Kivnon will be presenting its most advanced and safest AGV/AMR Forklift at the event
21 September 2022, Barcelona: Kivnon, an international group specializing in automation and mobile robotics, is attending Logistics & Automation in Spain and will be showcasing it’s safe and versatile K55 AGV/AMR Forklift Pallet Stacker. Putting the emphasis on forklift safety, Kivnon K55 is equipped with advanced safety features to guarantee safe operations as it collaborates, moves, and reacts in a facility.
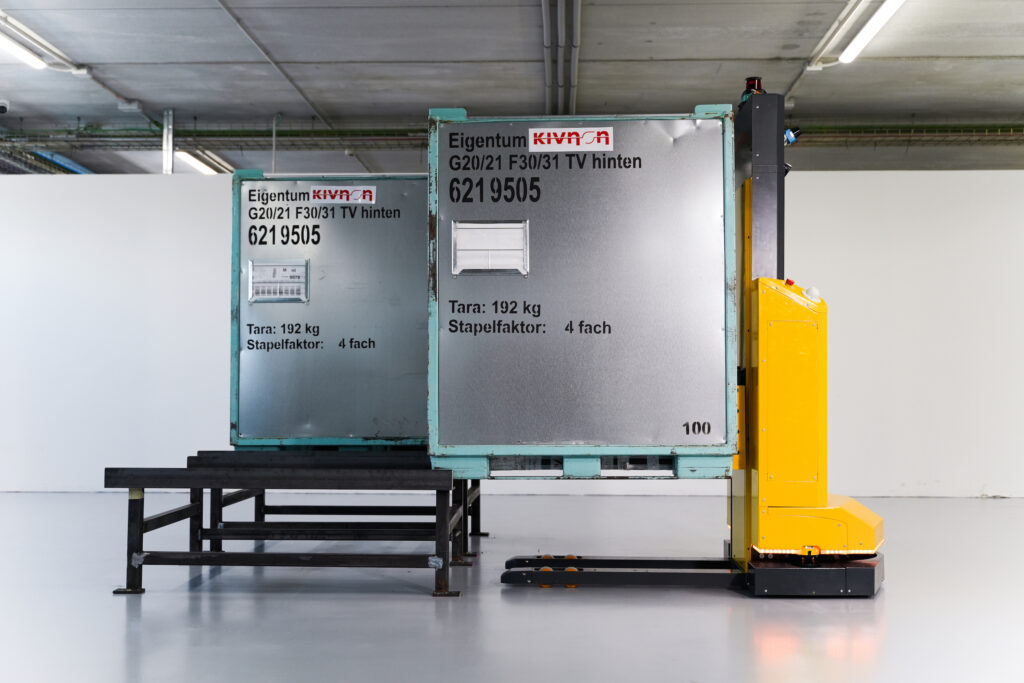

The Kivnon K55 is designed to move and stack palletized loads at low heights and performs cyclic or conditioned routes while interacting with other AGVs/AMRs, machines, systems, and people, making it a highly effective and safe solution. The model incorporates safety scanners that allow the vehicle to ensure 360-degree safety and operate seamlessly in shared spaces. The fork sensors help assess the possibility of correct loading or unloading of the pallet, keeping the transported goods safe.
Thierry Delmas, Managing Director at Kivnon, says, “AGVs/AMRs are revolutionizing internal logistics. The rising forklift safety challenge is of deep concern, and with the K55 we have taken a step forward to address the global issue. The Kivnon range is designed to ensure safe and reliable operations and to optimize operational efficiency.“
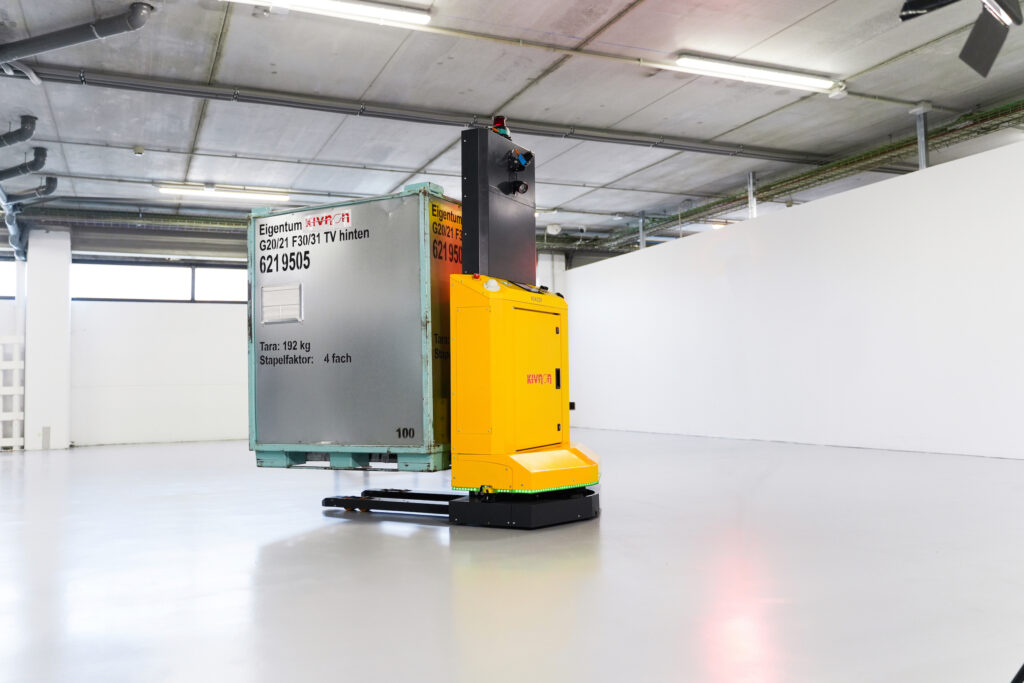

During the event, which runs from 26 – 27 October at IFEMA, Madrid, Kivnon will demonstrate the capabilities of the K55 Pallet Stacker. The vehicle can autonomously transport palletized loads of up 1,000 kg and lift them to heights of up to 1 meter. The vehicle is capable of performing cyclical or conditional circuits and interacting with other AGVs/AMRs, machines, and systems. Highly adaptable, the K55 is perfect for any open-bottom or euro-pallet storage application, receipt and dispatch of goods, and internal material transport. Its use will optimize safety, storage space, and process efficiency.
A robust industrial product, the K55 provides the reliability required to ensure continuity of production process and flexibility to adapt to specific application needs, with an online battery charging system that can function 24/7 with opportunity charges.
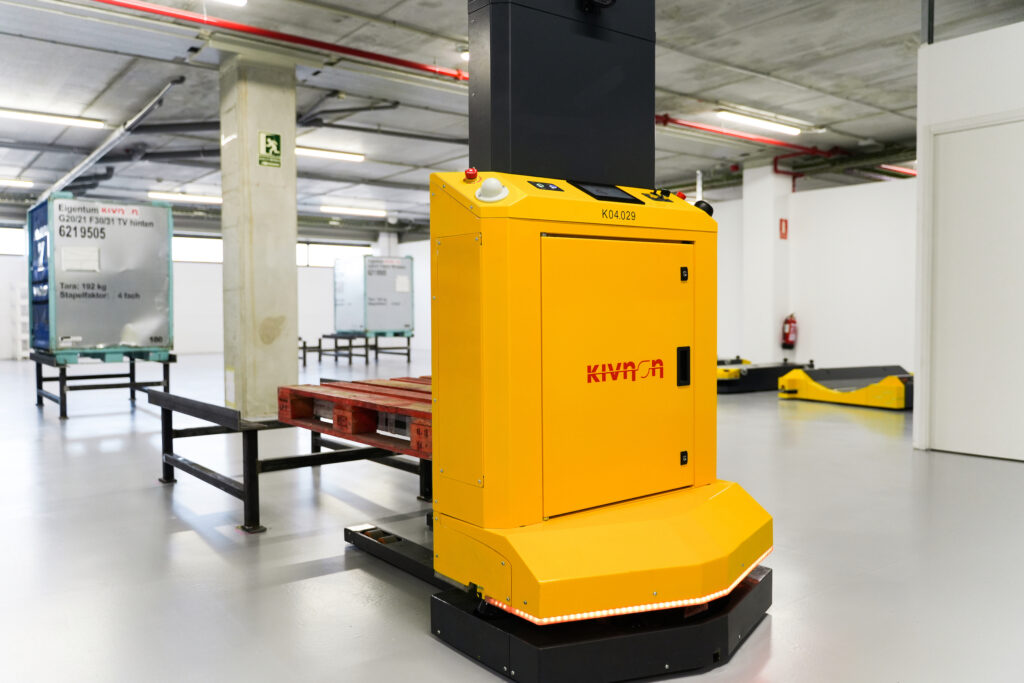

Delmas continues, “The Logistics and Automation show is an important networking event where customers can learn about the latest technologies and innovations. We pride ourselves on innovation and are excited to have this opportunity to showcase the capabilities of our products. In addition to the K55, our robust portfolio also includes twister units, car and heavy load tractors, low-height vehicles, and cart pullers, meeting multiple application needs”
The efficiency and precision of Kivnon AGVs/AMRs will be on display and Kivnon robotics experts will be available throughout the show to answer questions and arrange consultations at booth #3F43.
To register for the show, please visit https://www.logisticsautomationmadrid.com/en/
About Kivnon:
Kivnon offers a wide range of autonomous vehicles (AGVs/AMRs) and accessories for transporting goods, using magnetic navigation or mapping technologies that adapt to any environment and industry. The company offers an integrated solution with a wide range of mobile robotics solutions automating different applications within the automotive, food and beverage, logistics and warehousing, manufacturing, and aeronautics industries.
Kivnon products are characterized by their robustness, safety, precision, and high quality. A user-friendly design philosophy creates a pleasant, simple to install, and intuitive work experience.
Learn more about Kivnon mobile robots (AGVs/AMRs) here.