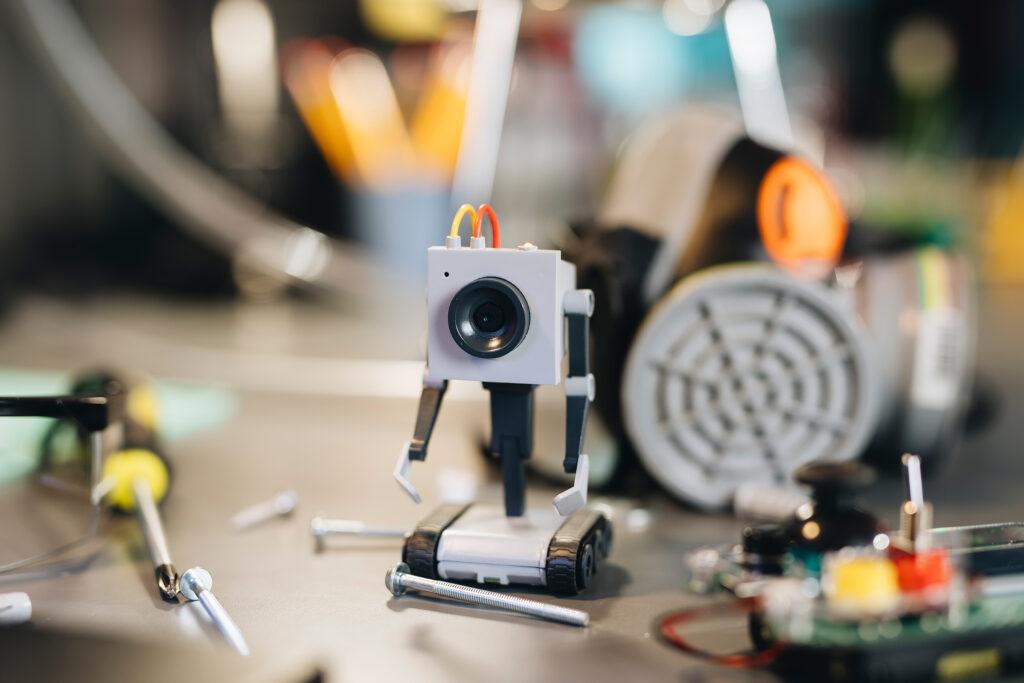
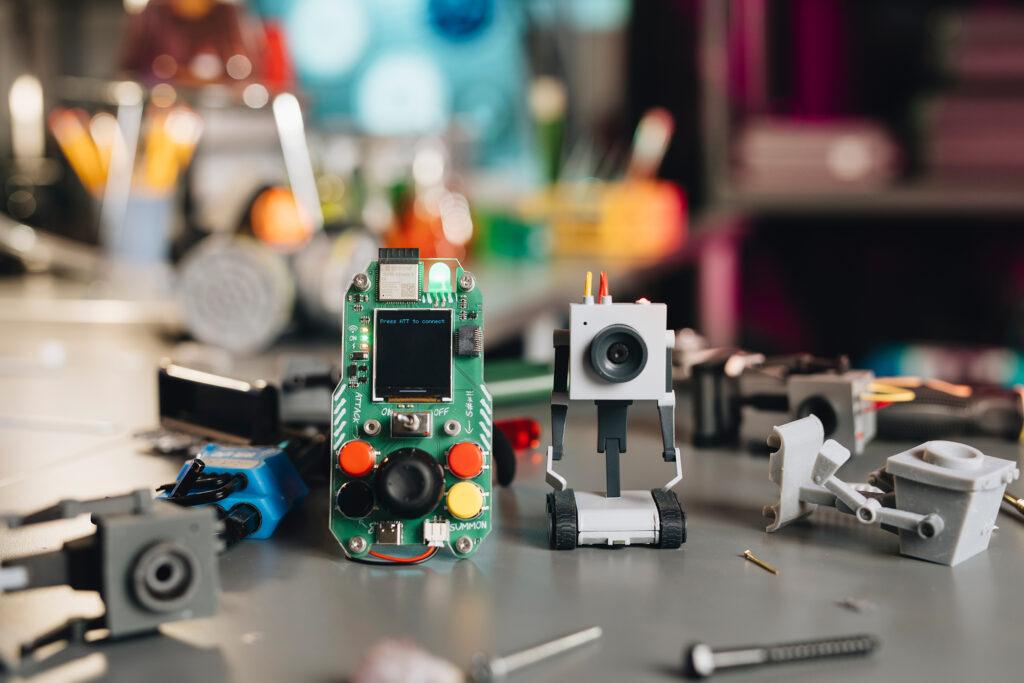
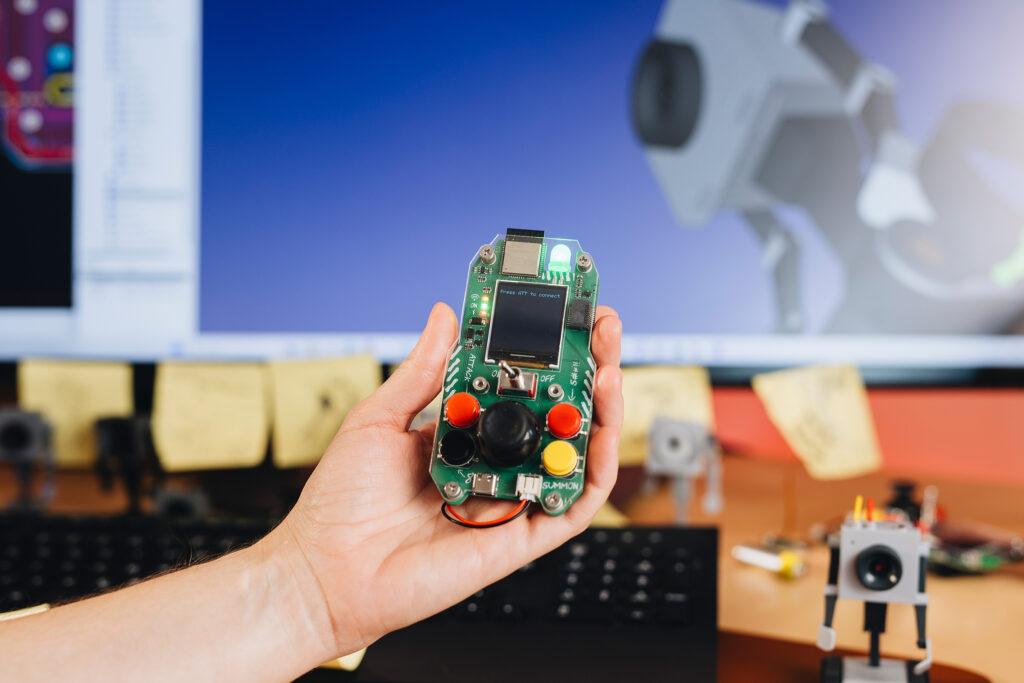
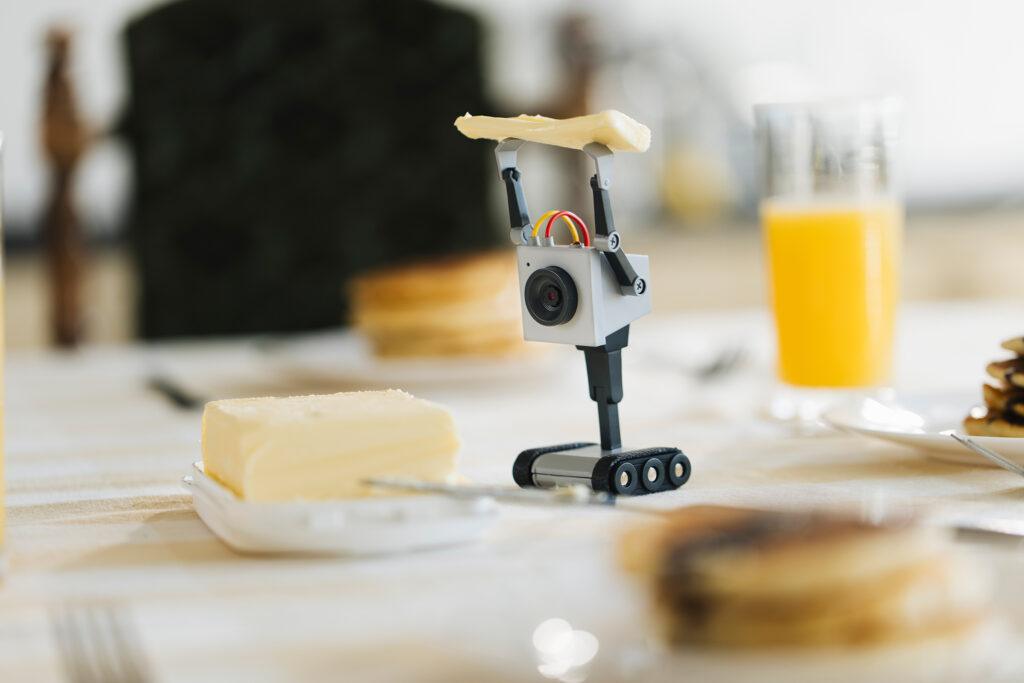
https://circuitmess.com/pages/butter-bot-teaser














Die Forschung zur Anwendung von Künstlicher Intelligenz in der Produktionssteuerung wird an der Universität in Potsdam mit einer Fabriksimulationsanlage von fischertechnik simuliert.
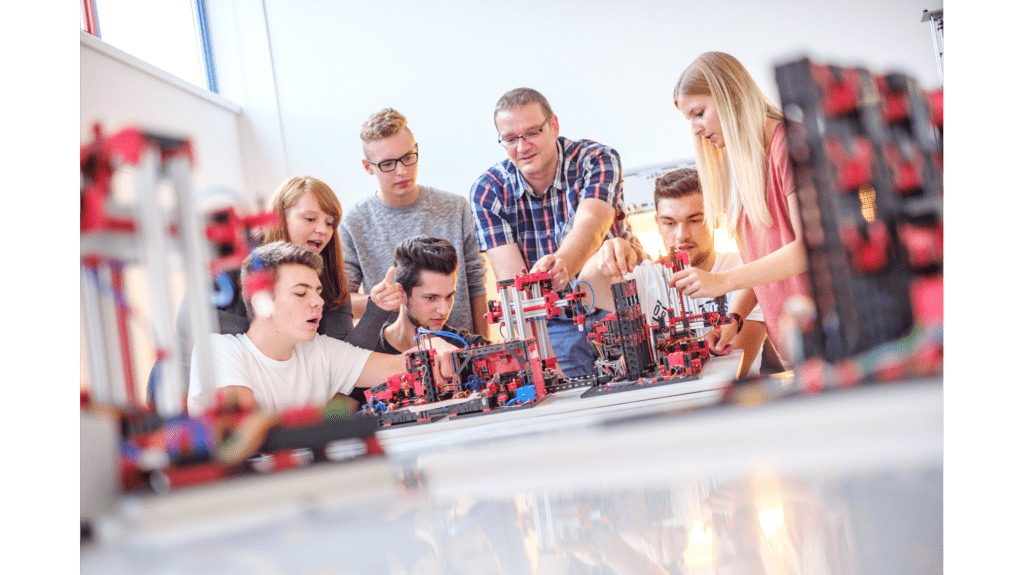
Marcus Grum ist Juniorprofessor für Wirtschaftsinformatik, insbesondere für KI-basierte Anwendungssysteme. Er beugt sich über ein ungefähr ein mal ein Meter großes Modell aus fischertechnik Bausteinen. Fasziniert schaut er zu, wie ein roter Holzstein von einem kleinen Hochregallager aus über ein Transportband zu verschiedenen Fertigungsstätten transportiert wird. Das Simulationsmodell von fischertechnik wird an Universitäten und in der Ausbildung eingesetzt, um den Bestellprozess, den Produktionsprozess und den Lieferprozess in digitalisierten und vernetzten Prozessschritten abzubilden.
An der Universität Potsdam wurde die fischertechnik Lernfabrik 4.0 in Kombination mit anderen Simulationstools und einem neuronalen Zwilling dazu verwendet, globale Fertigungssteuerungsprozesse nachzustellen. In einer Forschungsreihe wurde beispielsweise eine Marmeladenproduktion simuliert. Es wurde angenommen, dass Produkte weltweit an vier verschiedenen Fertigungsstätten gefertigt werden, die jedoch über unterschiedliche IT-Systeme verfügen.
Beleuchtet wurden sämtliche Prozesse, vom Beschaffen der Früchte bis hin zum Vertrieb an den Kunden. Die fischertechnik Lernfabrik 4.0 stellte eine von vier der vernetzten haptischen Fertigungsstationen dar. In der Anlage wurde der Prozess vom Einlagern der Früchte über das Einführen in die Kochmaschine zur Marmeladeherstellung bis hin zur Befüllung der Gläser und
das Ausliefern der Produkte simuliert. Das haptische Modell wurde an ein neuronales Netzwerk (ANN – Artificial Neural Network) angeschlossen. „Damit führten wir Versuchsreihen und Experimente durch, die valide Ergebnisse liefern und Produktionsineffizienzen aufzeigen. Wir können aus diesen Ergebnissen ableiten, wie derartige Ineffizienzen vermieden werden können“, erklärt Prof. Grum. Der Jungwissenschaftler wurde im vergangenen Jahr von der Stiftung Werner-von-Siemens-Ring für die Entwicklung eines methodischen Ansatzes geehrt, der es ermöglicht, Maschinen- und Geschäftsprozesse mit Hilfe von künstlichen neuronalen Netzen (KNN) zu modellieren.
Die zukünftige Forschung wird sich mit der empirischen Überprüfung der Anweisungen von neuronalen Netzen und entsprechenden Managementinterventionen befassen, die in realen Echtzeitproduktionen entstehen. „Auch hier wird die Fabriksimulationsanlage von fischertechnik zum Einsatz kommen“, sagt Prof. Grum.
Weiterführende Informationen zu den fischertechnik Fabriksimulationsanlagen: Simulationsmodelle für Industrie und Hochschulen – fischertechnik
Fraunhofer-Institute, Lamarr Institut, igus und Uni Bonn entwickeln Sprachmodell für kostengünstige Automatisierungslösungen in der Kommissionierung Köln, 1. Oktober 2024 – Mitte September fand bei igus in Köln ein Hackathon statt. Unter dem Motto „Künstliche Intelligenz trifft Robotics“ arbeiteten 17 Teilnehmer in drei interdisziplinären Teams daran, fortschrittliche Automatisierungslösungen für die Logistik zu entwickeln. Ziel des Hackathons war es, mithilfe eines großen KI-basierten Sprachmodells (Large Language Models, kurz: LLM) eine automatisierte Methode zum Verpacken von Pizzen zu schaffen. Die Veranstaltung fand in Zusammenarbeit mit dem Fraunhofer-Institut für Intelligente Analyse- und Informationssysteme IAIS, der Universität Bonn, dem Lamarr Institut und dem Fraunhofer-Institut für Materialfluss und Logistik IML statt. 20-mal Tonno, 10-mal Salami und 25-mal Margherita: So lautet die Bestellung des Supermarkts um die Ecke bei einem großen Hersteller von TK-Pizzen. Das klingt nach einer einfachen Aufgabe, ist jedoch immer noch Handarbeit, die aktuell manuell erledigt wird. Eine einfache und wenig anspruchsvolle Arbeit, für die sich oftmals kein Personal findet. Eine Lösung hierfür entwickelten 17 Teilnehmer der Fraunhofer Institute IAIS und IML, des Lamarr-Instituts für Maschinelles Lernen und Künstliche Intelligenz sowie Mitarbeitende der Universität Bonn innerhalb eines 5-tägigen Hackathons bei igus in Köln. Und zwar mithilfe von kosteneffizienter „Low Cost Robotic“ made in Cologne. Die Aufgabe des Hackathons lautete: Entwickelt eine Automatisierungslösung, die mithilfe von Künstlicher Intelligenz (KI) die Pizzen automatisch verpackt. Die Herausforderung bestand darin, einen Roboter so zu steuern, dass er über Sprachanweisungen direkt von Mitarbeitenden die richtigen Produkte erkennt, greift und in Mischpakete verpackt. Durch die Kombination von Generativen KI (GenAI) und Robotik sollte eine Lösung entwickelt werden, die diese repetitive Arbeit effizienter und kostengünstiger gestaltet. Automatisierung der Industrie mit KI und kostengünstiger Robotik Während des Hackathons arbeiteten drei Teams an einem realen Use Case, bei dem ein ReBeL Roboterarm vor einem Förderband mit verschiedenen Pizzaprodukten platziert wurde. Mithilfe einer Webcam und einem KI-basierten Segmentierungssystem (Segment Anything Model, SAM) erkannten die Systeme die verschiedenen Produkte auf dem Förderband und identifizierten ihre Position. Das Sprachmodell ordnete diese Objekte den gewünschten Produkten zu, basierend auf den natürlichsprachlichen Anweisungen. Anschließend legte der Roboter die Produkte in die Boxen, indem er die Anweisungen des Sprachmodells befolgte. Alexander Zorn vom Fraunhofer IAIS zeigte sich begeistert von den Ergebnissen des Hackathons: „Wir freuen uns sehr, mit dem igus Robotik-Know-how reale Proof-of-Concepts für Kunden in der Industrie zu entwickeln. Die Kombination von Künstlicher Intelligenz und Robotik bietet enorme Potenziale, um Arbeitsprozesse zu automatisieren und effizienter zu gestalten.“ Auch Alexander Mühlens, Prokurist und Leiter der Abteilung Low Cost Automation bei der igus GmbH, betonte die Bedeutung des Hackathons: „Die Zusammenarbeit mit den Instituten gibt uns die Möglichkeit, unseren Kunden zu zeigen, was alles mithilfe von KI und Low-Cost-Robotic möglich ist. Unser Traum ist es, Roboter über einen Sprachbefehl einfach steuern zu können, und das in jeder Anwendung.“ Der Hackathon zeigte, dass durch den Einsatz von LLMs und Robotik viele weitere Automatisierungsmöglichkeiten denkbar sind, wie beispielsweise das gleichzeitige Packen mehrerer Boxen, das Sortieren von Produkten nach speziellen Anweisungen oder das Überprüfen von Inhaltsstoffen auf Allergene mithilfe von Kamerasystemen. Die erfolgreiche Zusammenarbeit zwischen igus, dem Fraunhofer IAIS, dem Lamarr-Institut der Universität Bonn und dem Fraunhofer IML unterstreicht das Potenzial dieser Technologien für die industrielle Automatisierung. **Über die Partner** Das Fraunhofer IAIS ist eines der führenden Forschungsinstitute auf den Gebieten Künstliche Intelligenz (KI), Maschinelles Lernen und Big Data, während die Universität Bonn als Zentrum für Künstliche Intelligenz und Robotik bekannt ist. Das Fraunhofer IML in Dortmund brachte seine Fachexpertise in der Logistikautomatisierung und im Materialfluss ein. Während das Lamarr-Institut führend in der internationalen KI-Forschung und dem Maschinellen Lernen ist. |
Der stärkste Industrieroboter seiner Klasse
Konstanz, 08.10.2024 – Nach dem erfolgreichen Markteintritt von HORST1500, dem ersten Industrieroboter der neuen Generation an Digital Robots, hat fruitcore robotics auf der Motek in Stuttgart erstmals HORST1000 G2 vorgestellt. Der zweite Roboter dieser neuen Generation kombiniert innovative Antriebstechnologie mit intuitiver Bedienung und AI Copilot. HORST1000 G2 ist schnell zu installieren und zu programmieren – er erfordert kein Expertenwissen – und bietet zudem die besten Lebensdauerkosten am Markt.
Technologie-Führerschaft durch innovative Antriebstechnologie
Mit einer Traglast von bis zu 16 kg ist HORST1000 G2 der stärkste Roboter seiner Größenklasse am Markt. Der Roboter zeichnet sich, wie auch HORST1500, durch eine einzigartige, patentierte Antriebstechnologie aus, die wartungsfrei und besonders kosteneffizient ist und so die Lebensdauerkosten deutlich senkt. Eine 6-jährige Garantie auf den Antriebsstrang unterstreicht die Zuverlässigkeit und Wirtschaftlichkeit des Systems.
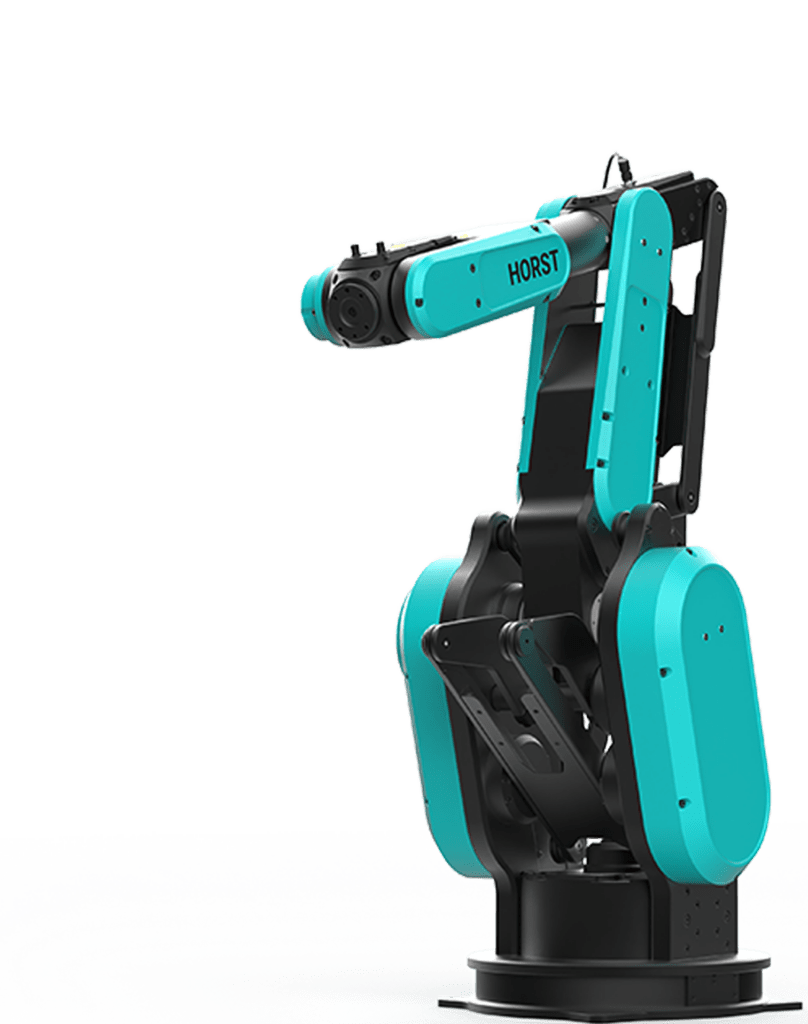
„Unsere Technologie vereint Innovation und wirtschaftlichen Mehrwert, um Automatisierung für eine breite Anwenderbasis zugänglich zu machen“, sagt Jens Riegger, Geschäftsführer (CEO) von fruitcore robotics. „Unternehmen, die auf unsere Roboter setzen, erzielen bereits nach wenigen Monaten einen beeindruckenden ROI und verschaffen sich einen klaren Wettbewerbsvorteil.“
Intelligente Steuerung und sichere Mensch-Maschine-Interaktion
Ein Highlight der neuen Digital Robot Generation ist der in der Steuerungssoftware integrierte AI Copilot, der den Roboter mit kognitiven Fähigkeiten ausstattet. Diese Technologie erlaubt es Anwendern, in Echtzeit mit dem Roboter zu kommunizieren und komplexe Aufgaben durch KI-Unterstützung schnell und präzise zu lösen. Der AI Copilot vereinfacht nicht nur den Support, sondern hilft auch bei spezifischen Programmieraufgaben. Das erhöht die Flexibilität weiter und reduziert die Abhängigkeit von Experten deutlich.
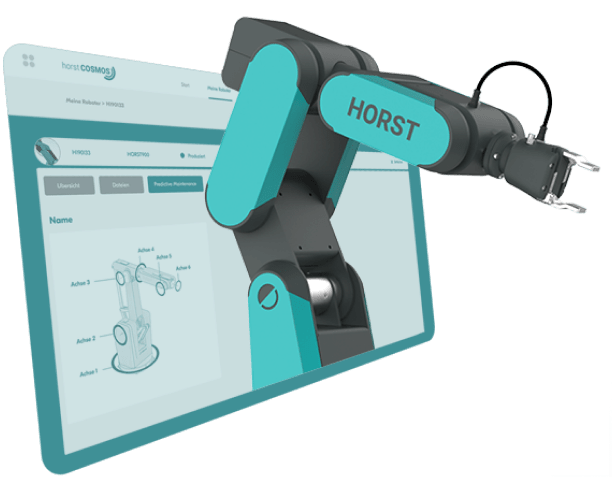
Darüber hinaus verfügt HORST1000 G2 über fortschrittliche Sicherheitslösungen, die für den sicheren Einsatz mit Menschen ausgelegt sind. Der Roboter kann, wie alle Roboter von fruitcore robotics, mit sicherreduzierter Geschwindigkeit und Sicherheitssensoren auch ohne Schutzzaun betrieben werden. Zudem ist er als sofort einsetzbares Solution Kit erhältlich, das alle Sicherheitsanforderungen erfüllt und wertvolle Zeit bei der CE-Konformität spart.
Optimiert für Maschinenbeschickung und raue Umgebungen
Mit einer Reichweite von 1141 mm und einer Traglast von bis zu 16 kg ist HORST1000 G2 für Aufgaben in der Maschinenbeschickung und im Teilehandling optimiert. Er bewegt mühelos schwere Tools und Bauteile über den gesamten Arbeitsbereich. Der Roboter ist mit der Schutzart IP54 ausgestattet. Das macht ihn ideal für raue Produktionsumgebungen.
Dank seiner kompakten Bauweise kann HORST1000 G2 nah an Maschinen heranfahren und tief in die Maschinen eingreifen, was die Flexibilität in beengten Produktionsumgebungen erheblich steigert. Der Roboter bearbeitet Trays mit einer Arbeitsfläche von bis zu 450 x 900 mm oder in quadratischer Form von bis zu 520 x 520 mm.

Durch intelligente Software-Features lassen sich verschiedene Maschinen-Fertigungsprogramme für unterschiedliche Arbeitsaufträge flexibel verwalten. Die reibungslose Einbindung von Maschinenfunktionen, wie der automatischen Türöffnung sowie die Kommunikation mit Spannmitteln bieten eine besonders effiziente Lösung für CNC-Maschinen. Zudem steigert die verbesserte Achsbeschleunigung die Effizienz beim Handling schwerer Teile und beim Einsatz ausladender Greifer.
Sofort einsatzbereit für CNC-Maschinen in der Metallverarbeitung
In Kombination mit dem Automatisierungsmodul für das Be- und Entladen von Maschinen bietet HORST1000 G2 eine sofort einsatzbereite Lösung, die speziell für das Be- und Entladen von Maschinen entwickelt wurde. „Das ermöglicht eine schnelle Implementierung in Produktionslinien, bei der nur 15 % des üblichen Projektaufwands anfallen“, erklärt Jens Riegger. Dank vorhandener Schnittstellen zu den meisten CNC-Maschinenherstellern lässt sich der Roboter nahtlos integrieren.
In der metallverarbeitenden Medizintechnik kommt der Roboter zur Herstellung chirurgischer Instrumente zum Einsatz, wo er effizient CNC-Fräs- oder Drehmaschinen belädt und entlädt oder Fertigungsprozesse vorbereitet. Auch in der metallverarbeitenden Automobilindustrie wird er für das Be- und Entladen von Maschinen eingesetzt oder sorgt bei Mess- und Prüftechnikaufgaben für gleichbleibend hohe Qualität.
Innovative Industrial Cameras for Robotics and Process Automation to Take Center Stage at Stand 6-36
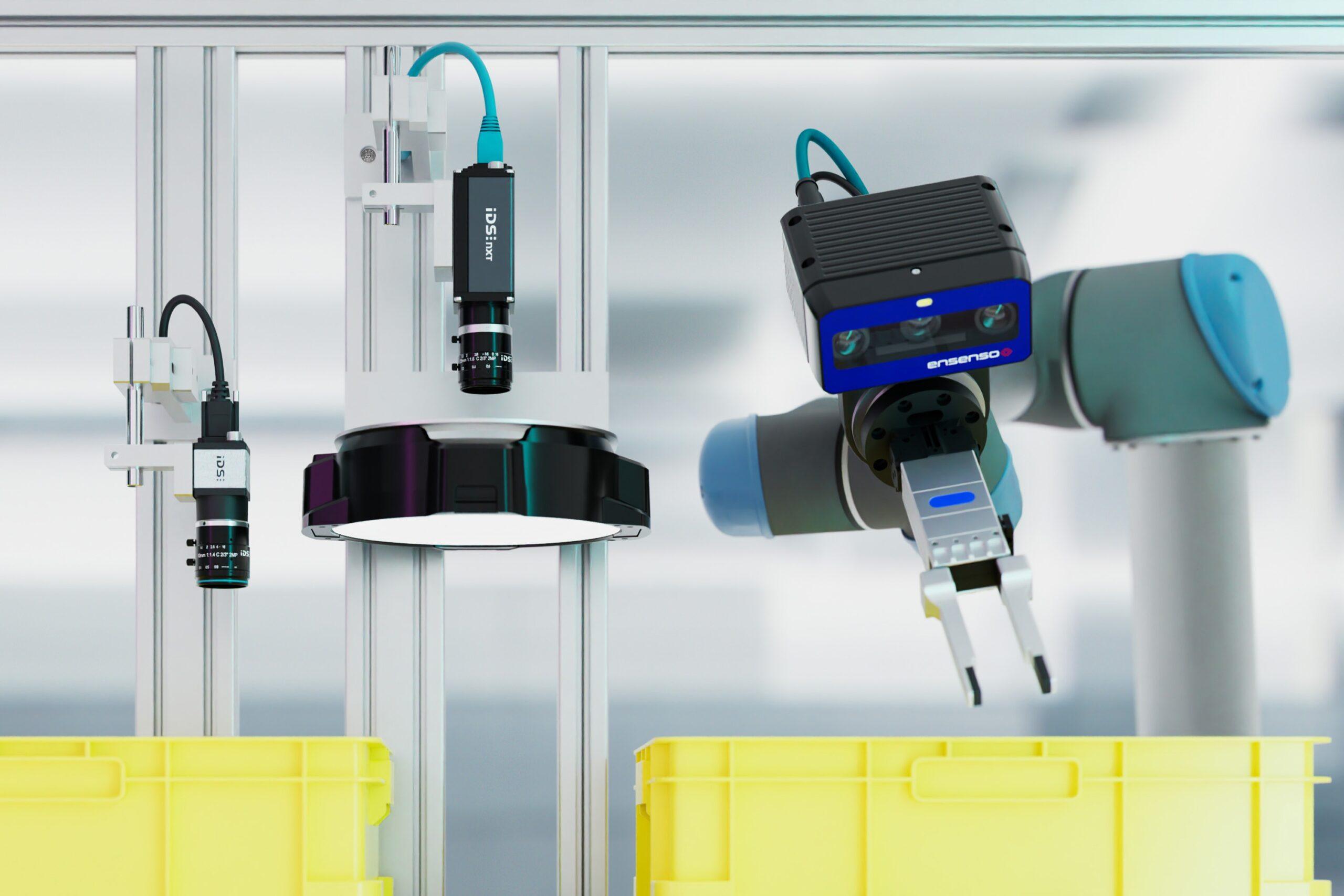

Detecting the smallest errors, increasing throughput rates, preventing wear – industrial cameras provide important information for automated processes. IDS will be demonstrating which technologies and products are particularly relevant at SPS / Smart Production Solutions in Nuremberg, Germany, from 12 to 14 November. If you want to experience how small cameras can achieve big things, stand 6-360 is the right place to visit.

Around 1,200 companies will be represented in a total of 16 exhibition halls at the trade fair for smart and digital automation. IDS will be taking part for the first time, focussing on industrial image processing for robotics, process automation and networked systems. Philipp Ohl, Head of Product Management at IDS, explains: „Automation and cameras? They go together like a lock and key. Depending on the task, very different qualities are required – such as particularly high-resolution images, remarkably fast cameras or models with integrated intelligence.“ Consequently, the products and demo systems that the company will be showcasing at SPS are highly diverse.
The highlights of IDS can be divided into three categories: 2D, 3D and AI-based image processing. The company will be presenting uEye Live, a newly developed product line. These industrial-grade monitoring cameras enable live streaming and are designed for the continuous monitoring and documentation of processes. IDS will also be introducing a new event-based sensor that is recommended for motion analyses or high-speed counting. It enables the efficient detection of rapid changes through continuous pixel-by-pixel detection instead of the usual sequential image-by-image analysis.
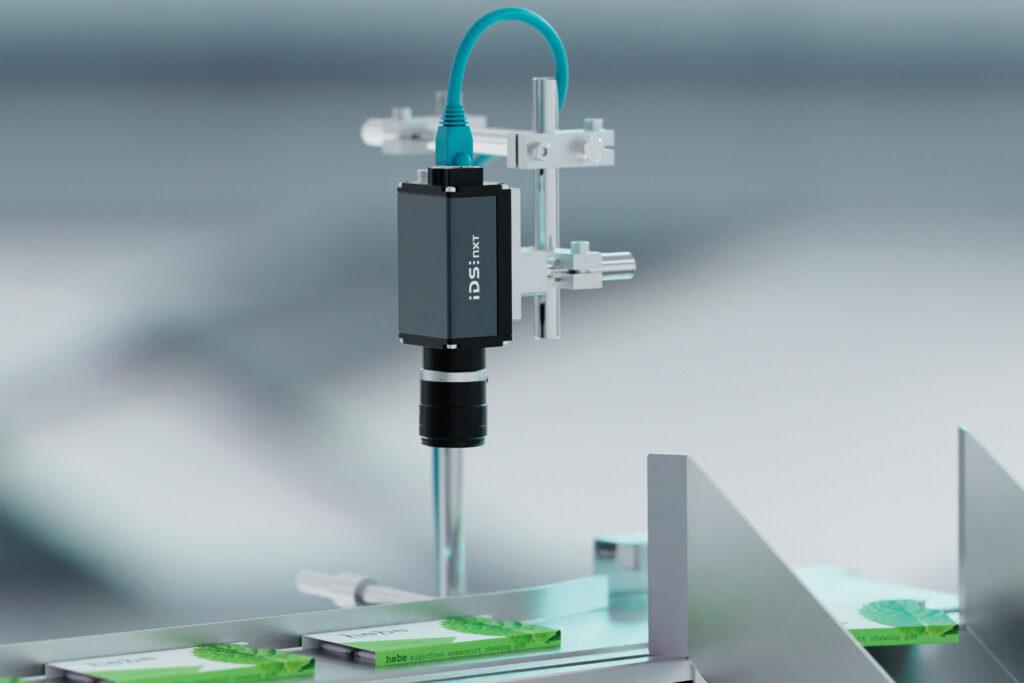

In the 3D cameras product segment, IDS will be demonstrating the advantages of the new stereo vision camera Ensenso B for precise close-range picking tasks as well as a prototype of the first time-of-flight camera developed entirely in-house. Anyone interested in robust character recognition will also find what they are looking for at the trade fair stand: Thanks to DENKnet OCR, texts and symbols on surfaces can be reliably identified and processed. IDS will be exhibiting at SPS, stand 6-360.
More information: https://en.ids-imaging.com/sps-2024.html
Montreal/Berlin, 18. September 2024 – Vention, das Unternehmen hinter der cloud-basierten Manufacturing Automation Platform (MAP), stellt auf seinem heutigen Demo Day in Berlin eine neue KI-Anwendung vor. MachineMotion AI ist der erste KI fähige Automatisierungscontroller mit beschleunigter Computertechnologie von NVIDIA.
Als Herzstück des Hardware- und Software-Ökosystems von Vention schließt MachineMotion AI die Lücke zwischen herkömmlichen speicherprogrammierbaren Steuerungen (SPS) und modernen Roboterprogrammierumgebungen. Der Controller der dritten Generation wurde entwickelt, um die Konzeption und Bereitstellung von Roboteranwendungen für produzierende Unternehmen jeder Größe erheblich zu vereinfachen.
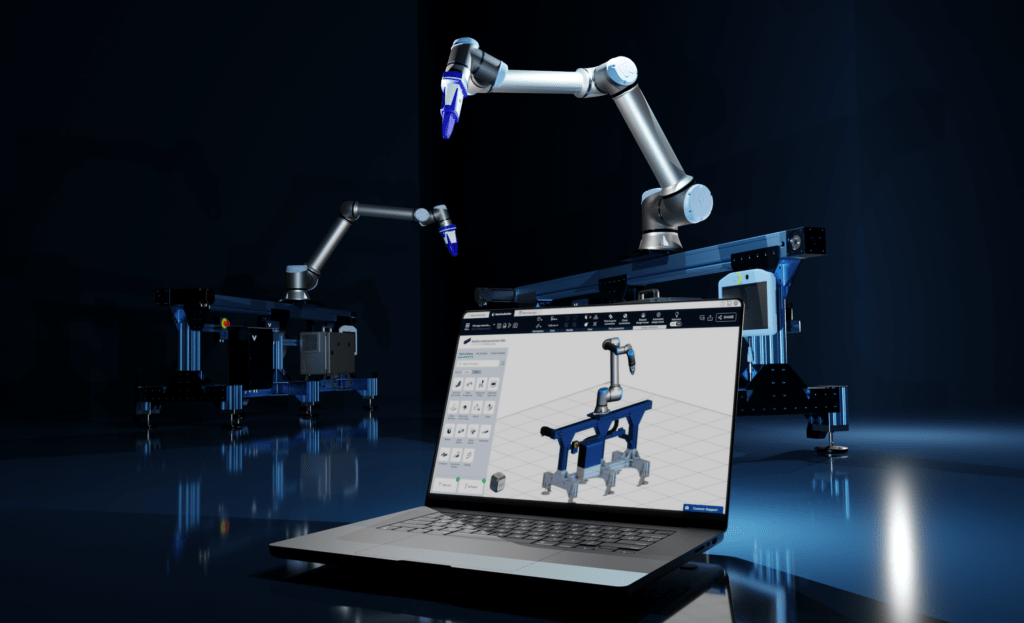
MachineMotion AI basiert auf der NVIDIA Jetson-Plattform für Edge-KI und -Robotik. Der Controller entwickelt KI-fähige Roboter mit NVIDIA GPU-beschleunigter Pfadplanung weiter und bietet die Möglichkeit, 2D-/3D-Wahrnehmungsmodelle auszuführen, die in synthetischen und physischen Umgebungen trainiert wurden.
MachineMotion AI ist mit führenden Robotermarken (z.B. Universal Robots, FANUC und ABB) kompatibel und lässt sich per Plug-and-Play mit Hunderten von Bewegungsgeräten und Sensoren verbinden – von Förderbändern und Aktuatoren bis hin zu Sicherheitsgeräten, Computer-Vision-Systemen, Telepräsenzkameras und mehr.
„Wir sind auf dem Weg, die industrielle Automatisierung zu demokratisieren und bauen dabei das umfassendste Unternehmen für industrielle Automatisierung und Robotik auf. Die heutigen Ankündigungen festigen Ventions Position als intuitivste Plattform für Automatisierung und Robotik und zeigen gleichzeitig die fortschrittlichen Funktionen, die Experten in der Branche benötigen“, sagt Etienne Lacroix, Gründer und CEO von Vention.
Weitere Informationen zu der Zusammenarbeit mit NVIDIA finden Sie hier. Demo Day in Berlin (18.9.)
Der diesjährige europäische Demo Day findet am 18.9. ab 14 Uhr in der Vention Europazentrale in Berlin statt. Etienne Lacroix, Gründer und CEO von Vention, wird vor Ort sein und für Pressegespräch zur Verfügung stehen. Mehr Informationen zum Event in Berlin finden Sie hier.
Über Vention
Vention hilft Unternehmen, ihre Produktionsbereiche durch eine demokratisierte Benutzererfahrung in nur wenigen Tagen zu automatisieren. Mit der digitalen Fertigungsautomatisierungsplattform MAP von Vention können Kunden automatisierte Geräte direkt über ihren Webbrowser entwerfen, bestellen und bereitstellen. Vention hat seinen Hauptsitz in Montreal und Niederlassungen in Berlin und Boston. Die über 300 Mitarbeiter betreuen mehr als 4.000 Kunden auf fünf Kontinenten und in 25 Fertigungsindustrien.
siehe auch meinen Vergleich zur ersten Generation: https://robots-blog.com/2024/08/22/unterschiede-zwischen-vex-iq-1st-generation-und-vex-iq-2nd-generation/
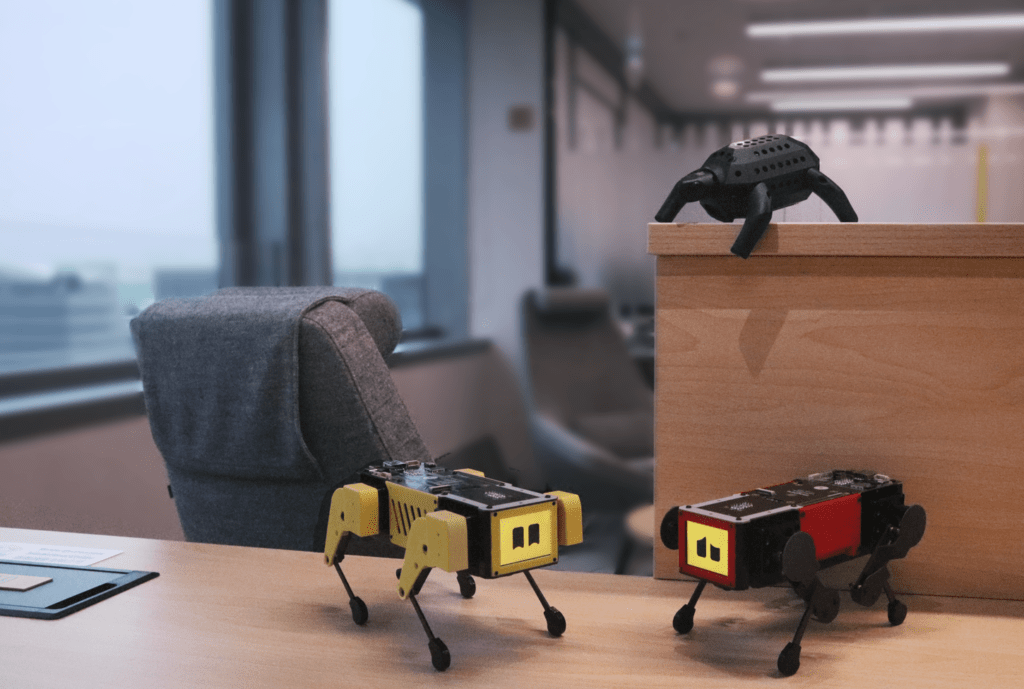
MangDang’s Kickstarter project „MD Robot Kit: Unlock your AI Robot Engineering Dream Job“ aims to promote the creativity and technical know-how of robotics enthusiasts. It offers two main robots, each addressing different needs and interests.
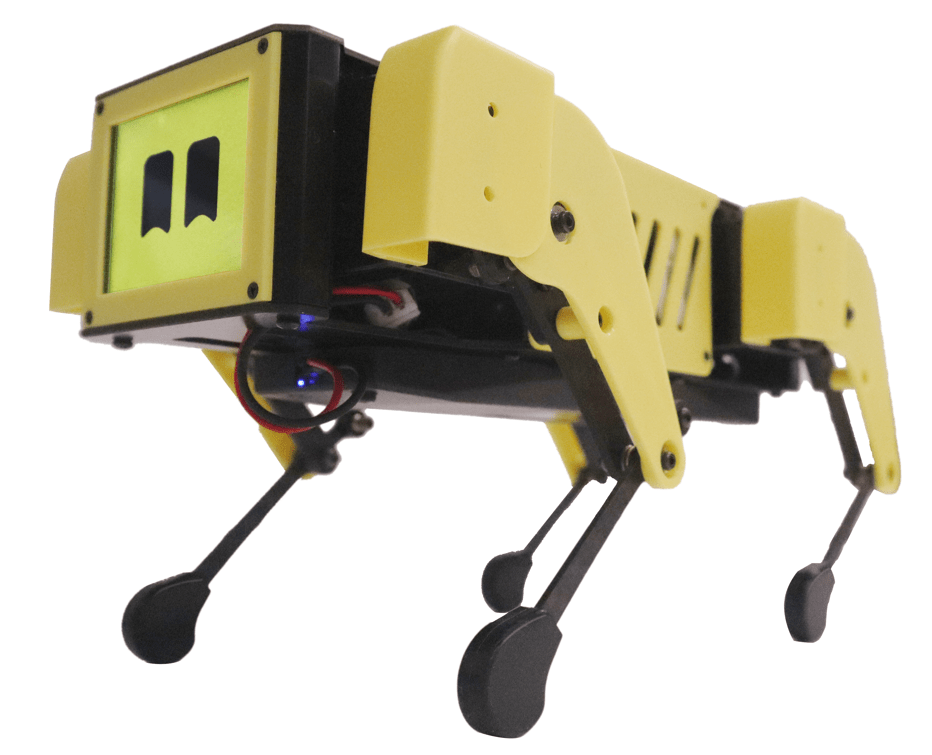
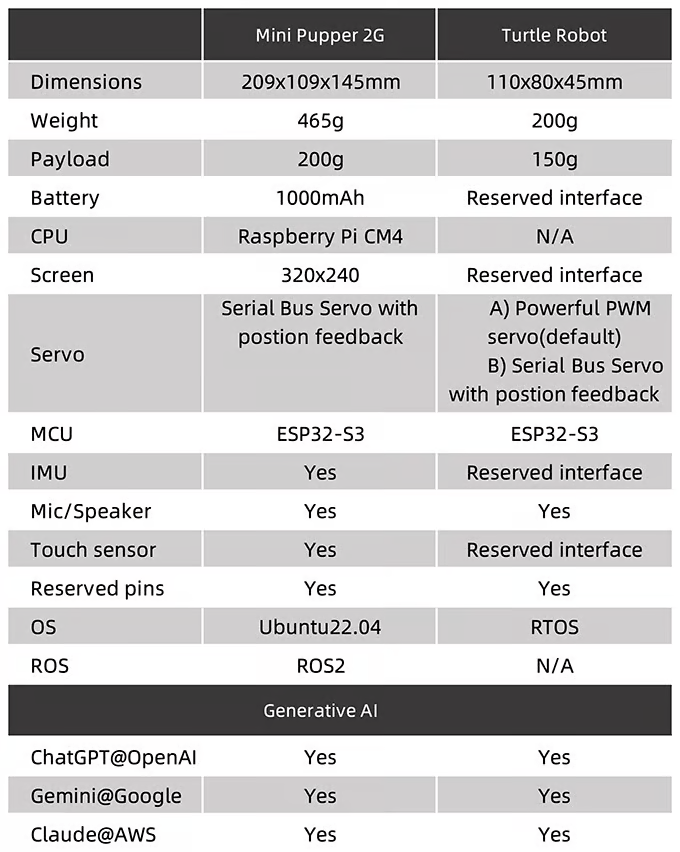
The first robot, the Mini Pupper, is available in several versions, including Mini Pupper 1, Mini Pupper 2, and the 2G and 2GA models. This robot is a low-cost, personal quadruped kit that comes with open-source software. The Mini Pupper supports multimodal generative AI platforms such as OpenAI’s ChatGPT, Google’s Gemini, and AWS’s Claude. It is also compatible with ROS1 and ROS2, which expands its capabilities in the areas of SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) and navigation. The integration of OpenCV allows the robot to perform deep learning with cameras. Thanks to the use of Raspberry Pi and Arduino, the Mini Pupper offers high adaptability and expandability, making it ideal for developers who want to realize their own projects.

The second robot presented is the Turtle Robot, which will be available soon. This robot is specifically aimed at schools, homeschooling families, and robot enthusiasts. While detailed specifications have not yet been fully released, it is clear that the Turtle Robot also aims to support learning and creativity in the field of robotics.
The campaign itself has set a funding goal of 9000€ and has clearly exceeded it with a sum of just under 19000€, which corresponds to over 200% of the original goal. The campaign runs from September 5, 2024 to October 5, 2024 and has attracted 80 supporters so far. A standout feature of the MD Robot Kits is their open-source nature, which allows users to assemble the robots in less than an hour. This makes them particularly accessible to a wide range of audiences, ranging from educational institutions to DIY enthusiasts. The project is designed not only to impart technical knowledge, but also to promote the joy of creating and customizing robots.

2. Turtle Robot:

VEX Robotics hat VEXcode für ein neues Jahr des Programmierens aktualisiert! VEXcode 4.0 für VEX IQ, VEX EXP und VEX V5 bringt den Benutzern einige aufregende neue Funktionen! Diese Bemühungen zielen darauf ab, die Benutzererfahrung zu optimieren und zusätzliche Optionen für die Barrierefreiheit zu unterstützen. Entdecken Sie die neuen Funktionen für jede Plattform unten und in den begleitenden VEX Library-Artikel!
VEXcode IQ 4.0 führt wichtige Updates ein. Zu den bemerkenswerten Ergänzungen gehören Switch Blocks, die einen nahtlosen Übergang von blockbasierter zu textbasierter Codierung auf einem physischen Roboter ermöglichen, verbesserte Speicher- und Ladefunktionen für webbasierte VEXcodeund neue Barrierefreiheitsoptionen wie „Blöcke vorlesen“. Diese Updates wurden entwickelt, um die Benutzererfahrung zu optimieren und Anfänger und fortgeschrittene Benutzer zu unterstützen.
Erfahren Sie hier mehr über diese Updates: https://kb.vex.com/hc/en-us/articles/29278709186708-New-Features-in-VEXcode-IQ-4-0
VEXcode EXP 4.0 bietet umfassende Updates, die das Bildungserlebnis für Lehrer und Schüler verbessern sollen. Diese Version bietet volle Unterstützung für den CTE Workcell, der eine nahtlose Integration von Industrierobotik in den Unterricht ermöglicht. Die neue Funktion „Blöcke wechseln“ ermöglicht einen reibungslosen Übergang von blockbasierter zu textbasierter Codierung und erleichtert so fortgeschrittenes Lernen. Darüber hinaus ermöglichen webbasierte drahtlose Projekt-Downloads effizientere Arbeitsabläufe, indem sie es Benutzern ermöglichen, direkt über ihren Webbrowser eine Verbindung zu einem EXP Brain herzustellen. Verbesserte Barrierefreiheitsfunktionen wie (Vor-)Leseblöcke, anpassbare Stimmen und kontrastreiche Themen machen VEXcode inklusiver und benutzerfreundlicher. Der aktualisierte AI Vision Sensor unterstützt jetzt AprilTags und AI Classifications, wodurch die autonomen Fähigkeiten verbessert werden. Mit diesen Verbesserungen unterstützt VEXcode EXP 4.0 weiterhin eine breite Palette von Bildungsanforderungen, von Anfängern bis hin zu fortgeschrittenen Roboterprogrammierungen.
Erfahren Sie hier mehr über diese Updates: https://kb.vex.com/hc/en-us/articles/29373428548372-New-Features-in-VEXcode-V5-4-0