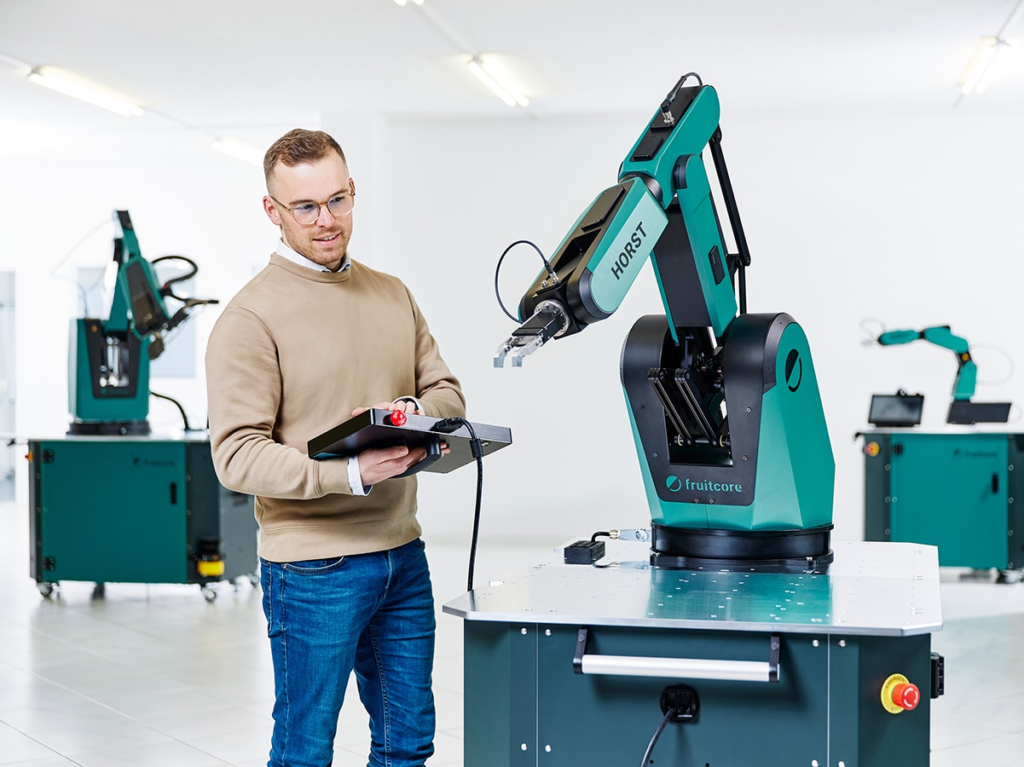
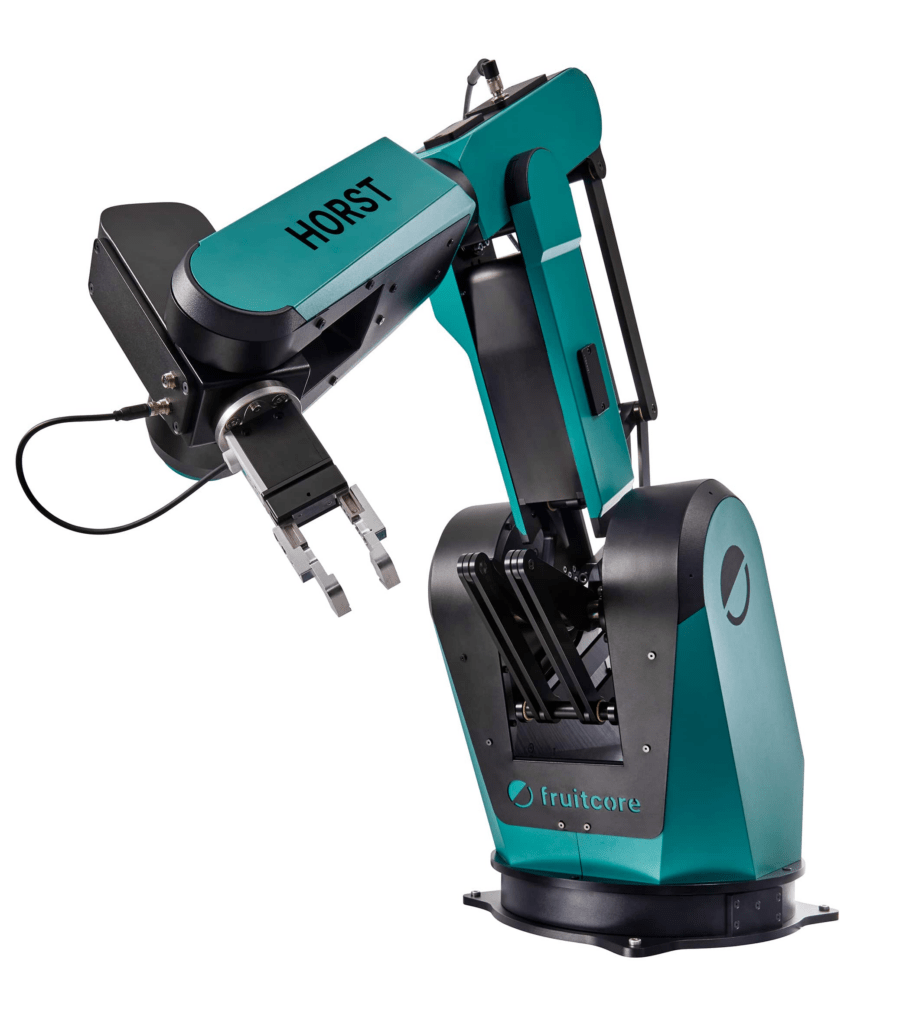
Constance, February 28th, 2023 – Up to 8 kilograms payload, a reach of 1,018 millimeters, short cycle times: fruitcore robotics is launching HORST1000, a new robot whose performance parameters enable a wide range of additional applications and better meet the growing market for industrial processes such as machine placement and pick & place applications.
HORST1000 is a completely newly developed robot kinematics system that incorporates all the knowledge gained from industrial practice in recent years. Building on existing technology innovations, fruitcore robotics‘ patented robot transmission for HORST1000 has been further optimized using a machine learning algorithm, resulting in a significant increase in performance. In terms of design, fruitcore robotics focuses on a compact footprint and aesthetics, as it has done with its robots that have already won multiple awards in the past, such as the Fokus Open Award and the German Innovation Award. With the introduction of the new model, the predecessor HORST900 will no longer be continued.

Performance improvement based on existing technology innovations
In HORST1000, key performance features such as payload, range and workspace have been significantly improved. The new all-rounder has a payload of up to 8 kilograms and a reach of 1,018 millimeters. The developers placed particular focus on the workspace of HORST1000. The threedimensional workspace has increased by 40 % compared to HORST900, allowing 50 % larger trays to be processed. From the base, HORST1000 can move around 230 millimeters further forward than its predecessor, which corresponds to a 43 % longer linear path. This allows customers to enter machines more easily. Higher acceleration values of the individual axes in the nominal load range also ensure shorter cycle times. In a classic pick & place process, this improves the cycle time by up to 20 %.
„The technological innovations of HORST1000 let us further increase the performance difference compared to current cobots,“ explains Jens Riegger, Managing Director (CEO) and Co-Founder of fruitcore robotics. Patrick Heimburger, Managing Director (Chief Revenue Officer) and Co-Founder of fruitcore robotics, adds: „We now allow an even wider range of applications and help our customers implement industrial processes such as machine placement and pick & place even more easily and efficiently.“
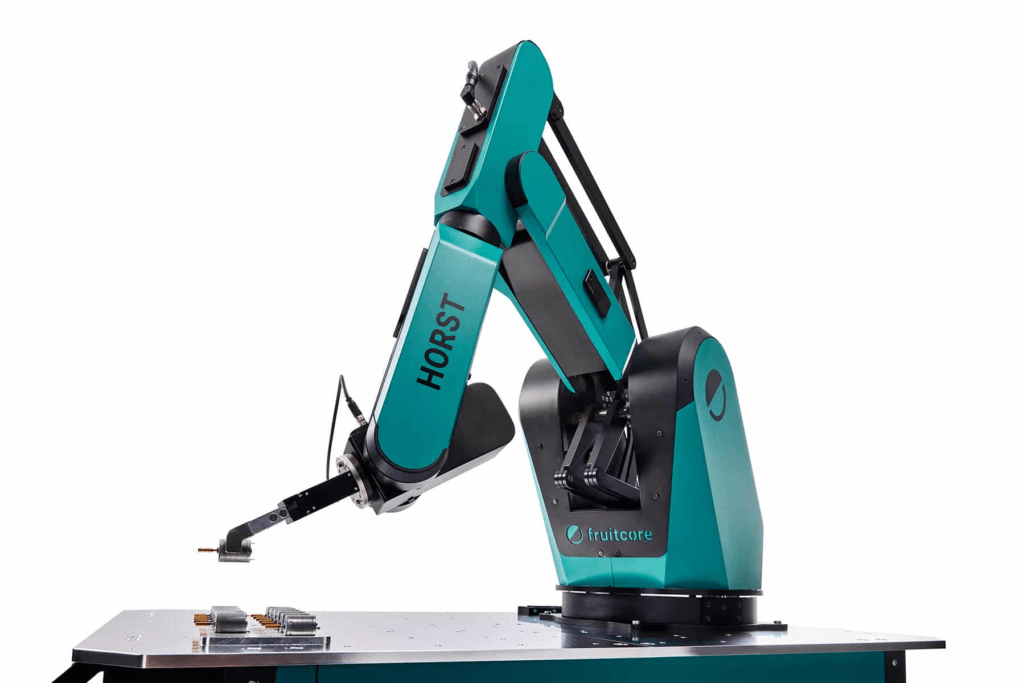

Optimized for Machine Loading and Pick & Place
Thanks to its range and workspace design, HORST1000 is tailor-made for loading and unloading any machine tools; especially for lathes and milling machines, the robot is also ideally suited due to its software and interfaces. The robot can reach deep into the machines, the high axis accelerations enable a short cycle time. In addition, the maximum payload of 8 kilograms also allows the use of heavy tools and complex multiple gripper systems. As an automation solution, Digital RobotHORST1000, like its predecessor HORST900 and its brothers HORST600 and HORST1400, includes not only powerful and cost-effective hardware. It follows a coordinated operating concept, which not only makes the operation of the robot particularly simple, but also the implementation of the entire application. All components involved in the process, such as grippers, CNC systems and safety systems, are operated via the horstFX graphical user interface and centrally networked with the horstCOSMOS IIoT platform.
For example, the machine tool can be integrated as a 3D model in horstFX and component variants can be easily traded via the program management of the operating software. Switching between two tools can be mapped on the software side via the multi-tool feature. In addition to the connection to the IIoT platform, all fruitcore robotics robots come with an IIoT surf stick with SIM card as standard. This offers companies the possibility to go online with the robot system without having to integrate it into their company network. Customers can establish an internet connection as required and use horstCOSMOS to view their robot fleet on dashboards, including the process data of the robot application. This allows processes to be optimized independently or in coordination with fruitcore robotics. In addition, availability is increased because maintenance can be carried out via predictive maintenance and a quick response can be made to service cases via remote maintenance.
Pre-orders now possible
HORST1000 can be pre-ordered from the manufacturer from now on. Delivery will take place from 01.06.2023. The price for the new all-rounder can be found on the manufacturer’s website.
Specifications HORST1000:
| Specification | HORST1000 |
| Max. Payload | 8 kg |
| Nominal Load | 5 kg |
| Max. Range | 1018 mm |
| Mounting Surface | 380 x 380 mm |
| Weight | Approx. 70k g |
| Repeatability | +/- 0,05 mm |
| Protection Class | IP54 |
| Sound Level | < 70 dB (A) |
| Power Supply | 230VAC, 50-60Hz, typ. 350W |
| Surrounding Temperature | 5-40 °C |
| Standard Color | RAL 5021 (Water Blue) |