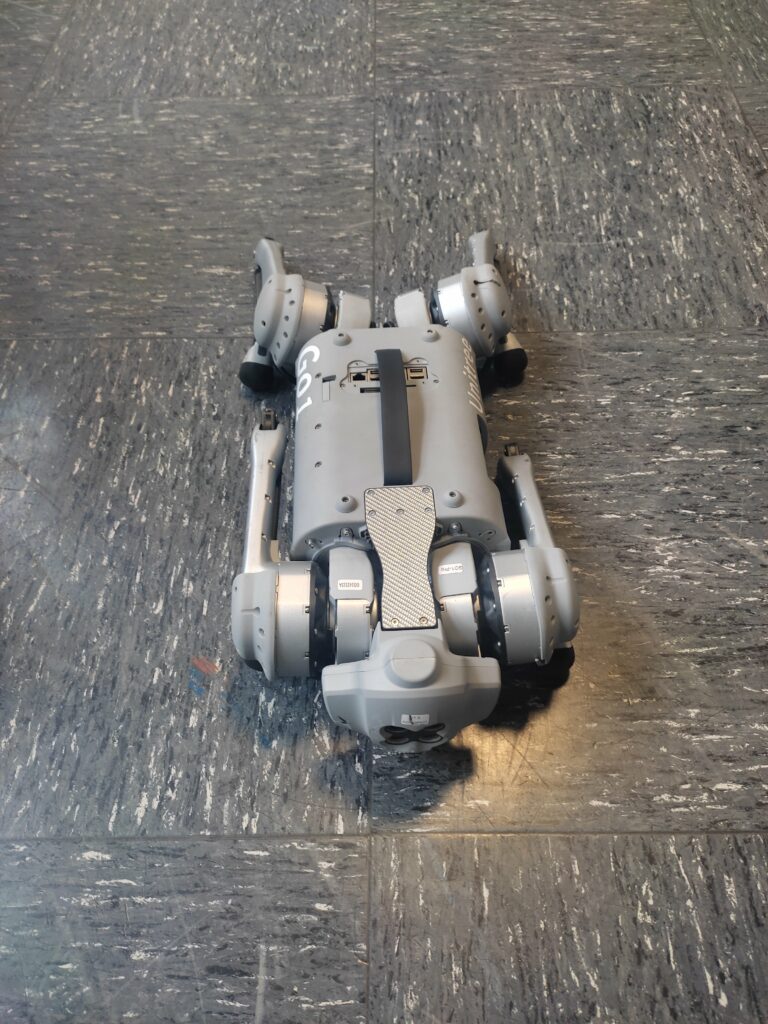
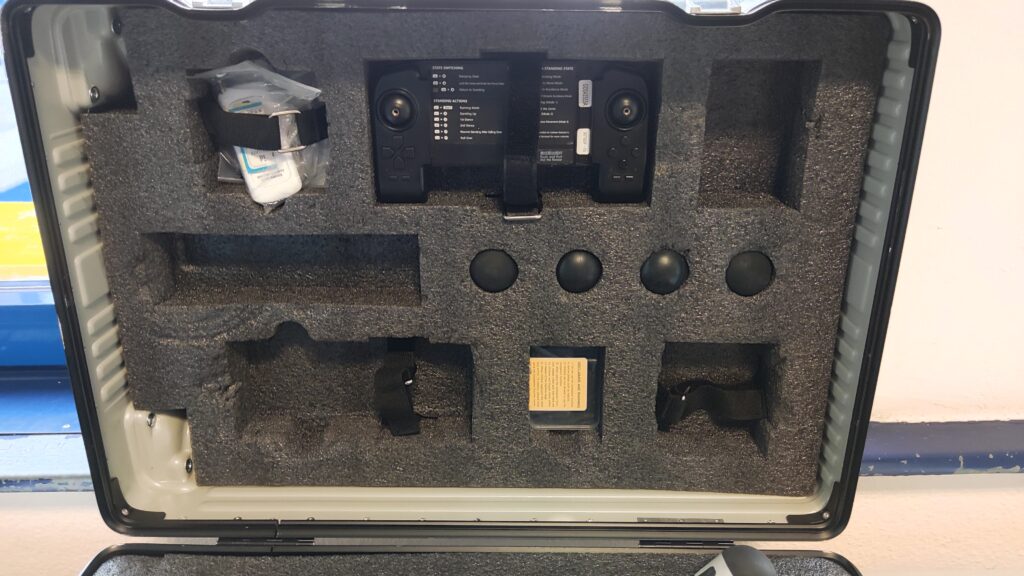
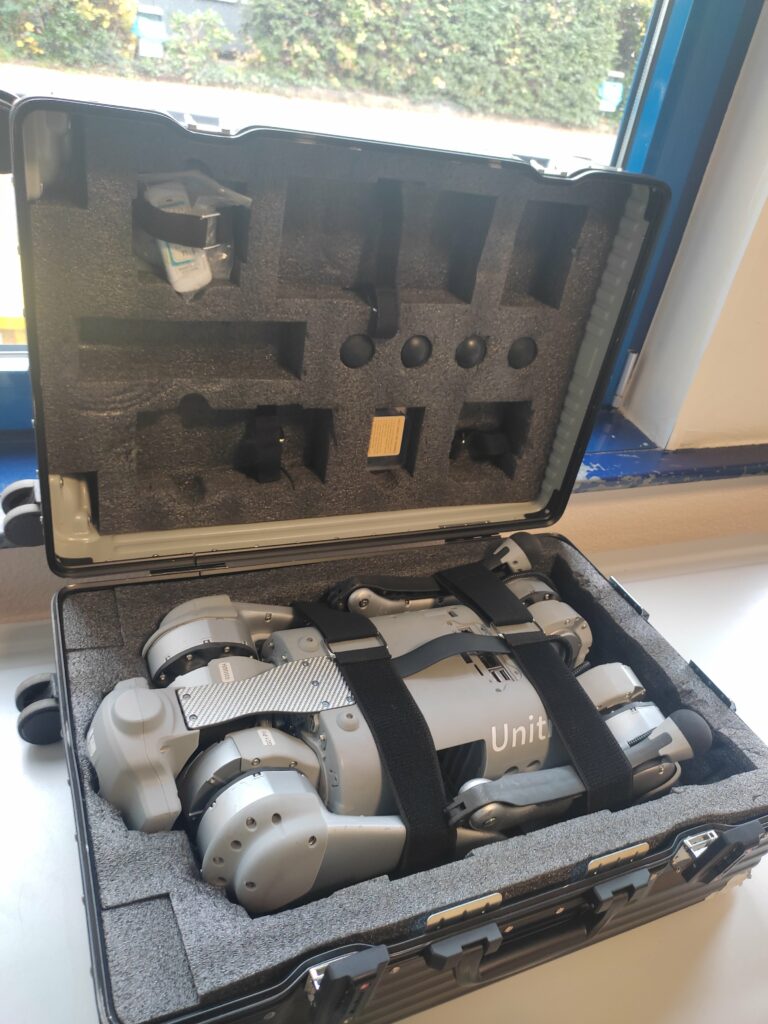
Unitree Quadruped Go 1 Dance Video 1+2. Find the latest News on robots, drones, AI, robotic toys and gadgets at robots-blog.com. If you want to see your product featured on our Blog, Instagram, Facebook, Twitter or our other sites, contact us. #robots #robot #omgrobots #roboter #robotic #automation #mycollection #collector #robotsblog #collection #botsofinstagram #bot #robotics #robotik #gadget #gadgets #toy #toys #drone #robotsofinstagram #instabots #photooftheday #picoftheday #followforfollow #instadaily #werbung #unitree #quadruped #robotics #mybotshop #dog #dance @mybotshop @unitreerobotics
Archiv des Autors: Sebastian Trella
Luwu Intelligence Technology Announces Launch of XGO 2 – World’s First Raspberry Pi Robotic Dog with An Arm
Luwu, a STEM education technology company focused on the research and development of advanced robotics, has announced the launch of XGO 2, an advanced desktop-sized AI quadruped robot with an arm. This state-of-the-art robot brings a new level of intelligence and functionality to the world of robotics. XGO 2 is now available on Kickstarter: https://www.kickstarter.com/projects/xgorobot/xgo-2-worlds-first-raspberry-pi-robotic-dog-with-an-arm
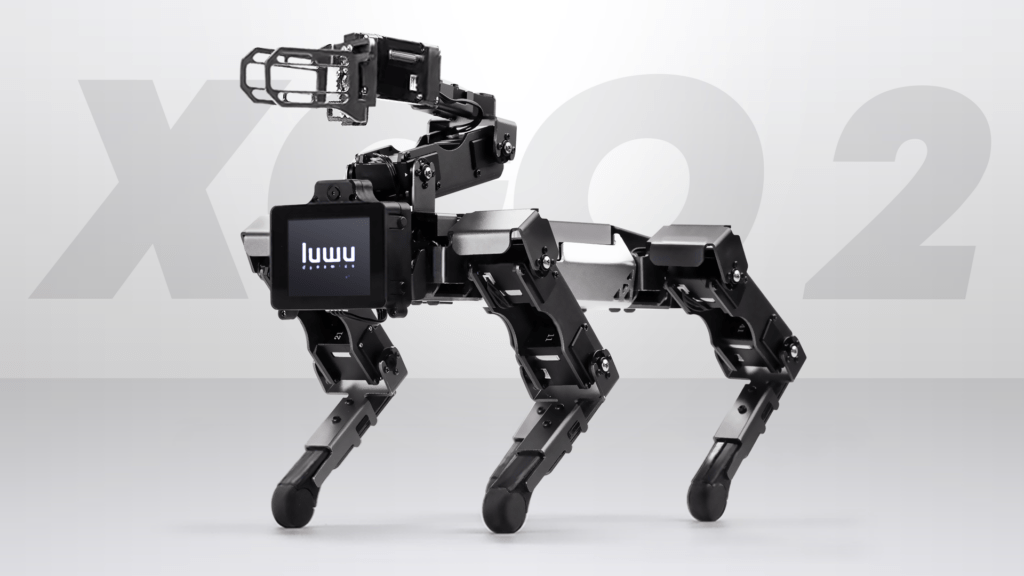
XGO 2 is an intelligent and agile robotic dog, capable of sophisticated movements, 12 degrees of freedom, and a variety of motions. Its open-source nature allows users of all programming levels to program and customizes it with Blocky and Python. Additionally, the advanced AI modules built into XGO 2 allow for visual, voice, and gesture recognition, enabling the robotic dog to hear, understand, and respond to users like a real dog.
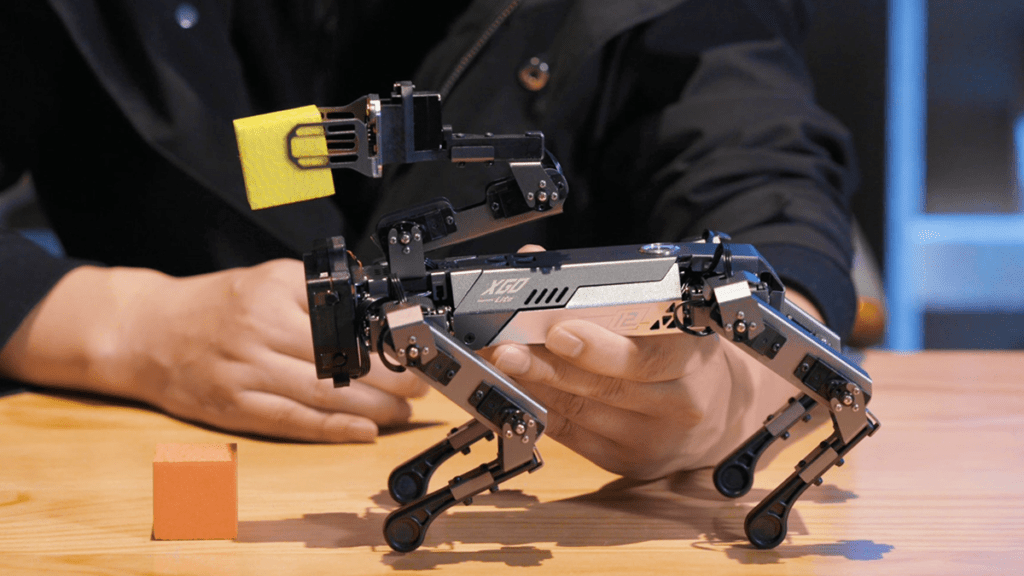
One of the most notable features of XGO 2 is its robotic arm. This arm allows it to perform tasks such as grasping and manipulating objects, making it more versatile and opening up a whole new realm of possibilities for the robotic dog to be used in various scenarios.
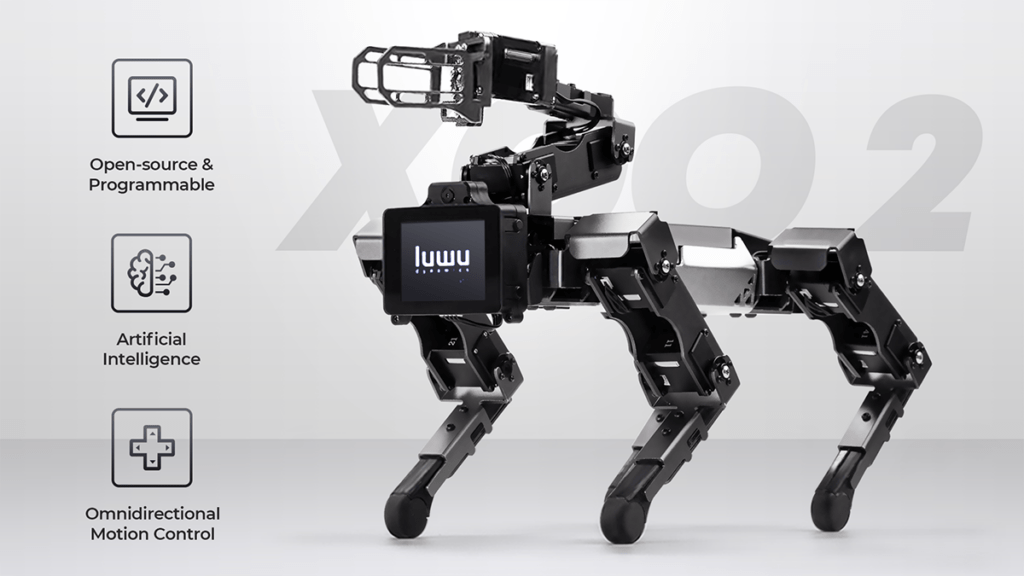
XGO 2 is also incredibly easy to control. Its user-friendly interface allows for easy programming and control, making it accessible to users of all skill levels. Whether you’re looking to create a new robot application, enhance your research, or simply have fun with a cutting-edge piece of technology, XGO 2 is the perfect choice. Its unique combination of intelligence, agility, and affordability makes it an ideal choice for anyone looking to add a robotic dog to their collection.
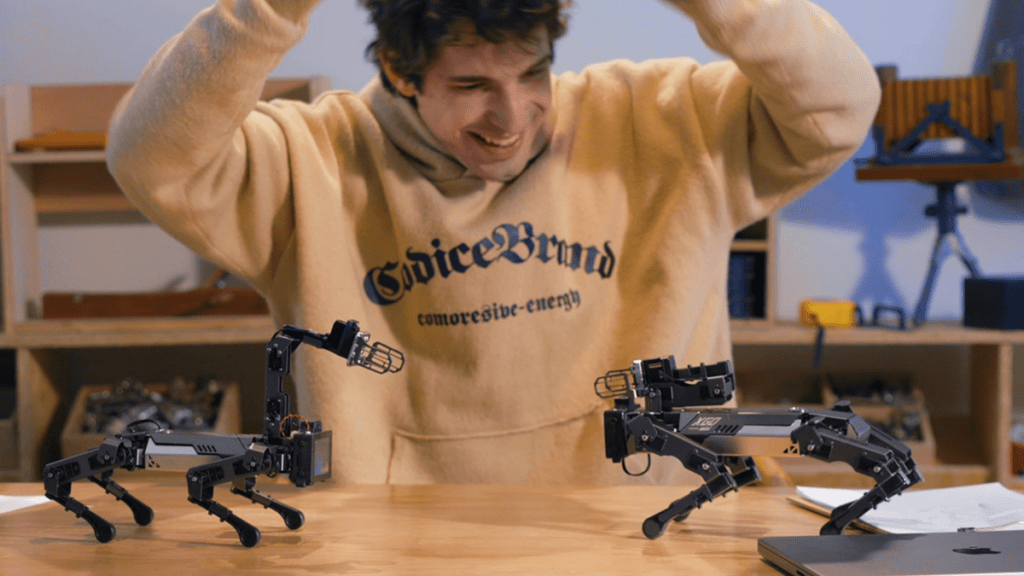

XGO 2, the World’s First Raspberry Pi Robotic Dog with an Arm, is an incredible robotics platform for entertainment, STEM education, and exploring creativity. XGO 2 is now available for pre-order on Kickstarter with special pricing for early supporters. Learn more here: https://www.kickstarter.com/projects/xgorobot/xgo-2-worlds-first-raspberry-pi-robotic-dog-with-an-arm
Cherry Tart: The Interactive & LEGO-compatible crafting Nature-Inspired robot kit for kids & adults to innovate
Inspired by Nature, Crafted by You
Are you ready to add a little spark of creativity and innovation to your life? Look no further than Cherry Tart – the first crafty sound-activated, bio-inspired building block kit for kids and adults. We believe that learning and fun should go hand in hand. And with Cherry Tart, that’s exactly what you’ll get.
Introduction
The Cherry Tart crafty series are designed to spark creativity and imagination with a hands-on STEM robot kit for future innovators. A combination of colorful LEGO-compatible building blocks with customizable skins creates a joyful and creative challenge for kids & adults. This kit provides nature’s beauty, enjoyment of design and building, and art. Cherry Tart crafty kit is a LEGO®-compatible and coverable building block that offers an innovative sound activation method to make your nature-inspired projects interactive and livelier.
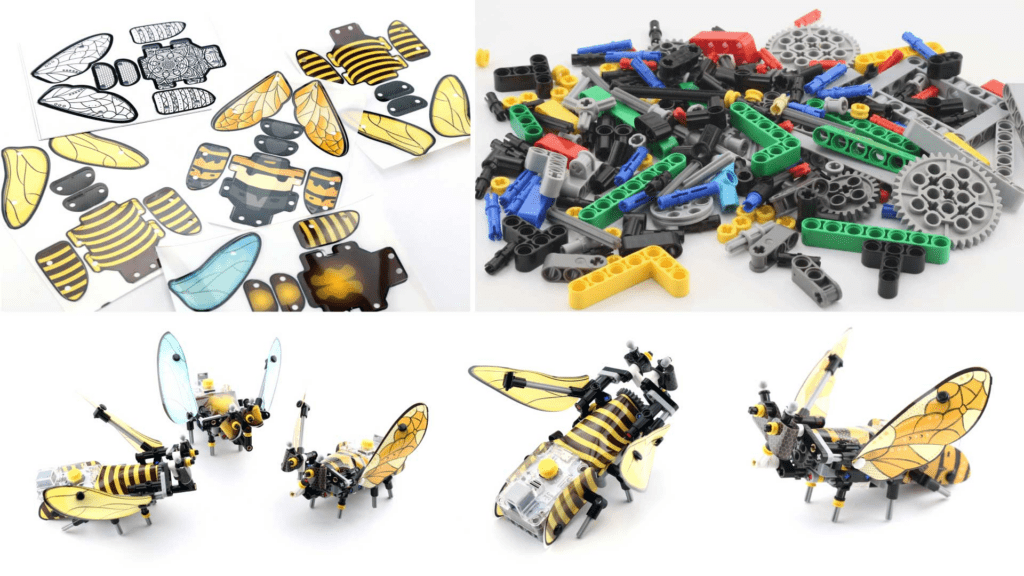

With this kit, you can create your own interactive, nature-inspired projects that come to life through sound activation. Whether you’re a seasoned robot builder or just starting out, Cherry Tart offers something for everyone.
Crafty robot kit benefits
The Cherry Tart crafty kit is not only LEGO®-compatible but also coverable with a wide range of foldable and customizable skins that allow for personal expression. You can cover your model with printed skins or paint and decorate your own skin. The result is an elegant conversation piece that’s a tasteful addition to any home, or maybe just to impress your friends and family.
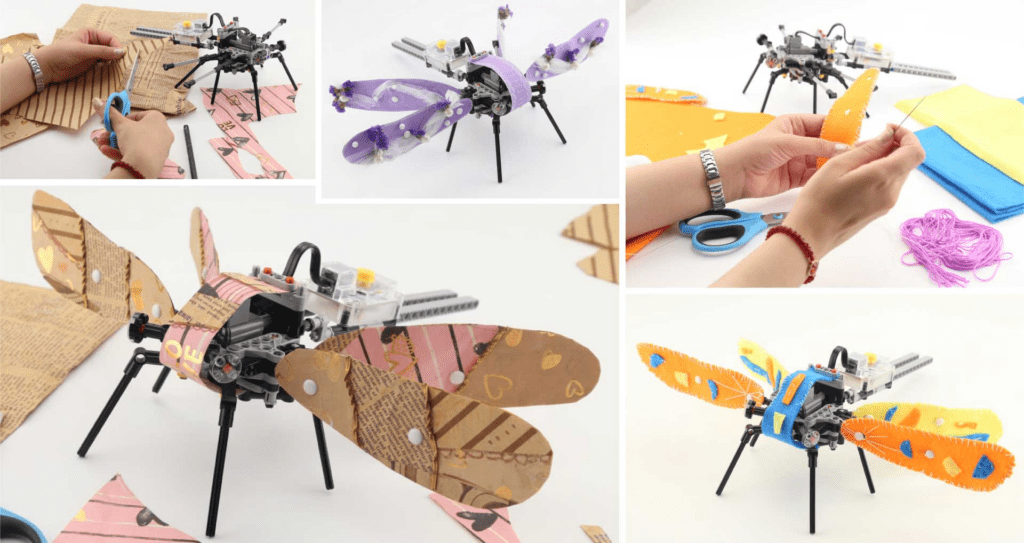
What you can build?
With Cherry Tart, you can create your own robot designs and program them to move, react to their environment, and even play games. The robot kit is easy to assemble and can be customized with your own crafts and materials, making it a great way to learn about robotics and unleash your creativity. Kids & adults can build sound-activated creatures. It actively involves the kids and encourages them to take physical action. Build the main model using LEGO-compatible building blocks. Select your favorite skin or paint your customized skin, take it out from the printed skin sheet, and snap them on your model. Turn the Cherry Core ON and select your desired mode. Surprised! The model comes to life. Change your model skin and try another one.
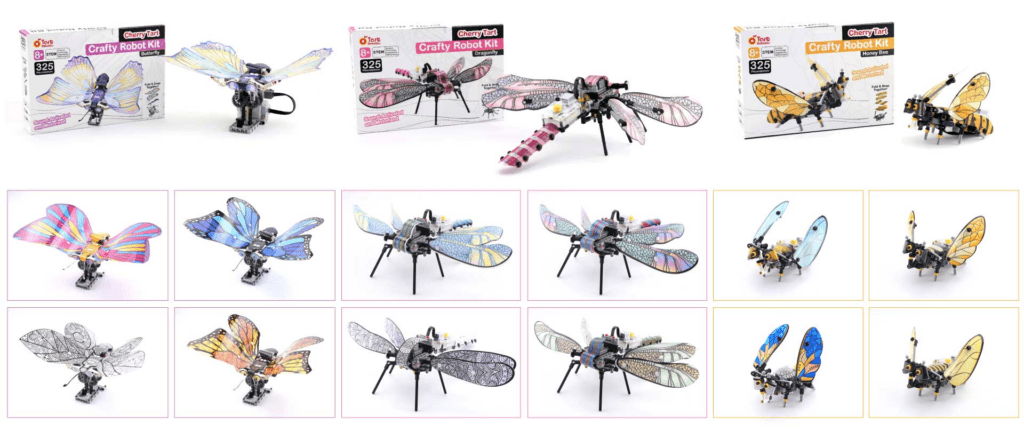

What’s Included?
Cherry Tart teaches kids and adults about robotics in a fun and engaging way. The kit includes everything you need to build your own robot and bring it to life, including a Cherry Core sound-activated microcontroller with a built-in rechargeable battery, a motor, LEGO®-compatible building blocks, and different printed and customizable skins.
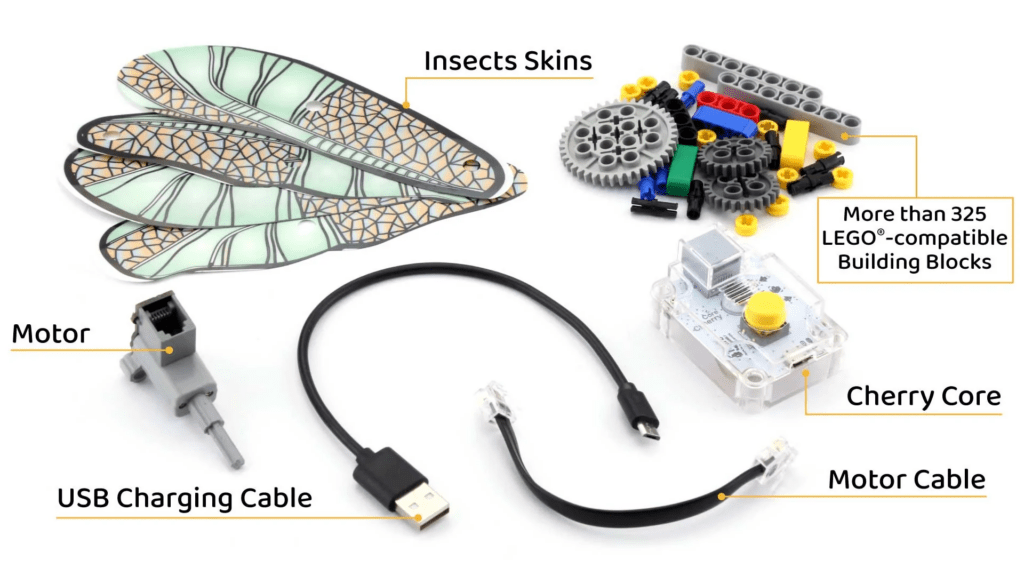
Coming soon on Kickstarter
After running two successful Kickstarter campaigns, Cherry Tart is back with a new, amazing, affordable product. Back the Kickstarter campaign and be one of the first to get your hands on the Cherry Tart crafty series. This is a great opportunity to support an innovative, educational, and fun product that will spark your creativity and imagination. Let’s build something amazing together!
4M KidzRobotix Motorised Robot Head
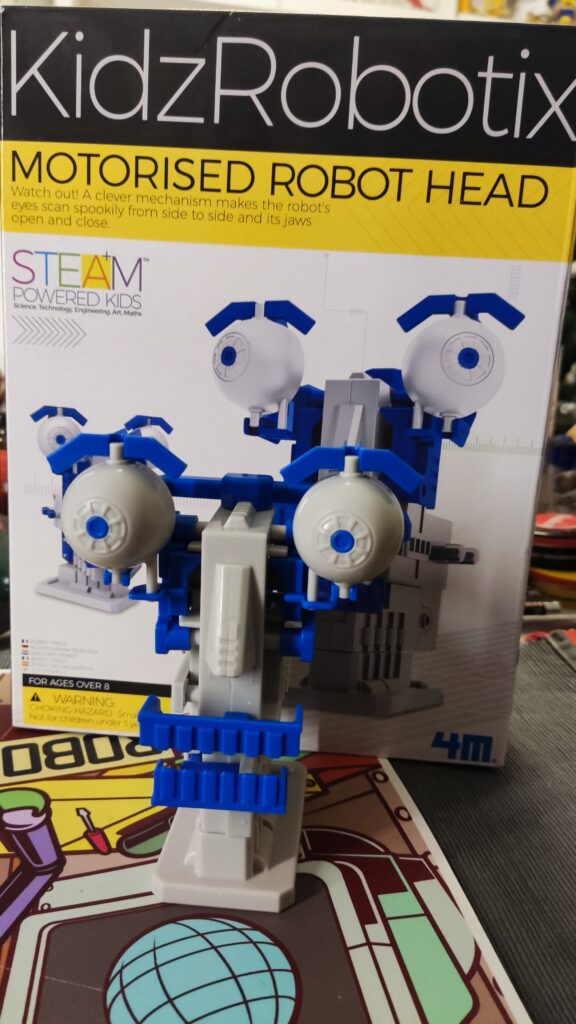




4M KidzRobotix Motorised Robot Head. Timelapse and Realtime Build. Find the latest News on robots, drones, AI, robotic toys and gadgets at robots-blog.com. If you want to see your product featured on our Blog, Instagram, Facebook, Twitter or our other sites, contact us. #robots #robot #omgrobots #roboter #robotic #automation #mycollection #collector #robotsblog #collection #botsofinstagram #bot #robotics #robotik #gadget #gadgets #toy #toys #drone #robotsofinstagram #instabots #photooftheday #picoftheday #followforfollow #instadaily #werbung #kidzrobotix #4m #robothead
Soon on Robots-Blog: Variobot variAnt
RBTX Robotik-Marktplatz jetzt in 18 Ländern verfügbar
RBTX powered by igus baut Angebot international weiter aus und macht Low Cost Automation in 10 weiteren Ländern zugänglich
Köln, 23. Januar 2023 – Mit seinem Low Cost Automation Angebot ist igus angetreten, die Einstiegshürden ins Automationszeitalter zu senken. Teil des Angebots ist seit 2019 auch RBTX.com. Der Robotik-Marktplatz hilft Interessierten dabei, so einfach, schnell und kostengünstig wie möglich die passende Automatisierungslösung für ihre individuelle Anwendung zu finden. Bisher war RBTX in acht Ländern verfügbar. Jetzt weitet igus das Angebot aus und startet den Robotik-Marktplatz in zehn zusätzlichen Ländern – drei weitere folgen bald.

Um die eigene Wettbewerbsfähigkeit zu sichern, setzen immer mehr Unternehmen auf die Automatisierung ihrer Prozesse. Die meist hohen Investitionskosten und das fehlende Know-how stellen jedoch nach wie vor oft eine Hürde dar – insbesondere für kleinere und mittelständische Betriebe. Hier kommt RBTX powered by igus ins Spiel: Das Angebot umfasst einen Online-Marktplatz für kostengünstige Robotik-Komponenten und Komplettlösungen, den RBTXpert Remote-Integrationsservice und Customer Testing Areas an verschiedenen Standorten weltweit, wo geplante Kundenanwendungen gemeinsam vor dem Kauf live getestet werden können. Getreu dem Motto: Test before invest. So macht RBTX Automatisierung für Alle zugänglich – ob Bäckerei, Pharmalabor oder Automobil-OEM. „Unser RBTX Online-Marktplatz ist im letzten Jahr stark gewachsen“, sagt Alexander Mühlens, Leiter Geschäftsbereich Automatisierungstechnik und Robotik bei igus. „Gestartet sind wir 2019 in Deutschland. Da unser Angebot sehr gut angenommen wurde und die Nachfrage stetig wächst, haben wir RBTX in den vergangenen Jahren bereits auf Österreich, Frankreich, Großbritannien, die USA, Kanada, Indien und Singapur ausgeweitet. Wir arbeiten jedoch kontinuierlich daran, in weiteren Ländern aktiv zu werden, um Low Cost Automation weltweit zugänglicher zu machen. Daher bieten wir RBTX ab sofort in zehn weiteren Ländern an: Polen, Schweiz, Dänemark, Italien, Japan, China, Taiwan, Südkorea, Vietnam und Thailand. Mit Spanien, Brasilien und der Türkei folgen bald noch drei weitere.”

Schnelle Roboter-Integration mit Remote-Services boomt
Auf RBTX.com haben Interessierte aktuell Zugang zu über 300 einzelnen Robotik-Komponenten von 78 Herstellern sowie über 150 Komplettlösungen aus der Praxis – inklusive garantierter Hardware- und Softwarekompatibilität. Der Online-Marktplatz bietet auch einen Ort, an dem sich Mensch und Roboter begegnen. In der Customer Testing Area können Kunden gemeinsam mit einem RBTXperten, dem Remote-Integrator-Service, die Machbarkeit ihrer geplanten Anwendung testen. Der RBTXpert verbindet sich per Live-Videocall aus dieser Umgebung mit Automatisierungswilligen für eine individuelle Beratung. „Allein in Deutschland führen wir bis zu 30 Projekte pro Woche durch. Auch in vielen anderen Ländern haben wir Customer Testing Areas vor Ort, sodass der RBTXpert in diversen Sprachen und Zeitzonen beraten kann“, betont Alexander Mühlens. „Dadurch bekommen noch mehr Interessierte weltweit direkten Zugang zu einem vielfältigen Angebot für kostengünstige Robotik. So gibt es zum Beispiel Klebeanwendungen bereits ab 5.804 Euro oder Qualitätskontrollanwendungen ab 5.476 Euro.“
Inspiring North West manufacturers with remote robotics
A virtual reality (VR) robotics showcase has been installed at AMRC North West to help the region’s businesses unlock the immense potential of robotic technology to boost their manufacturing processes.
The inclusion of Extend Robotics’ UR5e RoboKit and SenseKit module, is designed to showcase the potential of cutting-edge, accessible robotics technology and used to inspire new approaches to manufacturing.
Aparajithan Sivanathan, head of digital technology at the Advanced Manufacturing Research Centre (AMRC) North West, said: “When introducing new technologies, accessibility is crucial.
“The speed and simplicity of installation, coupled with the easy to use, intuitive VR controls, means Extend Robotics’ solution has immense potential to upgrade manufacturers’ existing robotics.”
AMRC North West is part of the University of Sheffield and a member of the High Value Manufacturing (HVM) Catapult. Its goal is to help the Lancashire region’s manufacturing community access advanced technologies that will drive improvements in productivity, performance and quality.
This latest piece of kit, purchased by the Samlesbury Enterprise Zone-based research centre, was fulfilled as part of Extend Robotics’ inclusion in Universal Robot’s UR+ ecosystem. This ecosystem, which provides access to more than 340 certified kits, components, grippers, software and safety accessories, seamlessly integrates with Universal Robots’ cobots.
Dr Chang Liu, is founder and CEO of Extend Robotics, a company which aims to develop human-robot interface software for non-robotic experts to teleoperate and programme robotic manipulators remotely for physical tasks.
Dr Liu said: “Our installation with AMRC North West demonstrates just how simple it can be to dramatically upgrade your robotics capabilities. In less than an hour we made it possible for their robotic arm to be remote operated from anywhere in the world. We hope this will inspire other manufacturers to explore how we can extend their capability using our technology.”
The set-up of the VR robotics technology by Extend Robotics took just one hour – and was completed using its unique software, seamlessly integrating with AMRC North West’s existing robotics hardware.
For further details about Extend Robotics, visit: www.extendrobotics.com.
Kosmos Robo-Truck
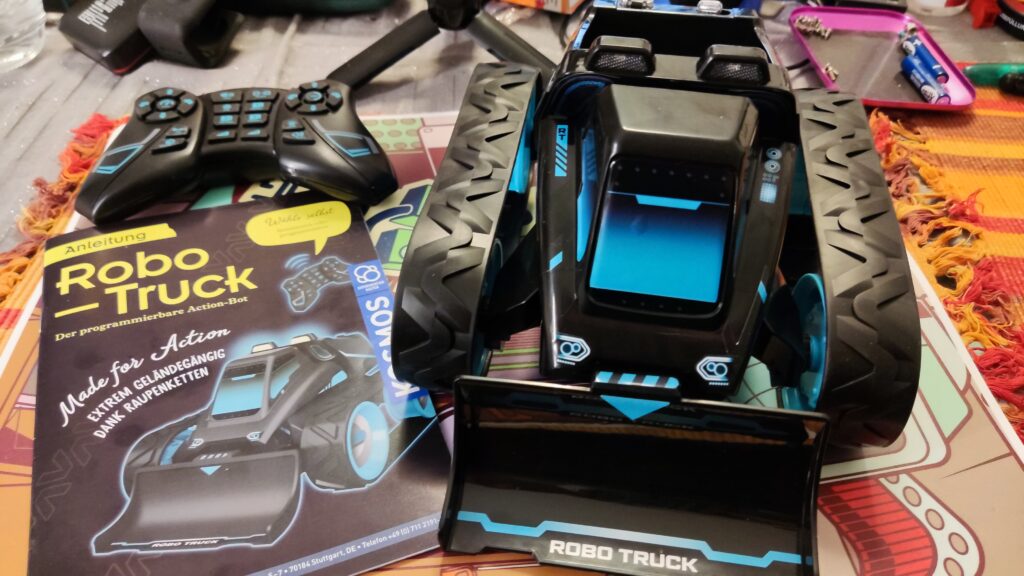
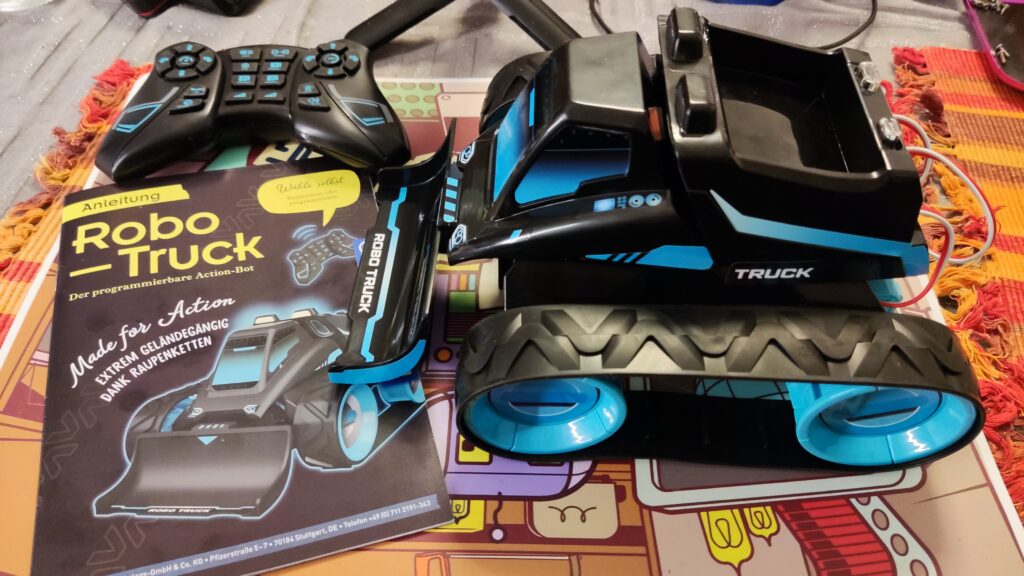
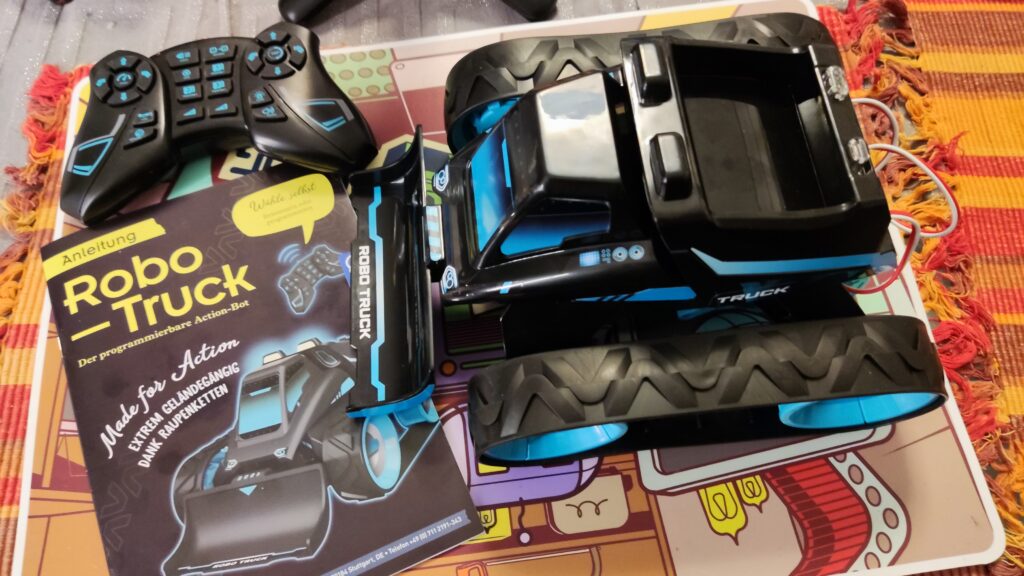
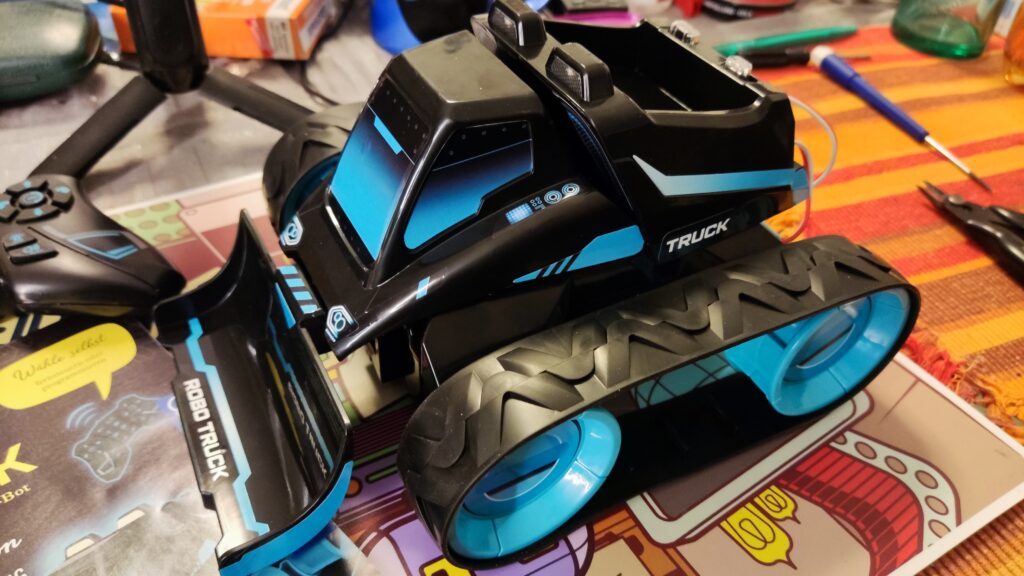
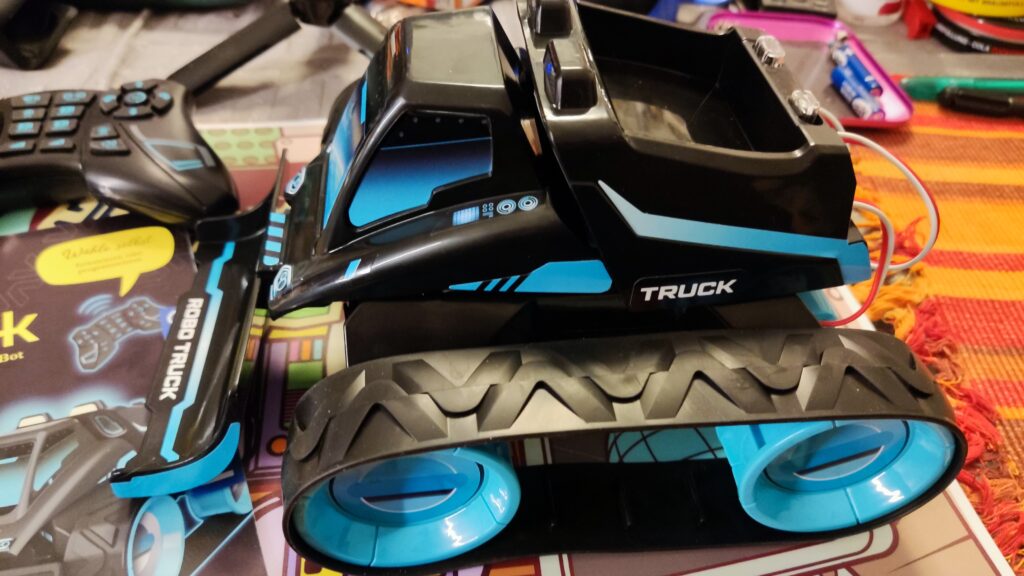







Kosmos Robo-Truck. Find the latest News on robots, drones, AI, robotic toys and gadgets at robots-blog.com. If you want to see your product featured on our Blog, Instagram, Facebook, Twitter or our other sites, contact us. #robots #robot #omgrobots #roboter #robotic #automation #mycollection #collector #robotsblog #collection #botsofinstagram #bot #robotics #robotik #gadget #gadgets #toy #toys #drone #robotsofinstagram #instabots #photooftheday #picoftheday #followforfollow #instadaily #werbung #kosmos #truck #robotruck @kosmos_verlag @kosmos_experimentieren
Spin Master to Acquire the HEXBUG® Brand and Portfolio of Creative Robotic Technology
TORONTO, Jan. 10, 2023 /CNW/ – Spin Master Corp. („Spin Master“) (TSX: TOY), a leading global children’s entertainment company, today announced it has reached an agreement to acquire the HEXBUG brand of toys from award-winning toy company, Innovation First International, Inc.

First entering the market in 2007, HEXBUG products feature robotic technology with ingenious movement inspired by nature, giving kids a whimsical and imaginative play experience. HEXBUG products appeal to kids‘ innate love for remote control and fast-moving creatures that exhibit fascinating life-like behavior. With over 100 different toys that range from buildable playsets to battling robots, HEXBUG products bring fun and excitement to robotics and foster children’s creativity to fuel hours of imaginative playtime.
„What excites us so much about HEXBUG is that the inventors have mastered both the science and the art of bringing creatures to life through technology, to deliver truly magical play experiences,“ said Anton Rabie, Spin Master’s Co-Founder. „With this acquisition, Spin Master will combine it’s innovation, global reach and diverse portfolio with HEXBUG’s innovative excellence to surprise and inspire kids in new ways.“
„At Spin Master we are focused on reimagining everyday play and are always looking for opportunities to strengthen our innovative portfolio through meaningful acquisitions,“ said Max Rangel, Spin Master’s Global President & CEO. „HEXBUG is an evergreen brand with a strong foothold within a niche category, opening an opportunity for Spin Master to own and ultimately grow the popular robotic range’s reach through our expanded global footprint while also leveraging this technology across our broader toy offering.“
„Spin Master is the business that can really take our years of foundational tech toy innovation to the next level and gain an even greater awareness for the brand here at home and around the world,“ said Tony Norman, CEO at Innovation First International, Inc.
Expected to close in February 2023, the acquisition of HEXBUG marks Spin Master’s 28th acquisition since the company was founded in 1994 and the 18th since its initial public offering in 2015.
About Spin Master
Spin Master Corp. (TSX: TOY) is a leading global children’s entertainment company, creating exceptional play experiences through its three creative centres: Toys, Entertainment and Digital Games. With distribution in over 100 countries, Spin Master is best known for award-winning brands PAW Patrol®, Bakugan®, Kinetic Sand®, Air Hogs®, Hatchimals®, Rubik’s Cube® and GUND®, and is the global toy licensee for other popular properties. Spin Master Entertainment creates and produces compelling multiplatform content, through its in-house studio and partnerships with outside creators, including the preschool franchise PAW Patrol and numerous other original shows, short-form series and feature films. The Company has an established presence in digital games, anchored by the Toca Boca® and Sago Mini® brands, offering open-ended and creative game and educational play in digital environments. Through Spin Master Ventures, the Company makes minority investments globally in emerging companies and start-ups. With over 30 offices in close to 20 countries, Spin Master employs more than 2,000 team members globally. For more information visit spinmaster.com or follow-on Instagram, Facebook and Twitter @spinmaster.
About HEXBUG
HEXBUG products first entered the toy industry in 2007, with the goal of giving children a positive experience with robotics at a young age. At first, people were drawn to the realistic bug-like attributes of its micro robotic creatures. Now, the brand has over 100 different toys that range from buildable playsets to battling robots. HEXBUG products continue to spark imaginations with their innovative technology loved by kids and adults of all ages.
About Innovation First International
HEXBUG, VEX Robotics, and RackSolutions are subsidiaries of Innovation First International, a privately held corporation. The company is founded on the belief that implementing innovation early in the design process is necessary to create simple, elegant products and solutions. Innovation First began producing electronics for unmanned mobile ground robots and is now a global leader in the technology, robotics, and STEM education industries.
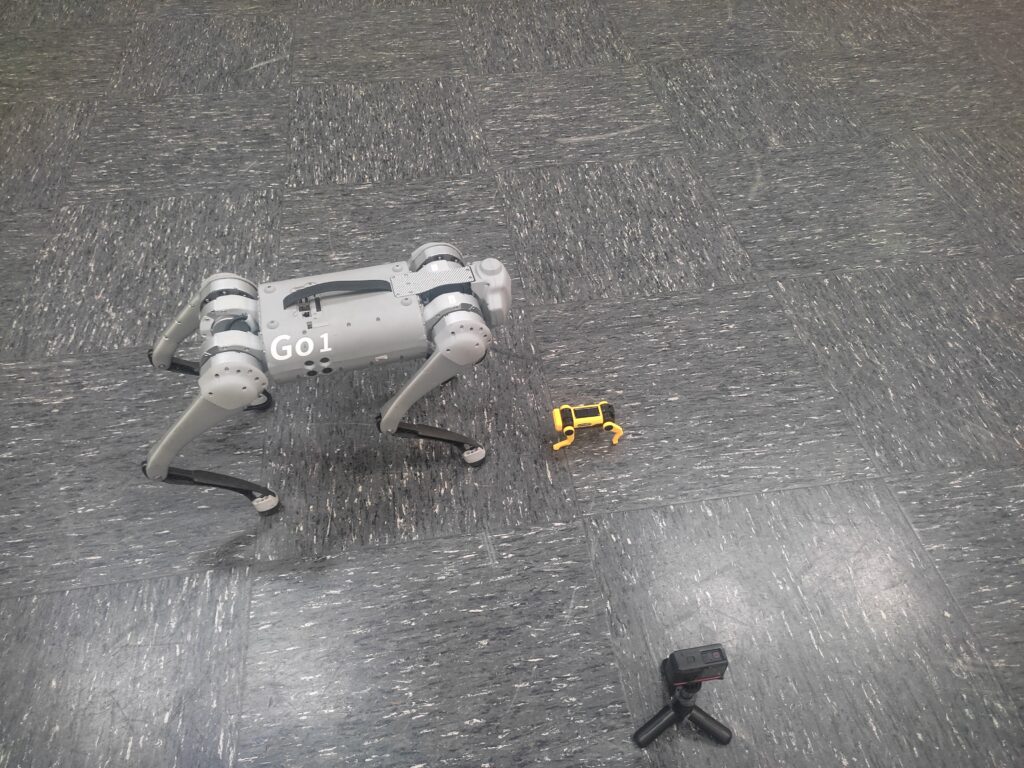
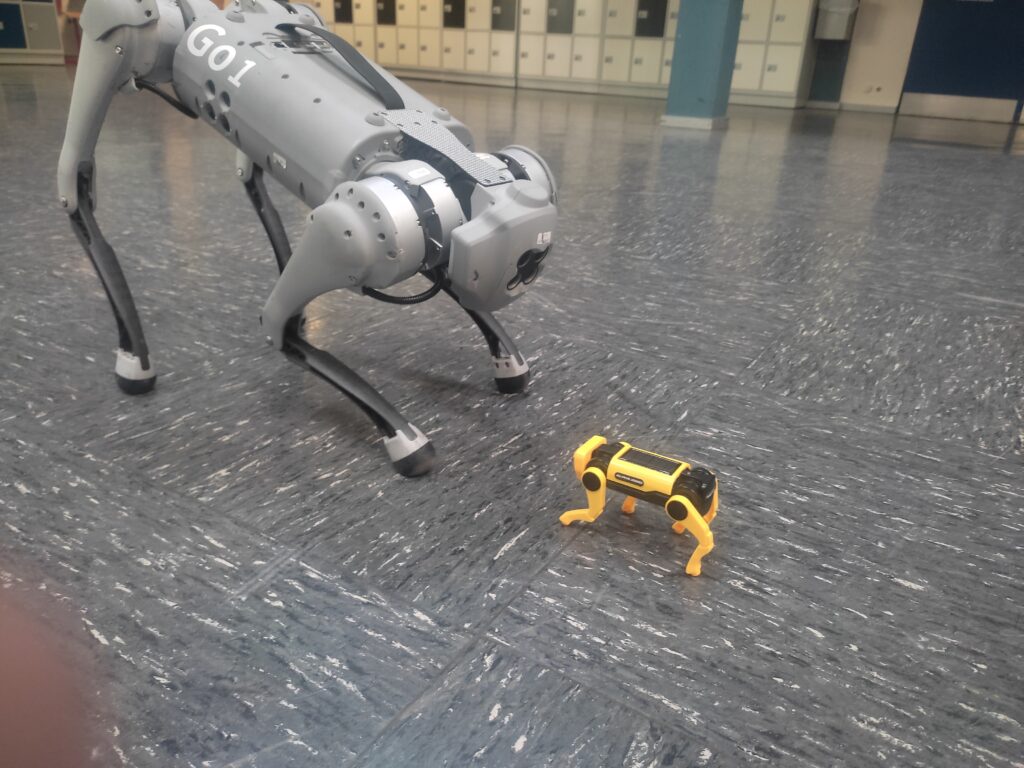
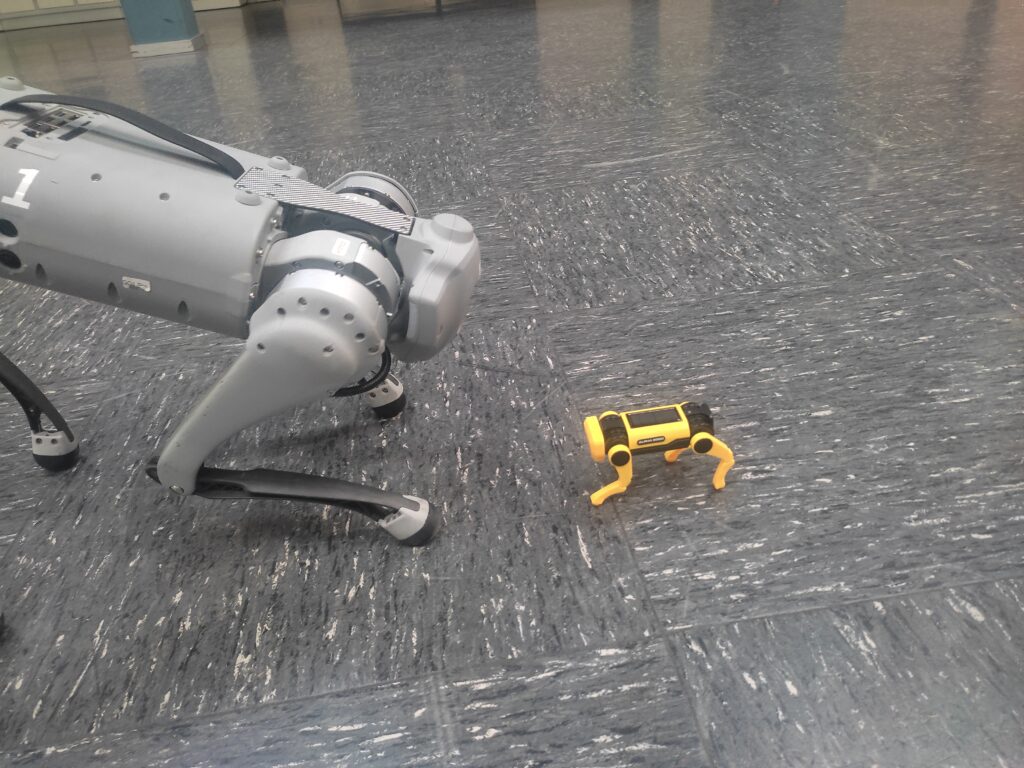
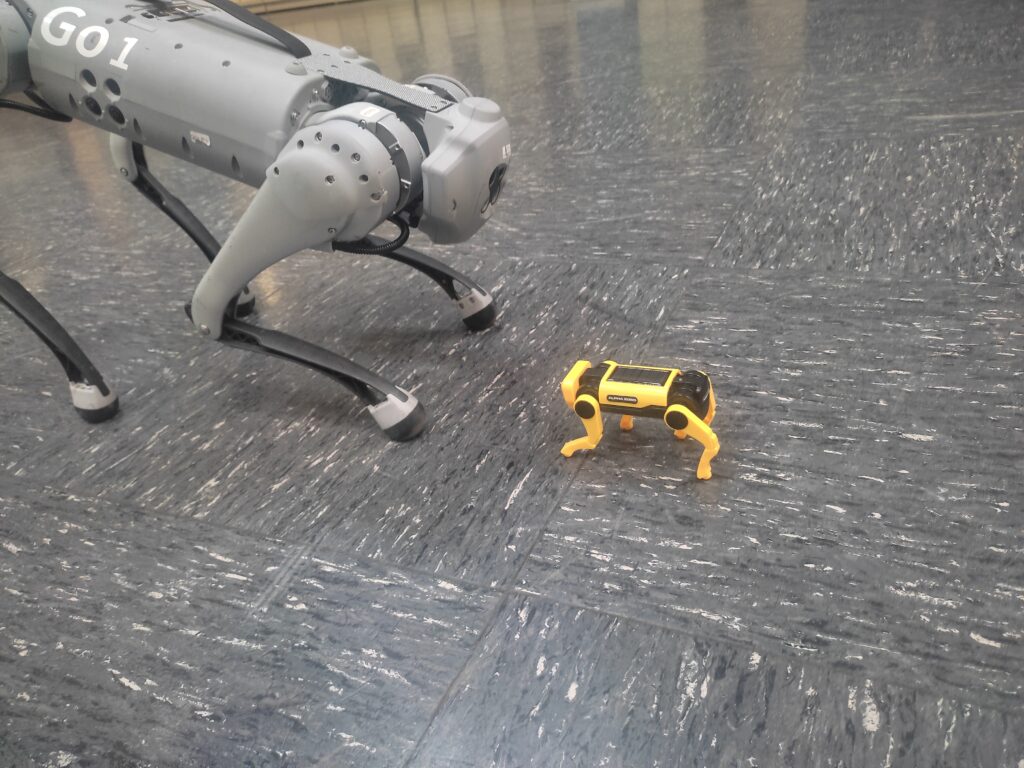
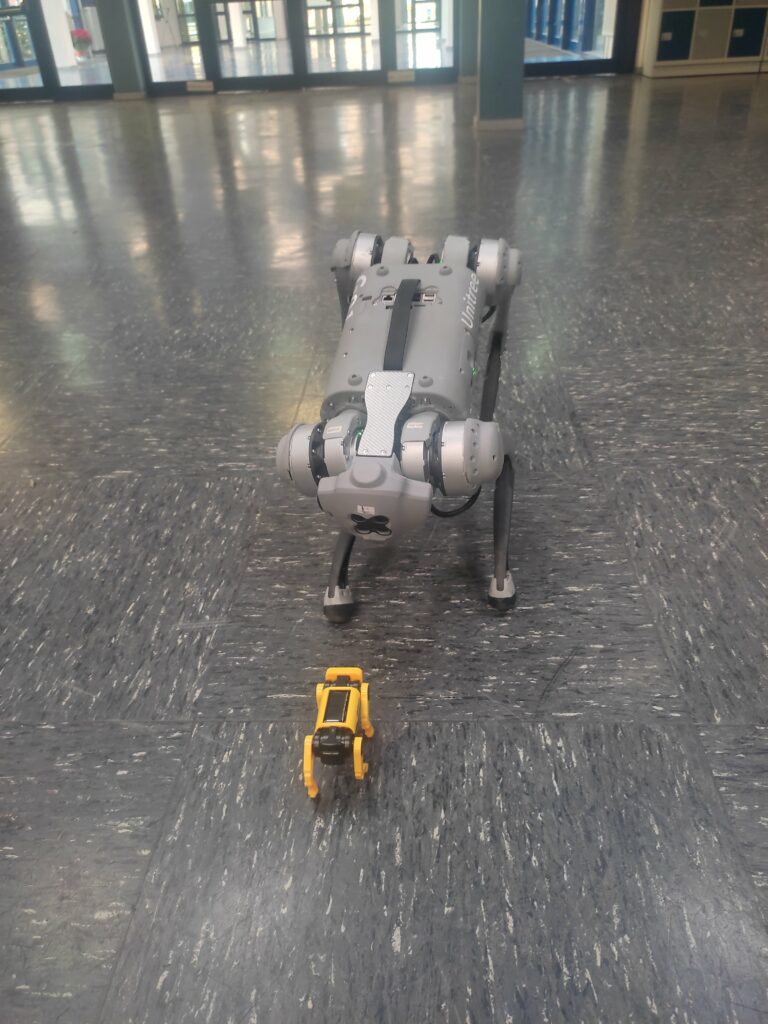
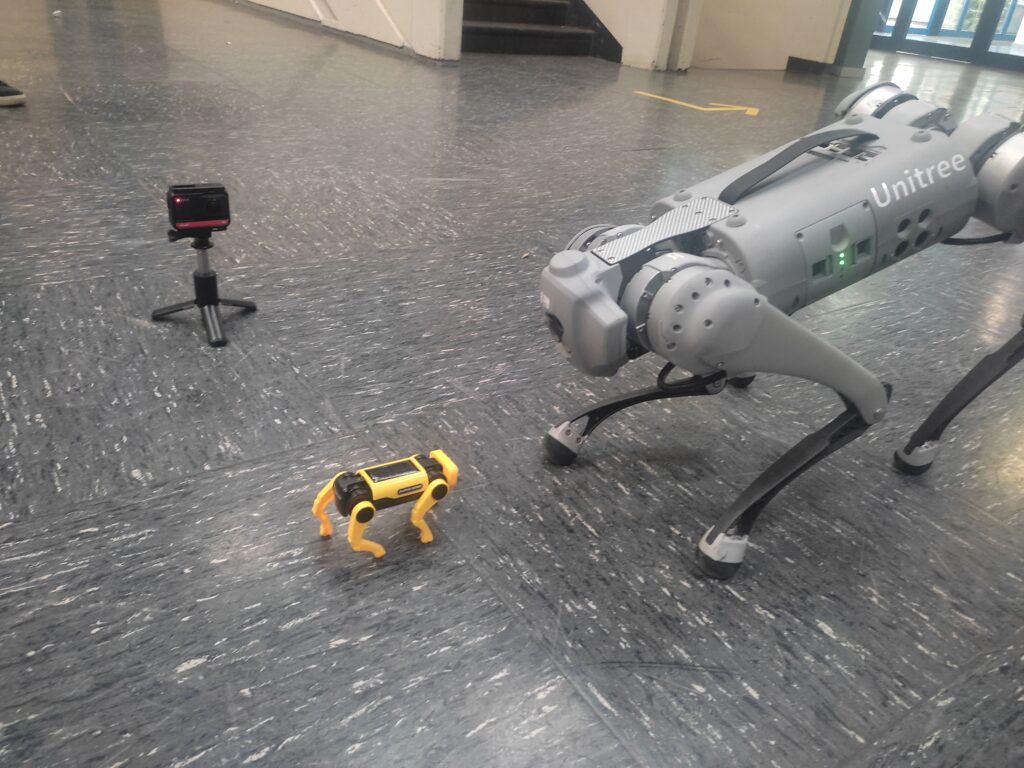
Unitree Quadruped Go 1 meets little robot dog puppy
Unitree Quadruped Go 1 meets little robot dog. Find the latest News on robots, drones, AI, robotic toys and gadgets at robots-blog.com. If you want to see your product featured on our Blog, Instagram, Facebook, Twitter or our other sites, contact us. #robots #robot #omgrobots #roboter #robotic #automation #mycollection #collector #robotsblog #collection #botsofinstagram #bot #robotics #robotik #gadget #gadgets #toy #toys #drone #robotsofinstagram #instabots #photooftheday #picoftheday #followforfollow #instadaily #werbung #unitree #unitreerobotics #quadruped #quadrupedrobotics














