Wie Sie Kosten senken und die Vorteile der Automationsklassiker Pick & Place, Prüfen und Dosieren am besten für sich nutzen
Autor: Alexander Mühlens, Geschäftsbereichsleiter Low Cost Automation bei der igus GmbHAus der Industrie sind Roboter schon lange nicht mehr wegzudenken – ob als Maschinenbestücker, Qualitätsprüfer oder Montagehelfer. Doch viele kleinere und mittelständischen Unternehmen (KMU) drohen ins Hintertreffen zu geraten. Denn oft wissen Sie garnicht, wo sie anfangen sollen. Welche Anwendungen lassen sich überhaupt automatisieren? Und häufig scheinen die Investitionskosten zu hoch und die Integration und Bedienung zu komplex.
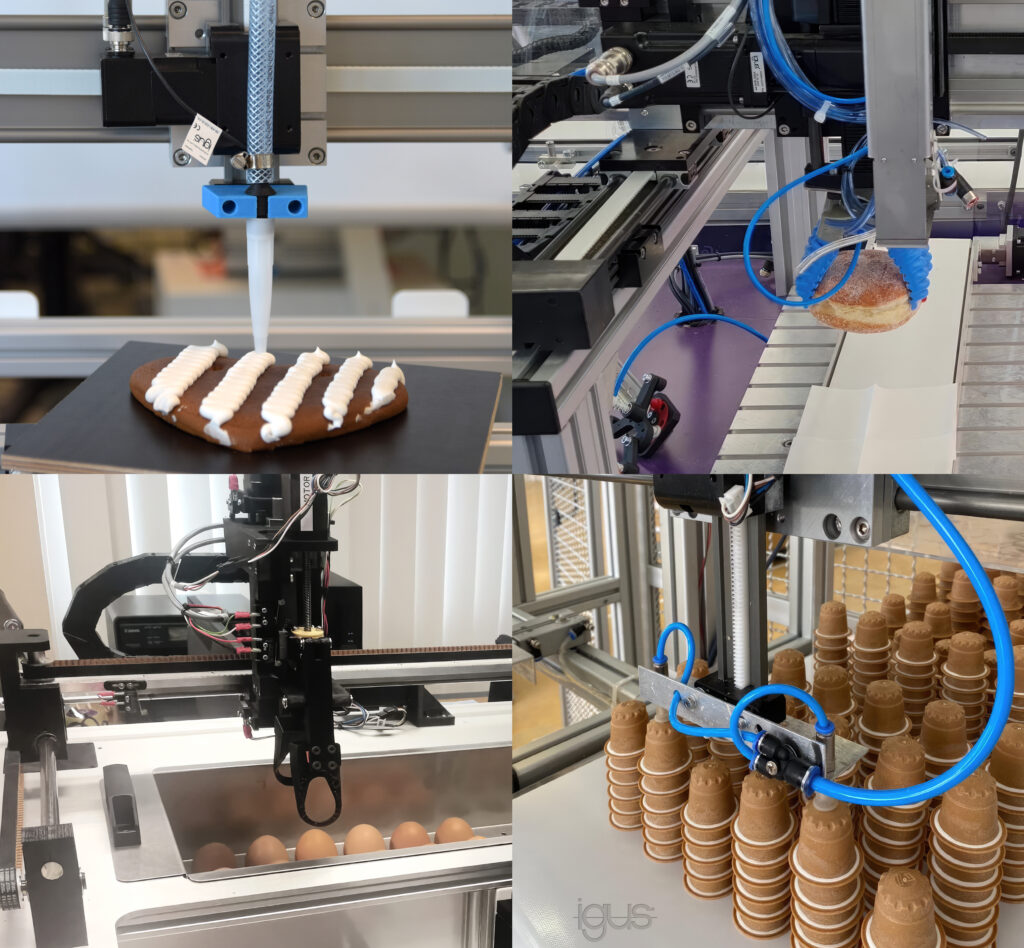

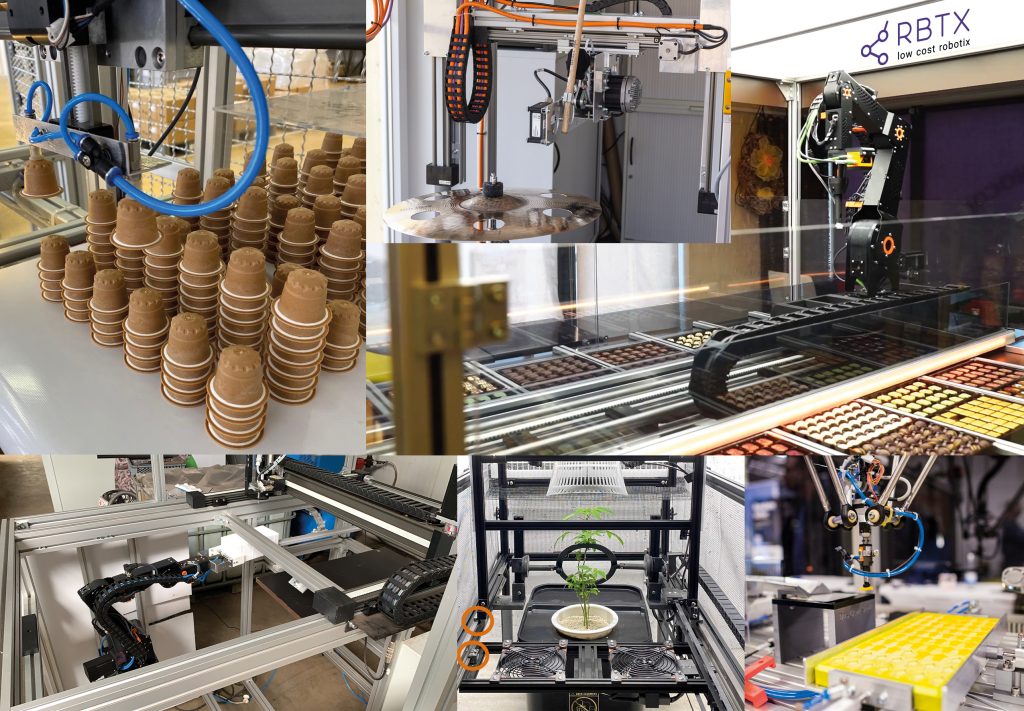
Picken, dosieren, schleifen oder prüfen: Es gibt eine Vielzahl an monotonen, repetitiven und anstrengenden Arbeiten, die sich einfach automatisieren lassen. Doch sich nur einen Roboter anzuschaffen, führt am Ende leider zu keiner Lösung. Am Ende muss das gesamte System aus Roboter und Komponenten wie Vision-Systeme, Greifer und Sensoren funktionieren. Doch insbesondere KMU wissen häufig nicht, wo sie nach einer Lösung suchen sollen und wie die passende Lösung überhaupt aussieht. Außerdem ist es wichtig, nicht zu komplex anzufangen. Der herstellerneutraler Robotik-Marktplatz RBTX hilft Automatisierungswilligen dabei, die einfachste und kostengünstigste, funktionierende Lösung zu finden.
Über 400 Komplettlösungen aus der Praxis
Das Besondere: Interessierte finden auf dem Marktplatz nicht nur Roboter und Einzelkomponenten, sondern Einblick wie es andere machen. Als Inspirationsquelle zum sofortigen Nachmachen finden sich online über 400 sofort adaptierbare Automatisierungsprojekte aus der Praxis. Von der automatisierten Regenwurmfarm über einen Berliner-Picker bis hin zum Agrarroboter, der Unkraut erkennt und vernichtet. Mehrere tausend KMU aus aller Welt haben auf RBTX.com bereits ohne konstruktionstechnische Vorkenntnisse Automationslösungen realisiert. 95 Prozent dieser Komplettlösungen sind für unter 12.000 Euro erhältlich. Die Low-Cost-Lösungen amortisieren sich nachweislich bereits ab 3-12 Monaten. Zu den Hauptanwendungsbereichen zählen unter anderem Pick & Place-Aufgaben, die Qualitätsprüfung sowie Klebe- und Dosieranwendungen.
Effizientes Handling von Produkten mit Pick & Place-Robotern
Ein Pick & Place-Roboter befördert ein Objekt zuverlässig von A nach B. Häufig handelt es sich dabei um wiederholende und zeitfressende Tätigkeiten, die viel Optimierungspotenzial innerhalb einer Produktion bieten. Ob bei der Maschinenbestückung, Palettierung, Sortierung oder Vormontage. Die Vorteile von Low Cost-Roboterlösungen haben einen Automatisierungstrend in Branchen wie Landwirtschaft, Lebensmittelindustrie, Medizintechnik bis hin zum Handwerk ausgelöst. Pick & Place-Systeme finden sich vor allem zunehmend in alltäglichen Endkunden-Anwendungen, zum Beispiel in Verkaufsautomaten.
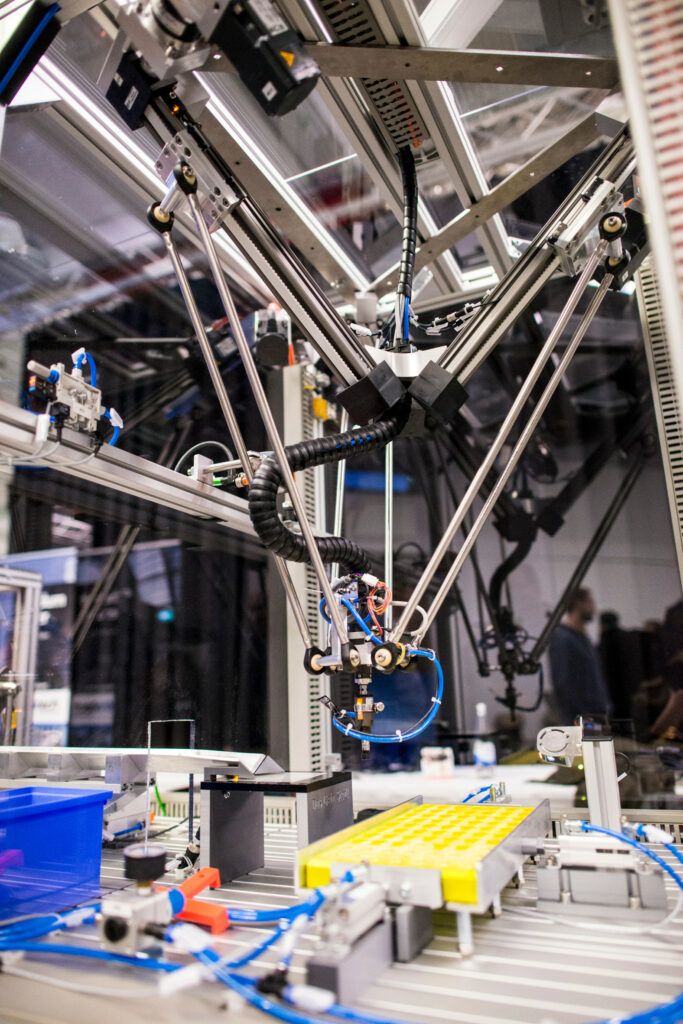
Verschiedene Robotertypen wie Gelenkarm-, Delta- oder Portalroboter können die unterschiedlichsten Anwendungsszenarios realisieren. So kommen Portalroboter zum Beispiel für das Greifen von Medikamenten zum Einsatz, um sie zur Ausgabe zu befördern, während ein SCARA Roboter als „Labor-Assistent“ das sichere Aufnehmen und Ablegen von Reagenzgläsern übernimmt – und das bereits für 7.820 Euro. Der Vorteil der Roboter-Systeme: Sie nehmen Bauteile präzise und mit konstanter Qualität auf und setzen sie am gewünschten Ablageort ab. Die Vorgänge sind exakt wiederholbar.
Automatisierte Qualitätsprüfung für mehr Präzision und Planbarkeit
Mit einer automatisierten Qualitätskontrolle lassen sich repetitive Prüfvorgänge effizient und präzise durchführen. Die Einsatzszenarien von Prüfrobotern sind so unterschiedlich und individuell wie die zu automatisierenden Arbeitsvorgänge. Ob Oberflächenprüfung, Maßprüfung oder Funktionsprüfung – Prüfprozesse und -merkmale unterscheiden sich in der Praxis stark. Mithilfe von RBTX wurde beispielsweise ein Robotersystem für das automatisierte Be- und Entladen einer Prüfstation für Leiterplatinen konfiguriert.
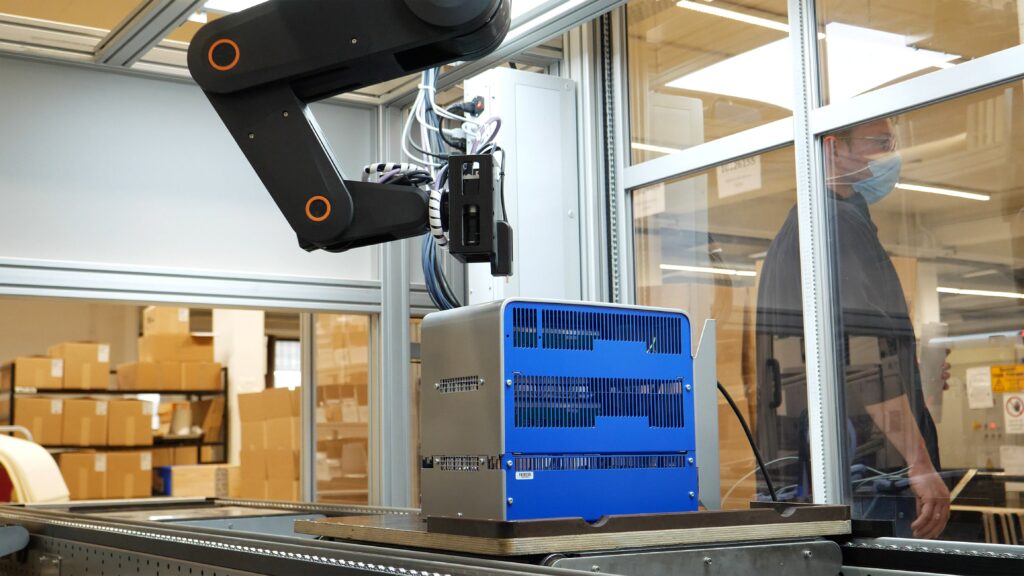

Ebenso ein Flächenportal, das mithilfe einer Kamera einzelne Uhren ansteuert, um visuell zu prüfen, ob sich Minuten- und Sekundenzeiger bewegen. Ein Roboterarm kommt unter anderem auch bei der End-of-Line-Prüfung von Ladegeräten für Elektrofahrzeuge zum Einsatz. Prüfprozesse lassen sich durch den Einsatz von Robotern effizient verschlanken und besser planen. Darüber hinaus arbeiten Roboter rund um die Uhr ohne Qualitätseinbußen. Es werden identische Vorgänge und eine präzise, gleichbleibende Messung des Prüfmerkmals sichergestellt.
Sicher kleben und dosieren – ohne Materialverschwendung
Neben Prüf- und Pick & Place-Aufgaben kann auch das Auftragen von Klebe-, Versiegelungs-, Lackiermitteln und Isolierschäumen effizient automatisiert werden. Meistens geht es darum Materialverschwendung zu vermeiden und präziser zu kleben bzw. zu dispensieren. Und dafür benötigt man keinen Roboter mit Investitionskosten im 6-stelligen Bereich. Mit Low Cost-Robotern kann fast alles verklebt werden. Sie erreichen eine Präzision von ca. 0,5 mm. Ein weiterer Grund ist die Arbeitsplatzsicherheit. Denn der Roboter kann problemlos mit Chemikalien in Berührung kommen und unterstützt bei unergonomischen Arbeiten. Vor allem Klebeprozesse an kleinen Werkstücken, erfordern ein hohes Maß an Konzentration und Präzision. Dabei ist es häufig wichtig, dass der Kleber das Bauteil exakt abdichtet. Dort liegt die Automation durch Roboter nah. Mithilfe von RBTX konnte zum Beispiel ein Kunde durch den Einsatz eines automatischen Dosierroboters die Geschwindigkeit beim Auftragen von Dichtungsmasse auf ein Metallteil, einem wichtigen Arbeitsschritt in seiner Produktion, vervierfachen. Die einfache Handhabung der Maschine ermöglicht es selbst ungeschulten Mitarbeitern, den Roboter sofort zu nutzen.
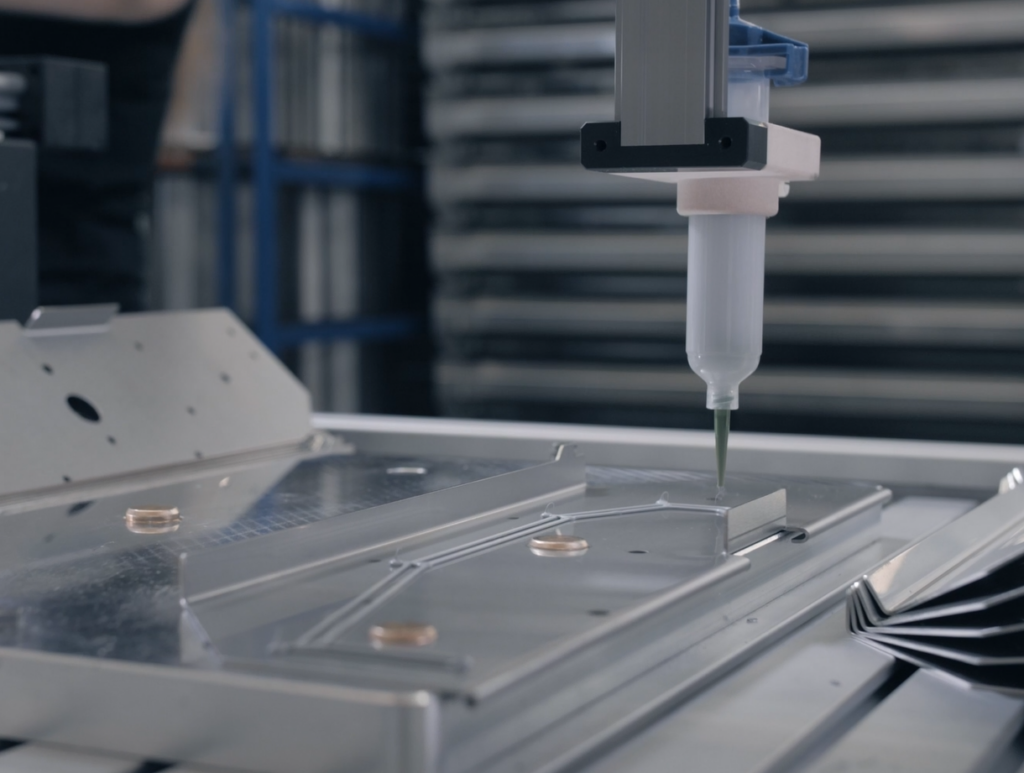

Für das Kleben und Dosieren lassen sich je nach Anwendung verschiedenste Robotersysteme einsetzen. Mithilfe eines eigenen Dosierroboter-Konfigurators können Anwender in nur wenigen Klicks eine individuelle Roboterlösung zusammenstellen, die präzise Klebe- und Dosiervorgänge automatisiert.
Wer noch nach Inspiration sucht, findet auf RBTX.com alle Anwendungsbeispiele aus der Praxis: https://rbtx.com/de-DE/solutions
RBTX ist eine eingetragene Marke der igus GmbH.