Gamification-Ansatz und zusätzliche Features machen Online-Konfigurator für Low-Cost-Portalroboter noch intuitiver
Köln, 5. Mai 2022 – Der motion plastics Spezialist igus hat seinem Online-Konfigurator für Low-Cost-Portalroboter mithilfe der Spiel-Engine Unity ein Facelift spendiert und die Bedienung dadurch noch effizienter gemacht. Ab sofort können Anwender noch schneller und leichter einen individuellen Portalroboter anschlussfertig konfigurieren – in nur 5 Minuten und mit Live-Preisauskunft. Mithilfe der Online-Tools kann jede Automatisierungslösung auch direkt im ausgewählten Arbeitsraum programmiert und getestet sowie die CAD-Daten und eine passende Zeichnung geladen werden. Selbst kleine und mittelständische Unternehmen können so barrierefrei in die Welt der Automation eintauchen – ohne Know-how von Fachkräften und CAD-Software.
Effizienz steigern, Fehler reduzieren und Kosten senken: Viele Unternehmen haben die Vorteile der Prozessautomatisierung längst erkannt. Doch die Auswahl des richtigen Roboters kann zeitintensiv sein – und Zeit ist bekanntlich Geld. Um den Einstieg in die Automatisierung noch leichter zu machen, hat igus im vergangenen Jahr einen Online-Konfigurator entwickelt. Mit wenigen Klicks können so auch Laien anschlussfertige Low-Cost-Portalroboter basierend auf gleitenden drylin Linearführungen ganz einfach konfigurieren. Linearroboter sind ohne Steuerung ab 1.000 Euro pro Stück erhältlich, mit Steuerung und Software ab circa 4.000 Euro. „Seit dem Start des Konfigurators haben wir viel positives Feedback zum Gamification-Ansatz und der intuitiven Bedienbarkeit bekommen“, sagt Alexander Mühlens, Leiter Geschäftsbereich Automatisierungstechnik und Robotik bei igus. „Nichtsdestotrotz haben wir uns gefragt: Können wir die Bedienung mit diesem Feedback weiter verbessern? Die Antwort war ein klares Ja. Daher haben wir den Konfigurator weiter optimiert und neue Funktionen hinzugefügt.“
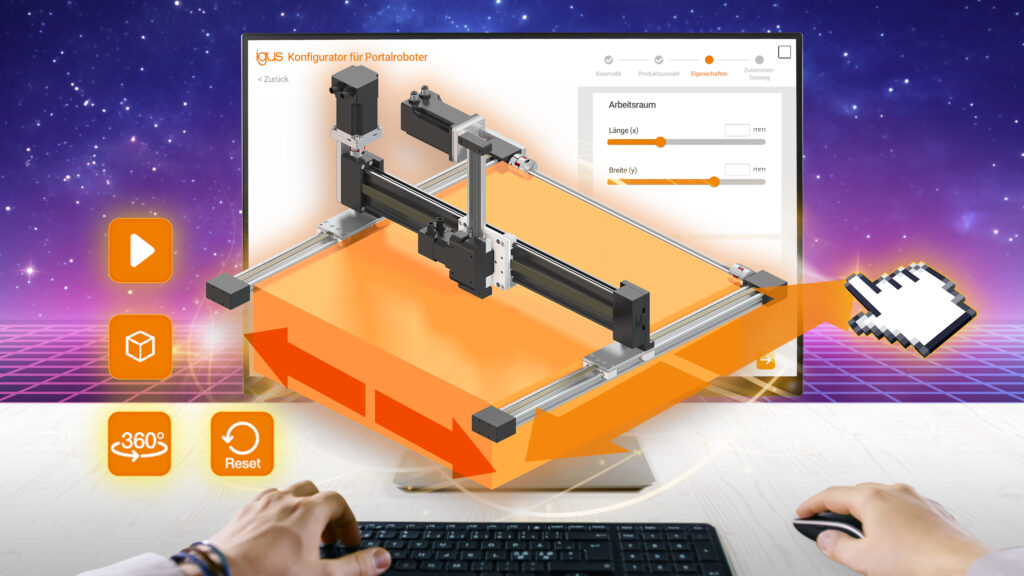
Individuellen Roboter konfigurieren – jetzt noch leichter durch Spiele-Plattform
Für das neue Design des Konfigurators haben die igus Entwickler Unity genutzt – eine Plattform, die bei der Entwicklung von Spielen für PC und Spielekonsolen zum Einsatz kommt. Entsprechend intuitiv ist die Bedienung des Konfigurators. Und die funktioniert wie folgt: Im ersten Schritt wählt der Anwender die Kinematik, also ein Linien-, Flächen- oder Raumportal. Die Optik erinnert dabei an ein Auswahlmenü aus einem Computerspiel, über das Spieler beispielsweise Rennwagen wählen. Mit diesen Standardkonfigurationen lässt sich bei klaren Rahmenbedingungen schnell der richtige Roboter auswählen. Darüber hinaus gibt es erstmalig die Möglichkeit, ein Sonderportal zusammenzustellen und anzufragen. Ob Eismaschine, Vermessungssystem oder Palettierroboter: Viele Anwendungen müssen spezielle Sicherheitsbestimmungen erfüllen, spritzwassergeschützt sein oder arbeiten zum Beispiel in besonders kleinen Bauräumen. Der Online-Konfigurator ermöglicht Anwendern, ein Sonderportal anzufragen, das den speziellen Anforderungen ihrer ganz individuellen Anwendung gerecht wird.
3D-Modell visualisiert Bauraum und Bewegungen des Portals
Der nächste Schritt: die Konfiguration des Portals. Hier stehen Schieberegler zur Verfügung, über die sich die Hublängen der X-, Y- und Z-Achse millimetergenau einstellen lassen. Ein dynamisches 3D-Modell des Portals, das sich in alle Richtungen drehen lässt, visualisiert dabei die Einstellungen in Echtzeit. „An dieser Stelle haben wir eine neue Funktion eingefügt“, freut sich Mühlens. „Mit einem Klick ist es nun möglich, auch den Bauraum des Portals darzustellen. Hierfür nutzen wir farbige Flächen. Somit gewinnen Anwender einen visuellen Eindruck davon, wie viel Platz ihre Automationslösung beansprucht.“ Um auch Transparenz in Sachen Kosten zu gewährleisten, erhalten Nutzer zudem eine Live-Anzeige des Preises ihrer Automationslösung. Fortgeschrittene Nutzer können das 3D-Modell auch als STEP-Datei exportieren und in einem beliebigen CAD-Programm weiterverarbeiten. Mit dem Online-Konfigurator ist es sogar möglich, Bewegungen des Roboters festzulegen – über die Eingabe weniger Parameter und ohne Programmier-Kenntnisse. „Wir folgen mit dieser Funktion dem Motto ‚Test before invest’. Bediener gewinnen dank des beweglichen 3D-Modells ein Gefühl für Roboterbewegungen und Taktzeiten“, so Mühlens. Nach der Online-Programmierung kann die Datei über eine App in Virtual Reality dargestellt oder in die echte Roboter-Steuerung geladen werden.
Online bestellt: Kurze Zeit später steht der Roboter vor der Tür
Sind Bediener mit der Konfiguration des Portals zufrieden, folgen die nächsten Schritte: Sie wählen eine passende Steuerung, die das Portal zu einer anschlussfertigen Low-Cost-Robotic Lösung komplettiert – ob ready-to-use mit igus robot control oder die Do-it-yourself Variante mit dryve D1-Steuerungskit. Kurze Zeit nach der Online-Bestellung steht die Automationslösung dann vor der Tür. Vormontierte Portale in Standardgrößen sind sogar innerhalb von 24 Stunden versandfertig. Ein weiteres Plus: Alle konfigurierbaren Portalsysteme sind durch die selbstschmierenden igus Polymere in allen Lagerstellen 100 Prozent wartungsfrei und sauber. Und zusätzliche Komponenten wie Greifer, Vision-Systeme, Motoren und Sensoren erhalten Automations-Novizen über den Low-Cost-Automation Marktplatz RBTX.