessons in which several mBot2 communicate with each other via the Internet. In this way, the data from various devices can be collected, visualized and processed and initial programming for AI and IoT (Internet of Things) applications can be learned.
„The small educational robot mBot2 makes programming child’s play and encourages children to play creatively and interactively,“ explains Alexander Hantke, Head of Solectric Education. „For children who are interested in electronics, robotics and programming, the mBot2 is the ideal gift. Especially when children realize how other family members are also enthusiastic about the topic, they are often carried away by it. But it’s also important to let children make their own mistakes with the mBot2 in order to keep the fun factor high over a long period of time.“
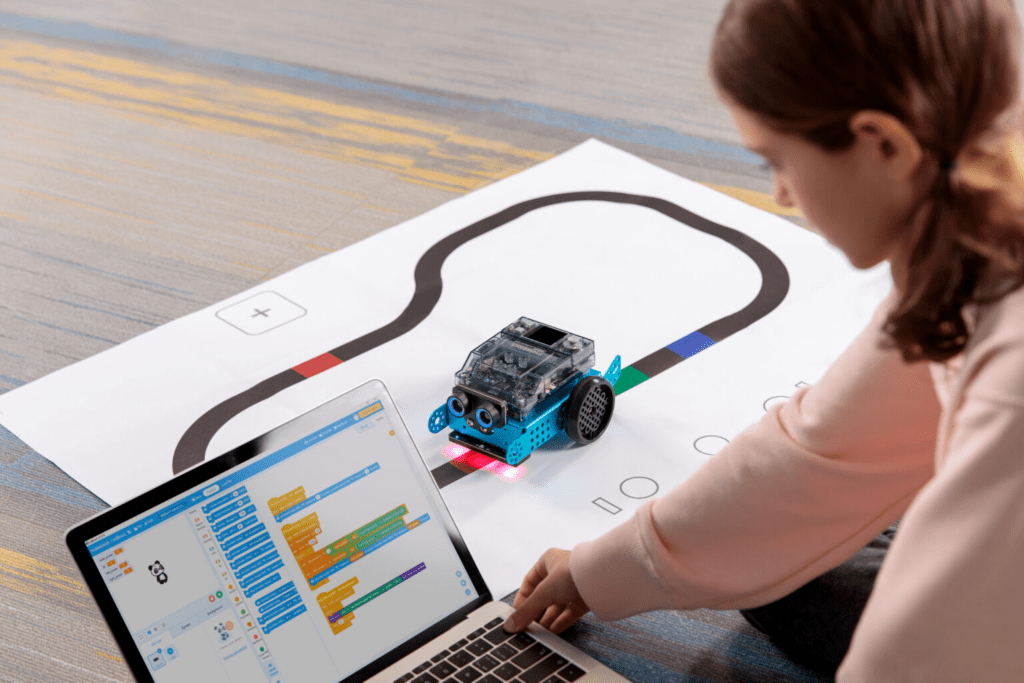
The CyberPi controller with a 1.44″ full-color display for displaying data, images and other information can be used not only as the robot’s data center, but also as a handheld device such as a game controller or monitoring device. The built-in memory and operating system make it possible to store and manage up to eight programs in the controller.
It gets really exciting when connecting multiple mBots2 creates a local network of robots that communicate with each other, share information, and perform tasks. If the mBot2 are connected to the Internet, they can perform advanced functions such as voice recognition, connect to a cloud or retrieve weather information. Maximum precision in controlling the rotation, speed and position of the wheels and the robot is promised by the 3-axis gyroscope installed in the CyberPi and the accelerometer for the optical encoder motors, which have a torque of 1.5 kg-cm, a maximum speed of 200 rpm and a detection accuracy of 1°.
mBlock – the powerful coding platform for easy entry into computer science and STEM lessons
The programmable robot helps kids learn how to code step-by-step through interactive drag-and-drop software. With the extensive tutorials and the included project cases, the young explorers can start with graphical programming and use the programming languages Scratch or Arduino C with one click. The mBlock software is compatible with Windows, macOS, Linux and Chromebook and also supports Android and iOS. Together with mBlock, the mBot2 becomes a powerful tool to get in touch with advanced technologies such as AI, IoT, and data science. Students start with block-based coding and move on to Python coding as they gain experience. The Python Editor supports the young programmers with smart functions such as intelligent autocomplete and syntax highlighting.
Extensible with mBuild modules and Makeblock components
The mBot2 can extend the radius of action with more than 60 different mBuild modules and connect up to 10 different sensors, motors, LEDs or other components in series at the same time. A micro-controller unit (MCU) is built into each module, which allows the modules to be connected without prior disconnection or a specific order. Meanwhile, add-on packages are also available for this programmable robot for children (not included) to teach programming, robotics, electronics and construction, while students can program and execute interactive missions through hands-on learning.
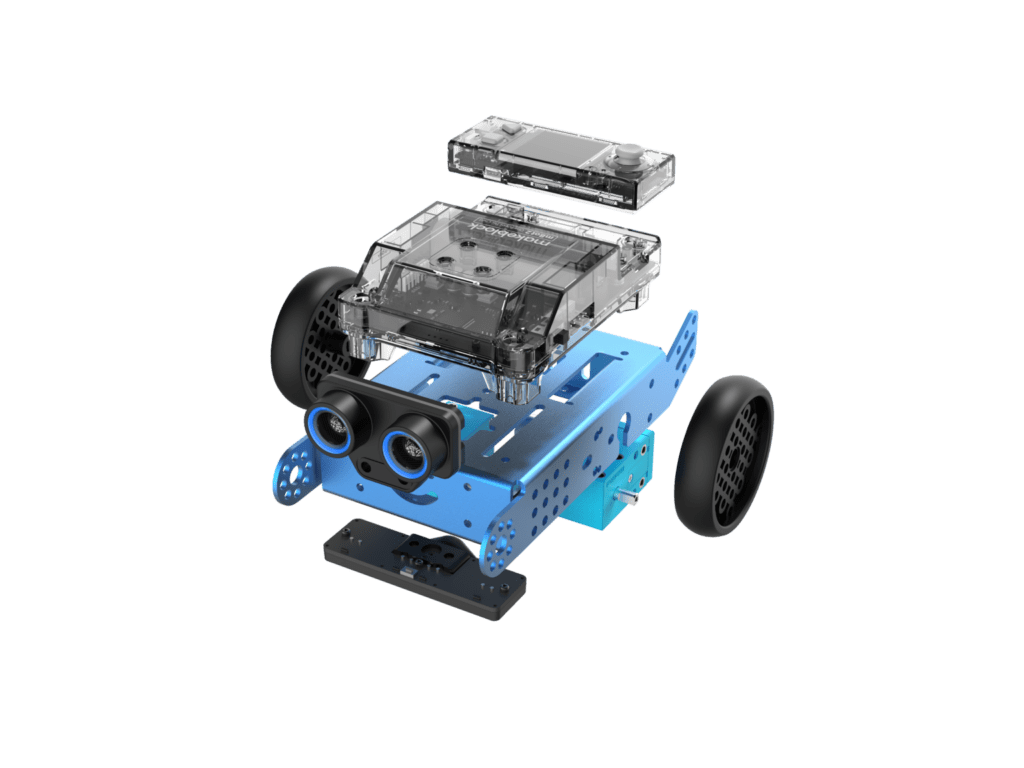
The mBot2 is equipped with a 2,500 mAh battery in the so-called mBot2 Shield, which can be conveniently charged via a USB C cable. The mBot2 Shield also has two connectors for encoder motors, two connectors for DC motors, and four connectors for servos. Some of the servo connectors can be connected to LED strips and analog/digital Arduino sensors.
For more information, please visit the Solectric online store: https://shop.solectric.de/educational/makeblock/mbot/3729/makeblock-mbot-2?c=4807