Guest Post by brickobotik:
LEGO Education ’s SPIKETM Prime is available on the market for more than one year by now. In our big test series, we presented in to you in detail. The Inventor 51515 which is the SPIKETM ’s home version, can also be bought by now. The software of both robots has reached a decent level. Earlier this year, we published our own e-book for the SPIKETM Prime Software that can be a helpful resource for everybody who still has questions about programming this robot. For people who like paperbacks more than digital e-books, we also sell it as a print-on-demand paperback on amazon.
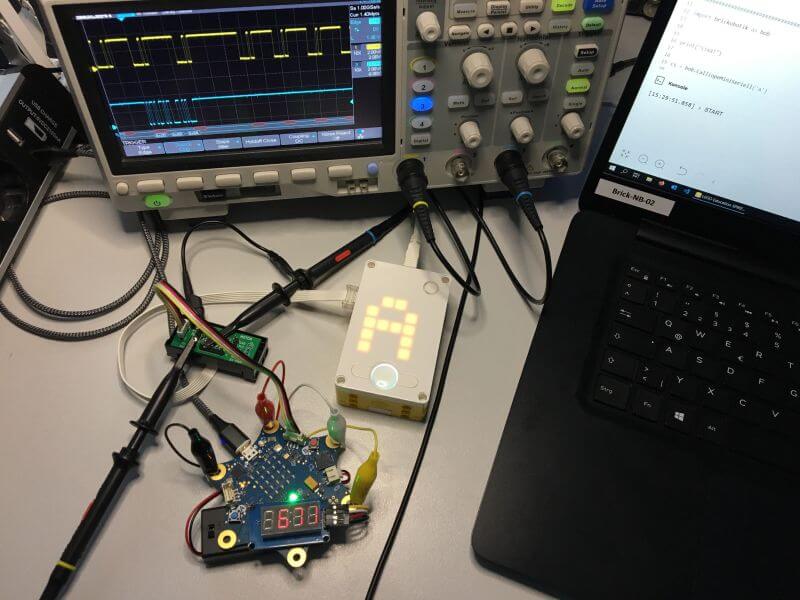
At brickobotik, we nevertheless continue to work with the SPIKETM Prime. On the one hand, we use it in our workshops and teacher-trainings. On the other hand, we are also interested in the electro-technics of the SPIKETM Prime. Therefore, we give you a little insight in our „briokobotik craft corner“ and present a little project on which we currently work.
An adapter board for the ultrasonic sensor
Many of you probably noticed the two Torx screws on the back of the ultrasonic sensor in the SPIKETM Prime and the Mindstorms Inventor set which you can ‚t find on the other sensors. If you unscrew these two screws, you can remove the white ultrasonic sensor device so that only the black shell remains in your hand. Here, the cable of the LEGO Powered Up connector ends up in a female header. This 8-pin female header has a pitch of 1.27 mm which cannot be accessed easily with conventional Arduino cables. That is why we decided to develop an adapter that breaks out the 1.27 mm pitch to 2.54 mm which is the conventional dimension of the Arduino, perfboards, breadboards etc.

Technical details about the breakout board
There are six signals within the Power Functions 2.0 connection:
1x 3.3 V power supply
1x GND
2x digital in-/output (GPIO), which can also be used for UART (115200 Baud, 8N1) Please note: The GPIOs do not supply enough current to operate the LEDs directly! A transistor circuit is necessary to supply an LED from the 3.3 V rail.
2x PWM for the motors
Please note: The voltage of these signals is supplied directly by the SPIKE ’s battery! Aocording to our measurements it is between 8.4 V and 6.3 V.
Each GPIO signal is provided with a resistor in series that provides a minimal protection against wrong GPIO configurations. They can easily be bypassed with a solder bridge.
On the left and right side, the same signals are spread out. On one side, you find the two GPIOs together with the power rails and on the other side, you find the PWM signals with the power rails. The signal lines to the left and right do not only fan out to contacts of
2.54 mm pitch but also to contacts of 2.00 mm pitch for the Grove connector system.
The respective 3.3 V power supply lines are by default open solder bridges. In this way, two independent power supplies will not compete destructively if for example a Calliope mini or other microcontroller is used. The open solder bridges can be closed with a bit of solder if required.
New possibilities with the breakout board
With our breakout board, connecting and using other sensors and motors with the SPIKETM Prime becomes much easier. It also opens the possibility of connecting the SPIKETM to a microcontroller like the Calliope mini. But you should note one important constraint: projeots like these are primarily suitable for advanced users. The wiring as well as the programming needs experience with the electronics and the respective sensor protocols.
Technical details about the control
The Powered Up signals are directly controllable via the SPIKETM Prime app but only using Python projects and on one’s own account. There is no „UltrasonicBreakout“ Python module or something similar by LEGOO . Nevertheless, descriptions and instructions for the respective MicroPython classes and methods can be found in the internet. People with experience with other MicroPython devices, especially with operating the MioroPython REPL, can quickly familiarize with the necessary details.
Order your own adapter board!
At briokobotik, we are going to continue to work with the adapter board and test its conneotion to different sensors. But we would also like to give the possibility of experimenting with connections to the SPIKETM Prime to all other home constructors and electro-technios enthusiasts who like to try it themselves. So, if you are interested in this adapter board and would like to purchase it, just send us an email to [email protected]. We will collect all requests and if there are enough people interested, we will inform you via email about the possibility of preordering the adapter board.
You don ‚t want to tinker but you are interested in a certain sensor that could be conneoted to the SPIKETM Prime? Visit our website at www.briokobotik.de and leave a oomment or a message with your requests for future projects and we will try to take them into account.