Helping Students Learn Python within a Familiar Coding Environment and at Their Own Pace
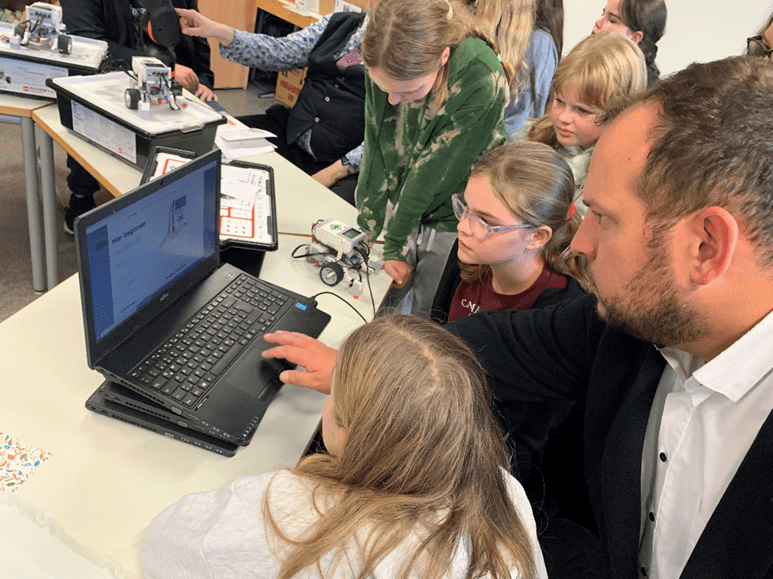
GREENVILLE, Texas, Dec. 9, 2024 /PRNewswire-PRWeb/ — VEX Robotics, a leader in K-12 STEM education, announces the launch of “Switch,” a revolutionary method for learning Computer Science. Switch is a research-based, patented feature within VEXcode, VEX Robotics’ coding platform for all its products. To date, VEXcode has offered students both block-based and python coding languages. With the introduction of Switch inside VEXcode, students can simplify their transition between these two languages by integrating Python commands directly within their block-based code.
Research has consistently shown that block-based coding is best for novice learners to begin programming. However, as students progress they are motivated by the authenticity and power of text-based coding. Research also shows that this transition, from blocks-based to text-based coding, is not trivial, and is often the reason students do not continue to study Computer Science. Switch provides educators with a new tool that fosters a deeper understanding of programming concepts.
Students can now learn Python syntax, editing, and writing at their own pace—all within the familiar block-based environment. Switch offers several key features to facilitate this learning process:
- Convert: Instantly convert one or more normal blocks into a Switch block with a single click, allowing you to see the underlying Python code.
- Edit: Within a Switch block, you can edit the Python code directly, just as you would with regular text editing.
- Write: Add new blank Switch blocks to write Python code from scratch, complete with auto-complete suggestions to assist you.
- Drag and Drop: Rearrange and move Switch blocks just like normal blocks, enabling you to edit the program’s structure through drag-and-drop actions.
- Syntax: Begin with converting a single block to a Switch block to see and learn the Python syntax, and progress to more complex code when you’re ready.
- Learn More: Advance to writing multi-line Python code with proper indentations to deepen your understanding, all within a Switch block.
- Familiar: All of this is done within the comfort of the block-based environment you’re already familiar with, making the transition to text-based programming smoother and more intuitive.
Switch’s scaffolded approach supports learners transitioning from block-based to text-based coding, building confidence and proficiency in a single, supportive environment. The development of Switch demonstrates VEX Robotics’ commitment to providing schools with programs that strengthen STEM education for students of all skill levels.
“Teaching Computer Science is important but also challenging,” said Jason McKenna, Vice President of Global Education Strategy. “Educators are seeking ways to teach programming in an approachable manner that allows students to transition from block-based to text-based coding. Switch is an innovative solution in our ongoing efforts to make STEM and Computer Science Education accessible to all students.”
In addition to facilitating a seamless transition from blocks to text-based coding, Switch assists students in the following key areas:
- Enhanced Differentiated Learning: Switch enables students to progress at their own pace by only converting specific parts of their code to Python when they are ready. This adaptability supports differentiated learning, allowing educators to personalize instruction for students who may excel or need additional support.
- Syntax Guidance and Error Reduction: With built-in autocomplete functionality and automated indentation, Switch helps users learn Python syntax with fewer errors. This guidance allows students to focus on understanding programming concepts rather than being hindered by syntax errors, thereby reducing frustration and fostering confidence.
- Integrated Learning Pathway within VEXcode: Switch is an integral feature of VEXcode, allowing students to start with block-based coding, incorporate Python using Switch, and eventually move to full text-based coding—all in one platform. This structured pathway supports students’ progression from novice to advanced levels in a cohesive environment, reinforcing continuity in their programming journey.
“Research conducted by our team offers empirical evidence for the effectiveness of Switch,” said Dr. Jimmy Lin, Director of Computer Science Education. “The findings contributed to our understanding of how to design environments that support students of varying experience levels and confidence in transitioning from blocks-based modalities to Python”
VEXcode with Switch is free and compatible with the following VEX Robotics platforms: IQ, EXP, V5, and CTE Workcell. Additionally, VEXcode with Switch is available with a subscription in VEXcode VR, an online platform that enables users to learn programming by coding Virtual Robots (VR) in interactive, video game-like environments. VEXcode with Switch is accessible on Chromebooks, Windows, and Mac computers.
“Throughout December, in celebration of Computer Science Education Week, we’re inviting everyone to try Switch with VEXcode VR or with their VEX hardware,” said Tim Friez, Vice President of Educational Technology. “Our new Hour of Code activities and resources enable students to explore Switch coding across both hardware and virtual platforms.”
Transitioning from blocks to text can be challenging, but with the patented Switch features, it doesn’t have to be.
Discover how Switch and VEXcode can empower your students to master Python at their own pace. Visit switch.vex.com to learn more.