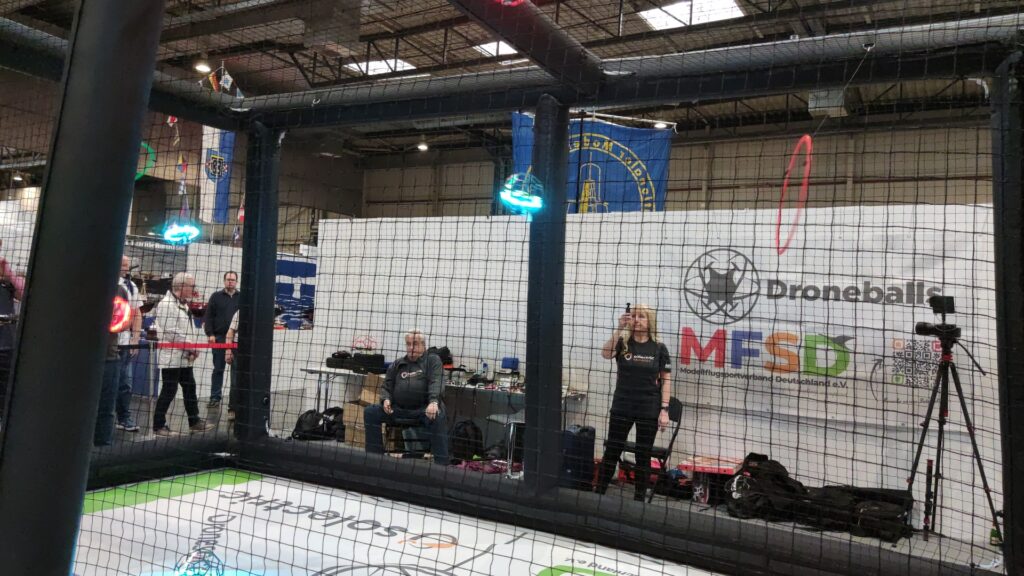
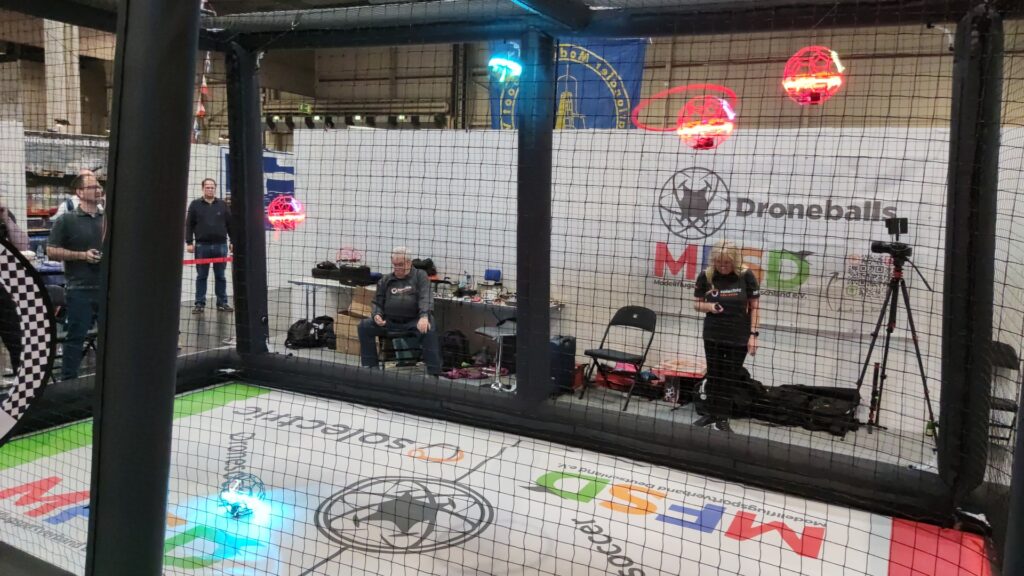
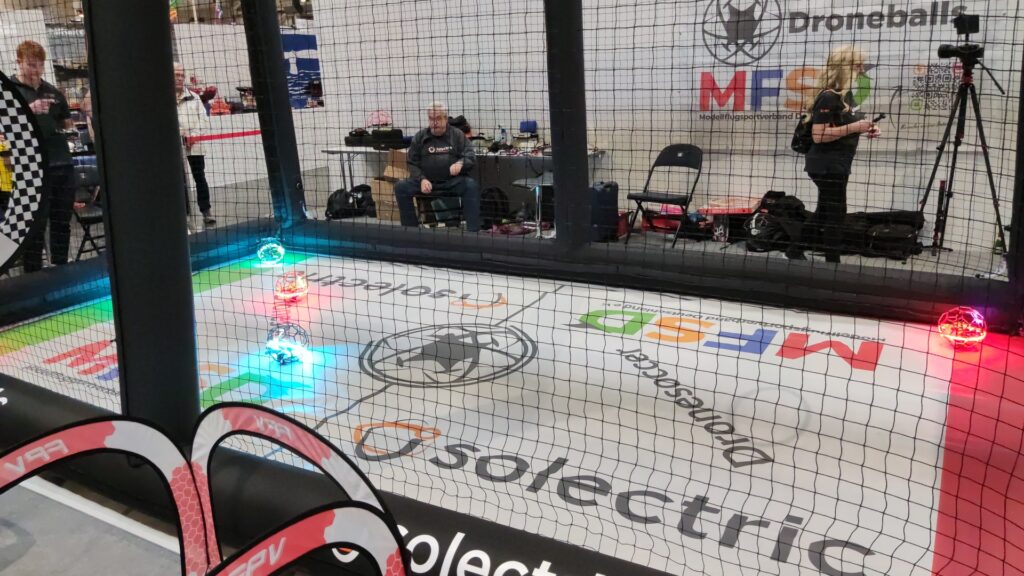



























Sebastian Trella from Robots-Blog had the opportunity to conduct a short interview with Roy Barazani from „the OffBits“.
· Robots-Blog: Who are you and what is your job at the OffBits?
Roy: I am Roy Barazani – The OffBits founding father
· Robots-Blog: What inspired you to create the OffBits toy?
Roy: I guess I’ve always been fascinated by the idea of re-design. Even as a child I used to break my toys apart and try to rebuild them in new and different ways. Looking back, this allowed me to develop my imagination and ability to fantasize.
· Robots-Blog: How did you come up with the name „the OffBits„?
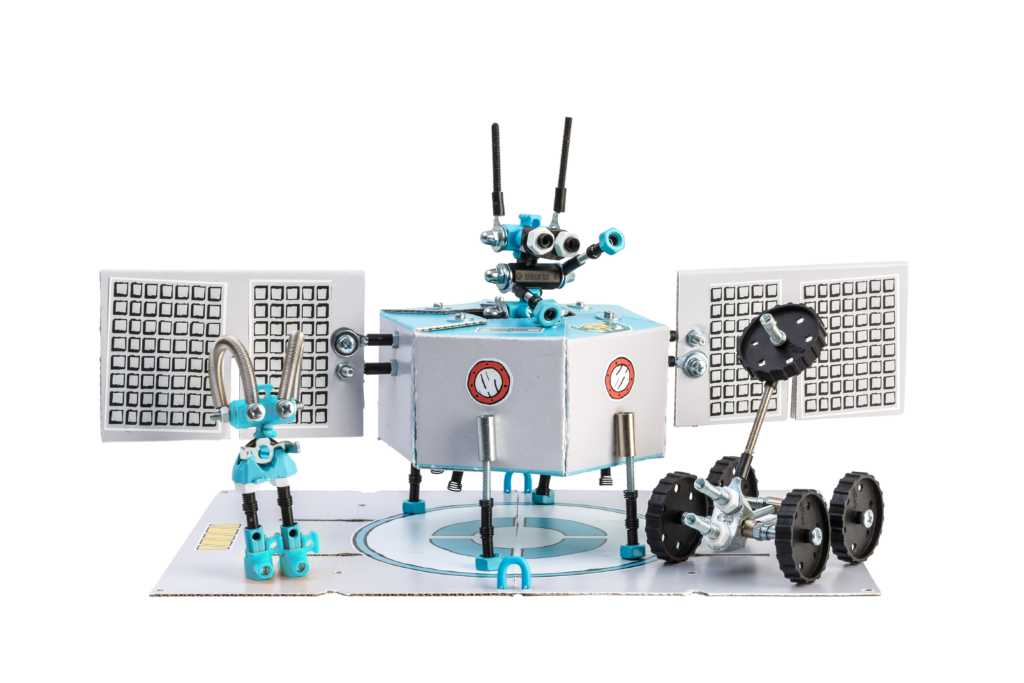
Roy: The OFFBITS started out by playing with random parts I found in my toolbox while working on an exercise before starting my design studies in college. Suddenly I found I had made a little robot! I kept this idea with me during my studies, and for my final project built a whole city of them made from recycled parts. It was really well received and I knew I had a great idea in my hands. It took a few years of development and testing in Maker Faire events and boutique design stores and now I finally feel they are ready for the world.

· Robots-Blog: Do you have a lot to do with robots in your job/everyday life?
Roy: Yes, I love robots and I have collected robots for years!
· Robots-Blog: How did sustainability factor into the creation of the OffBits?
Roy: I see The OFFBITS as a new way of playing with toys, an “open-source” platform with no rules, so each creation can be as unique as the one who built it. I love the way people can take the original design and then make something completely different. Also, the fact it is made of components we all have around us means there are no cost or availability limits to what people can do with them.
Offbits are a sustainable and eco-friendly educational toy that encourages zero-waste principles and practices through a fun and interactive experience. It’s a great way to bring awareness and inspire positive actions in preserving the environment.
We don’t think you need many toys, but what you do choose should be made to last.
The possibilities are endless with The Offbits, you can create anything from a simple robot to a complex model while using sustainable materials and reducing waste.
· Robots-Blog: And which is your favorite robot from the OffBits?
Roy: I love all my robots family!
· Robots-Blog: Can you tell us about any challenges you faced while designing the OffBits?
Roy: From a design perspective, working with standard hardware components brought many unique challenges. For example, choosing the right mix of bits in the kits (both functionally and aesthetically) required a lot of trial-and-error type work, and then of course there is the issue of connecting parts that weren’t designed to fit together.
· Robots-Blog: How do you envision the OffBits evolving in education fields?
Roy: This is a S.T.E.A.M toy helping young minds grow in the fields of Science, Technology, Engineering, Art and Math. The OffBits toys encourage the development of fine motor skills, spatial reasoning, problem-solving, and imaginative play.
The hands-on building process allows users to learn about robotics and engineering concepts in a fun and interactive way. The step-by-step instructions for building and programming the Offbits kits, making it easy for users of all ages to understand the principles behind the technology.
The OffBits offer educational resources such as workshops, online tutorials, and educational material that could help kids to learn about sustainable practices and technologies.
· Robots-Blog: What can you tell us about your community?
Roy: The Offbits community feature allows users to share their creations and ideas, providing inspiration and a sense of collaboration. The Offbits users have challenges for every level. When they create, share and pass the challenge they can earn tokens for their future purchases.
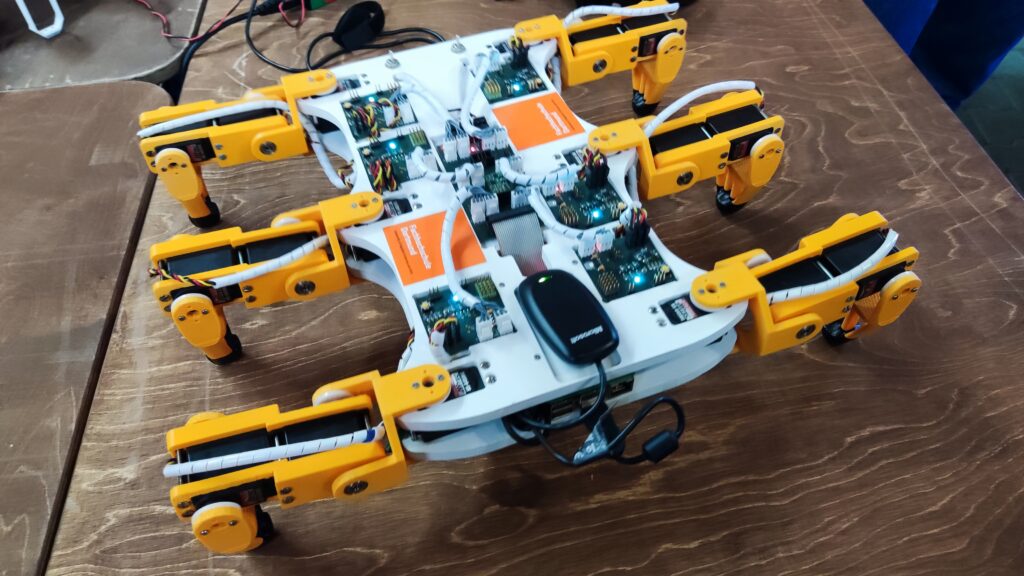
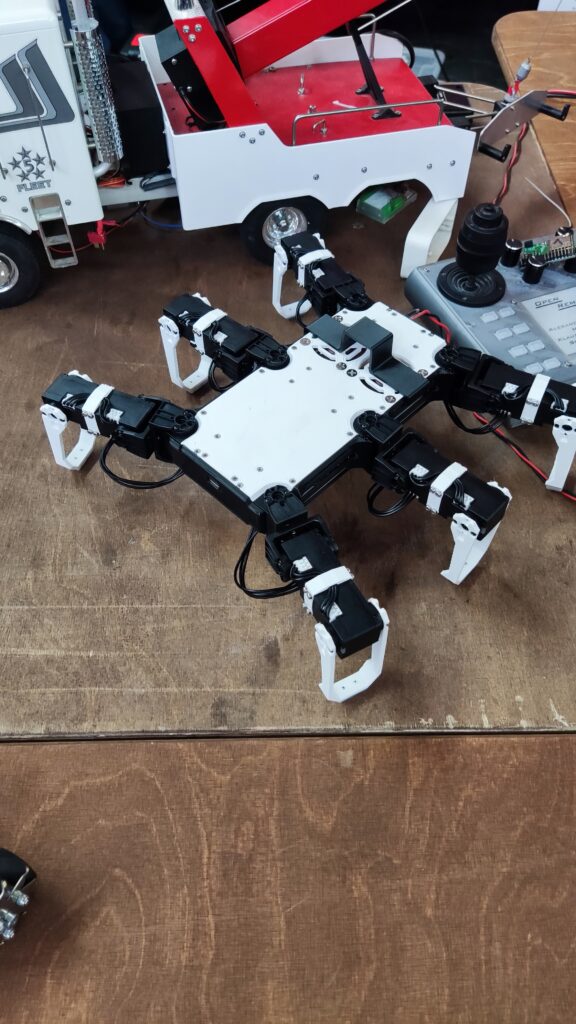
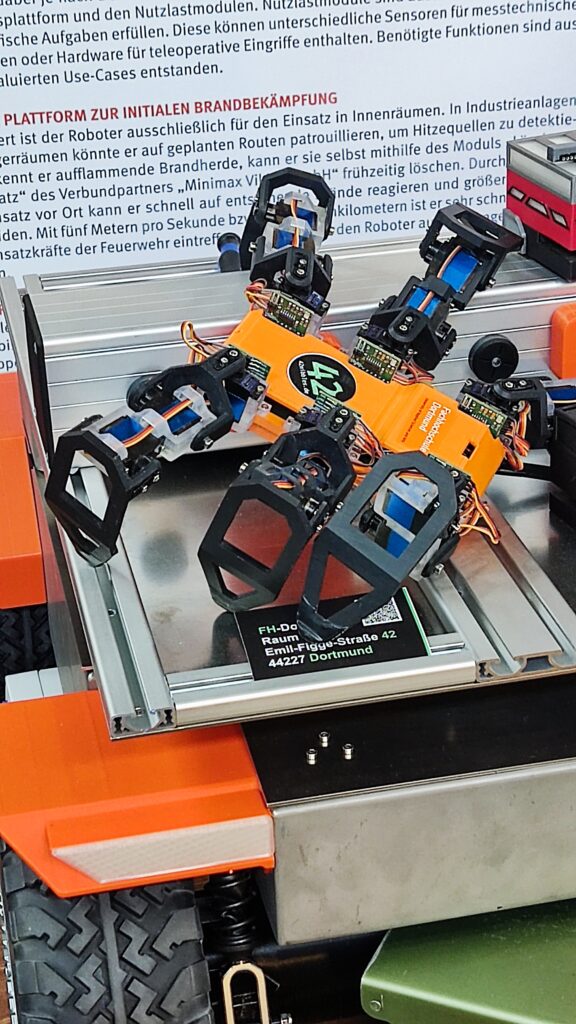
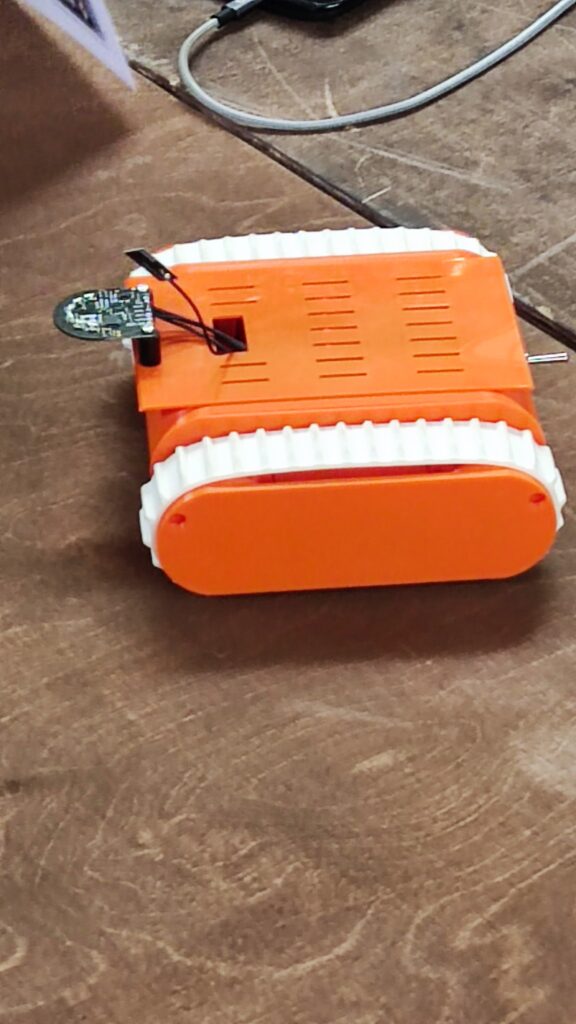
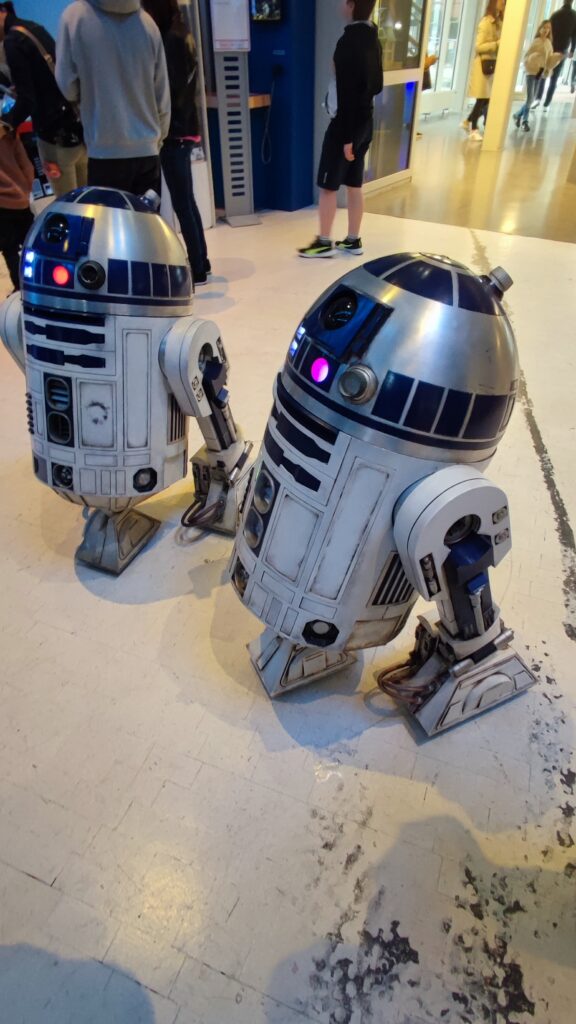
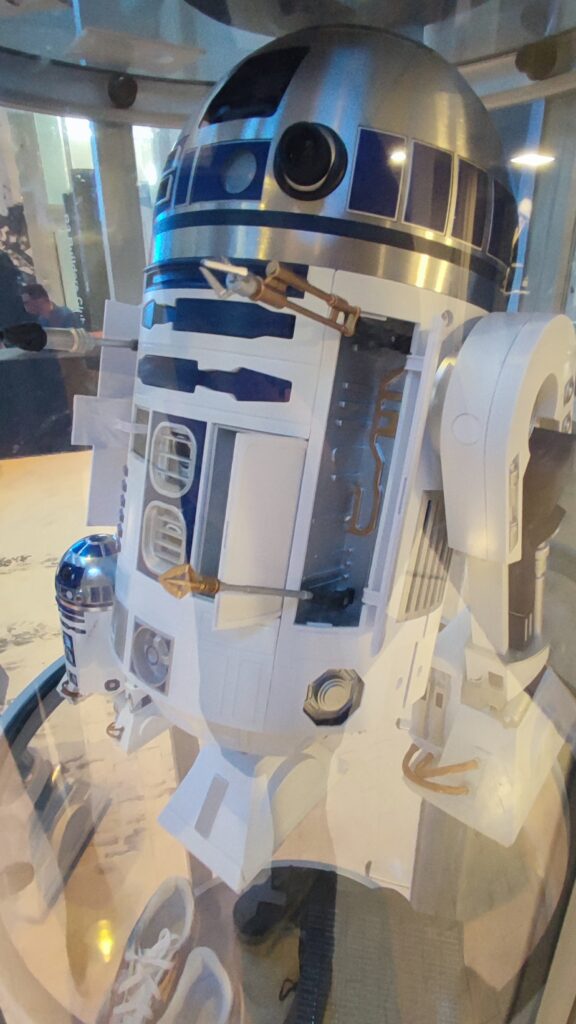
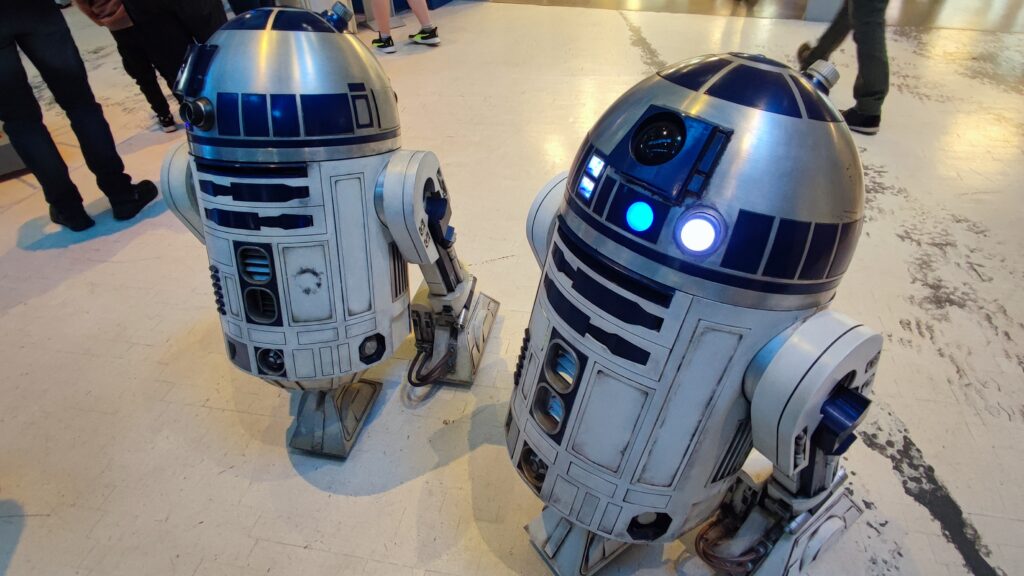
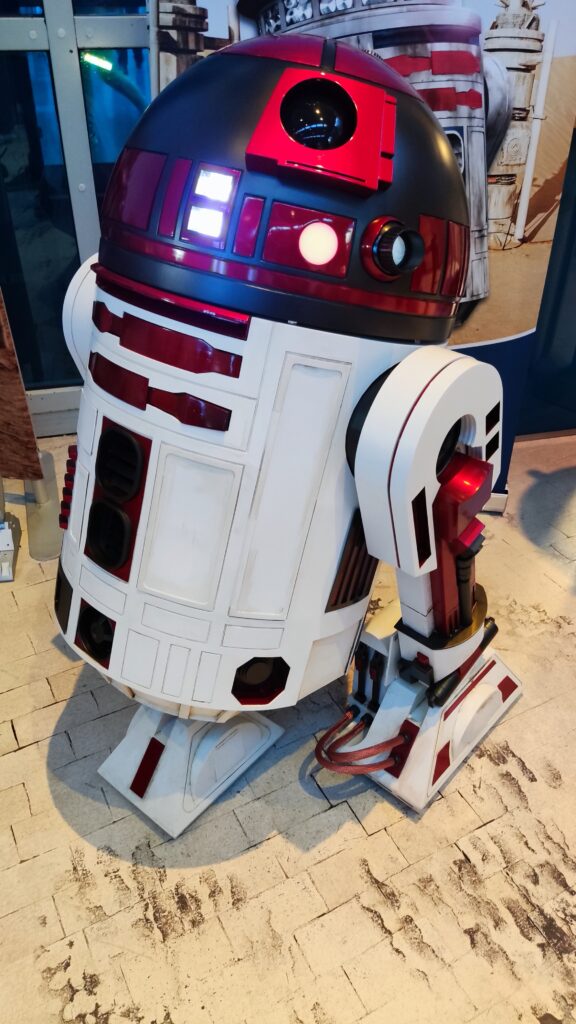
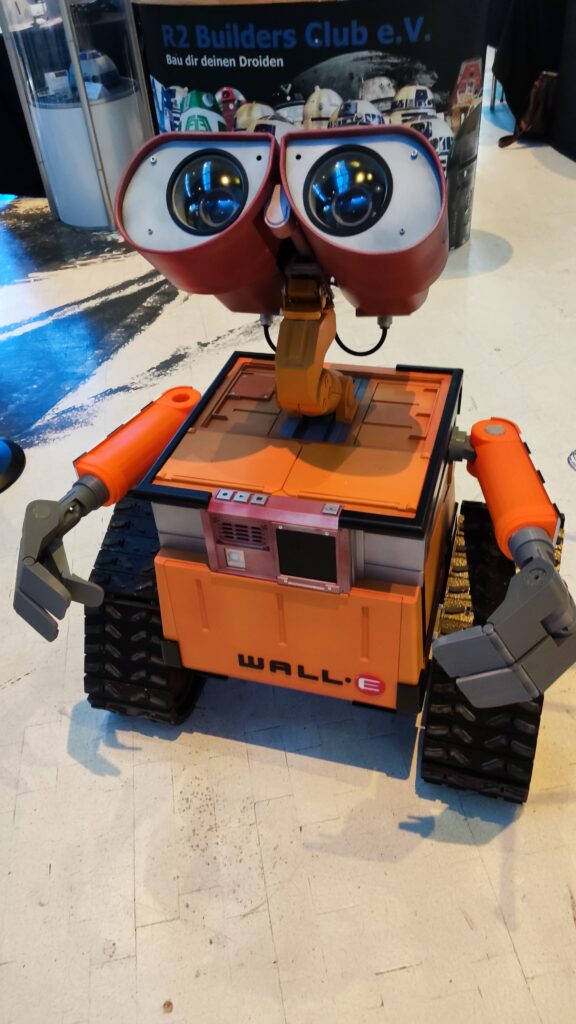
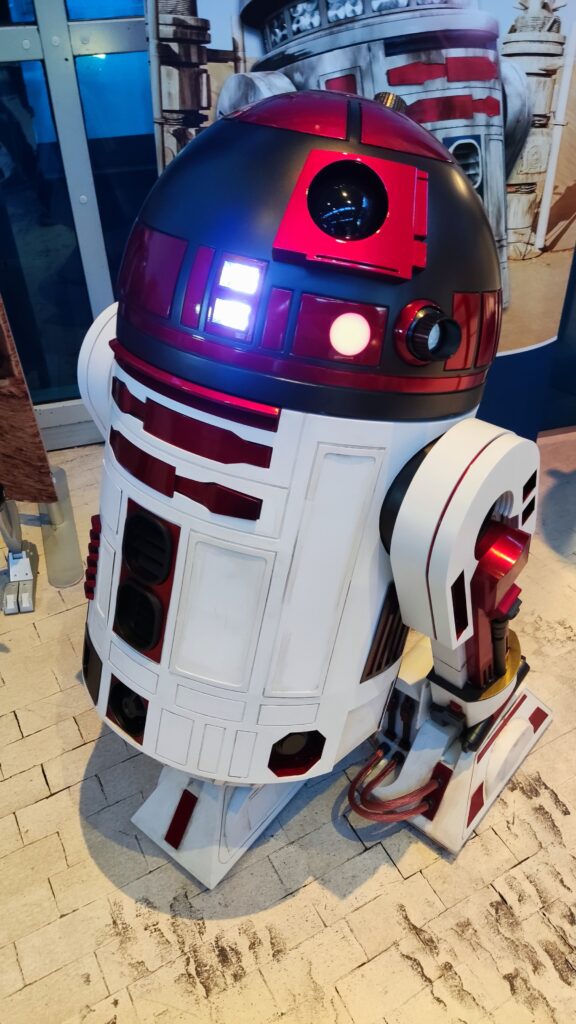
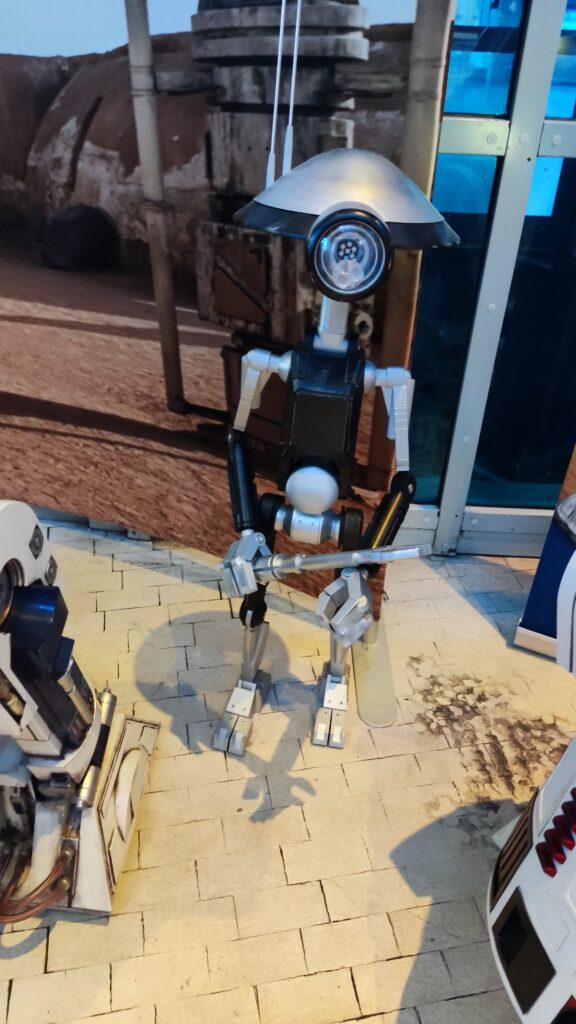
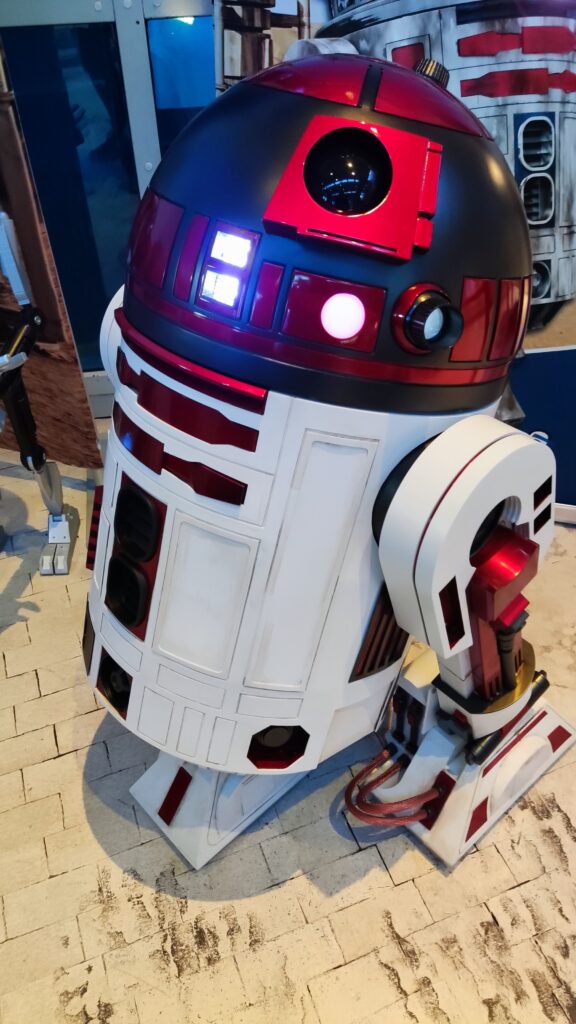
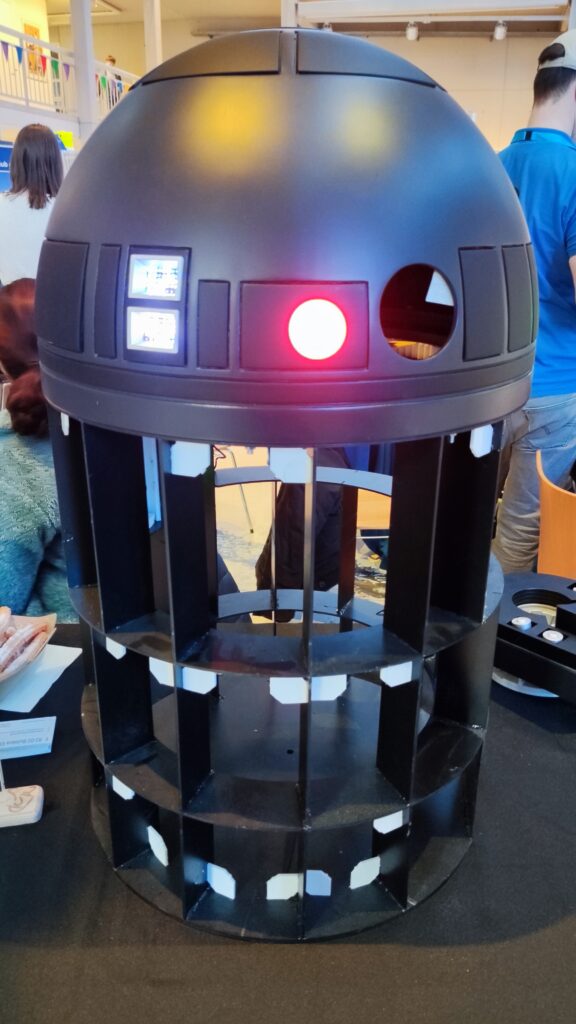
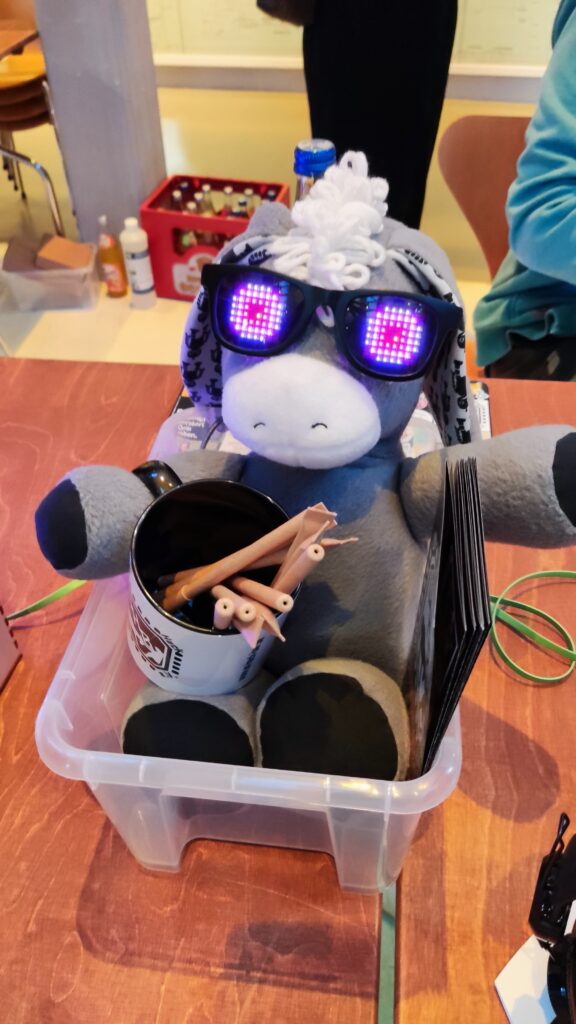
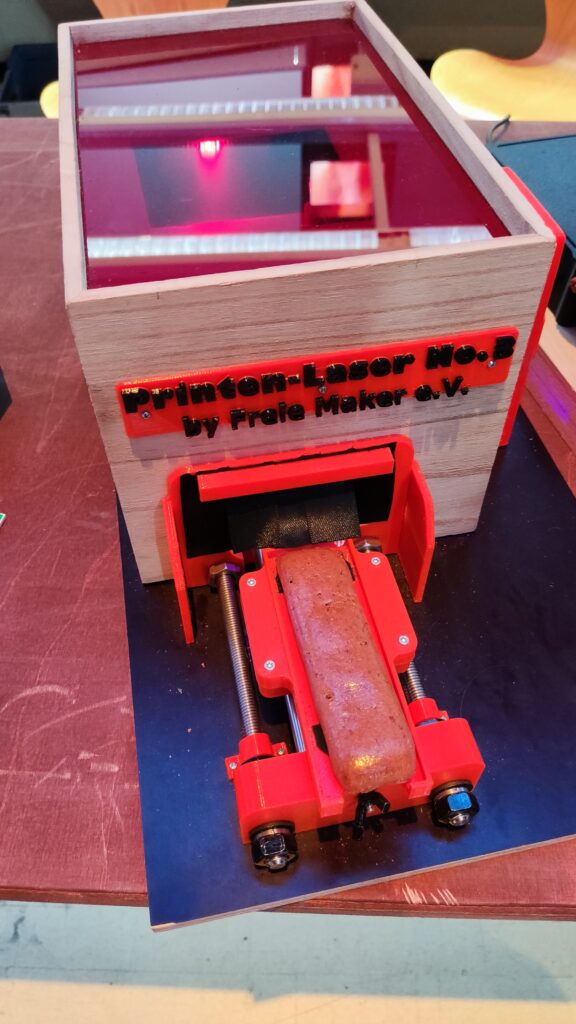
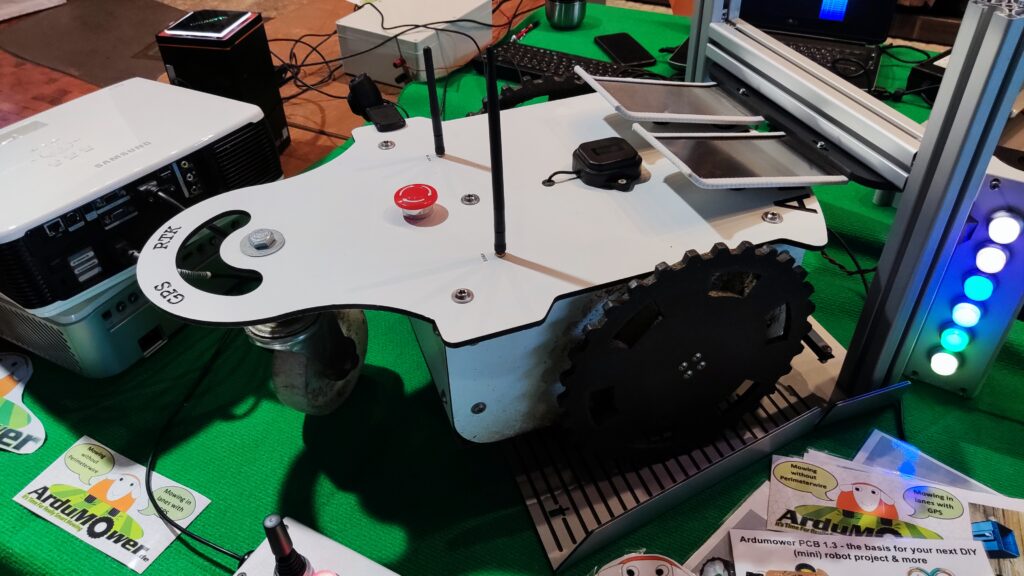








































NSK is working to assist society by developing new service robot technology, including robotic devices for moving patients in medical settings. In October 2021, the company joined a Japanese government initiative to implement robotic technology in hospitals and help prevent the spread of Covid-19. NSK is now working to develop its robotic technologies further through dialogue with frontline medical staff.

New robots are currently in development around the world to assist humans and help solve societal issues. As part of this effort, NSK wants to create robots for use in settings where many people are moving around, including medical facilities and hospitals. The company’s smooth movement and low noise technologies are ideal for robotic applications in this field.
Among the candidates for development at the initial planning stage was an autonomous mobile robot. However, after observing the inner workings of a hospital, with its narrow corridors and high footfall rates, NSK concluded that a motorised assistance robot which could help staff during patient transfer would be a more useful contribution to workplace efficiency.
The company knew that its proposed robot could reduce the physical burden on medical staff and help facilitate work-style reform in the healthcare sector. Based on this approach, the company built a robotic prototype that helps staff to move heavy objects such as stretchers and trolleys in hospitals. As part of the Japanese government initiative, NSK is currently demonstrating the use of its motorised assistance robot at a major hospital. The end goal is eventual adoption by the healthcare sector for daily use.
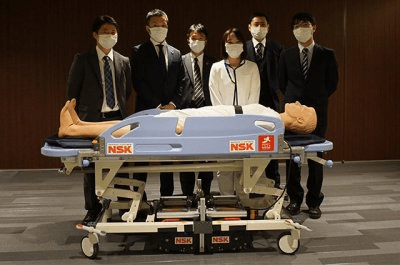
NSK is focusing on essential user issues when developing the assist robot, deploying idea verification in short cycles. For example, rather than spending three years to develop the robot in its entirety, NSK is seeking feedback from customers every three months, implementing improvements incrementally during the development process.
The robot developed by NSK uses a motor drive that facilitates smooth starting and acceleration, as well as deceleration and tight turns. NSK ultimately wants to create a usable robot that fits user requirements, leveraging its know-how to aid people working in frontline healthcare. Innovative projects of this type support the company’s ethos of better meeting the needs of society, while simultaneously creating opportunities for new business growth.
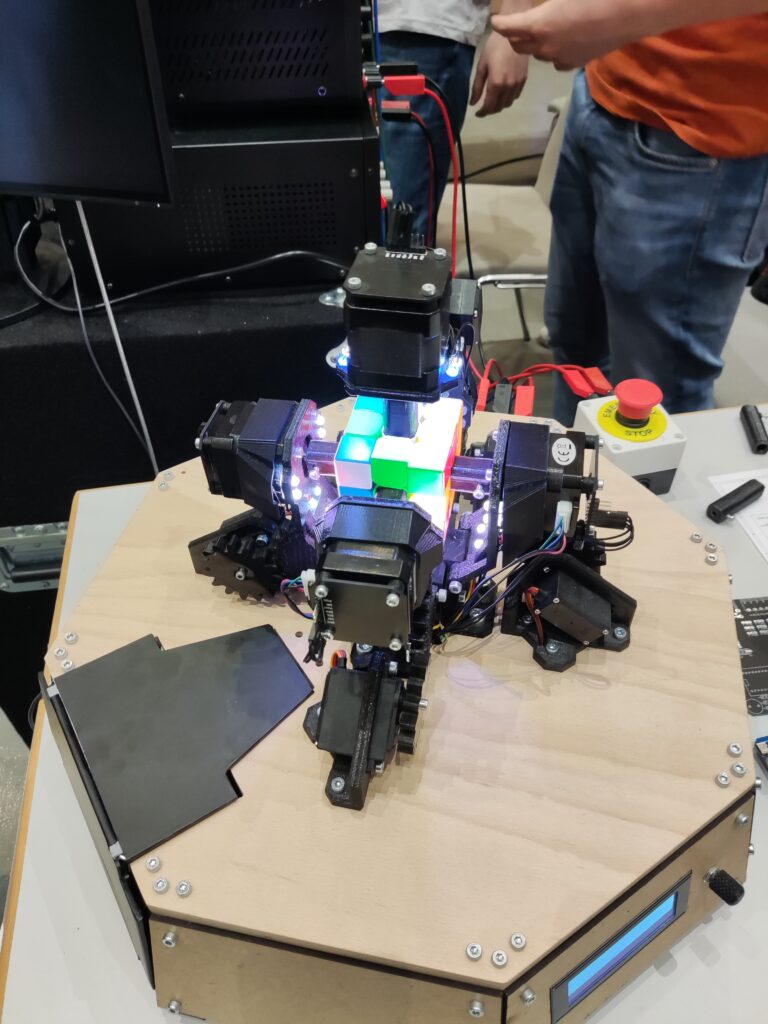
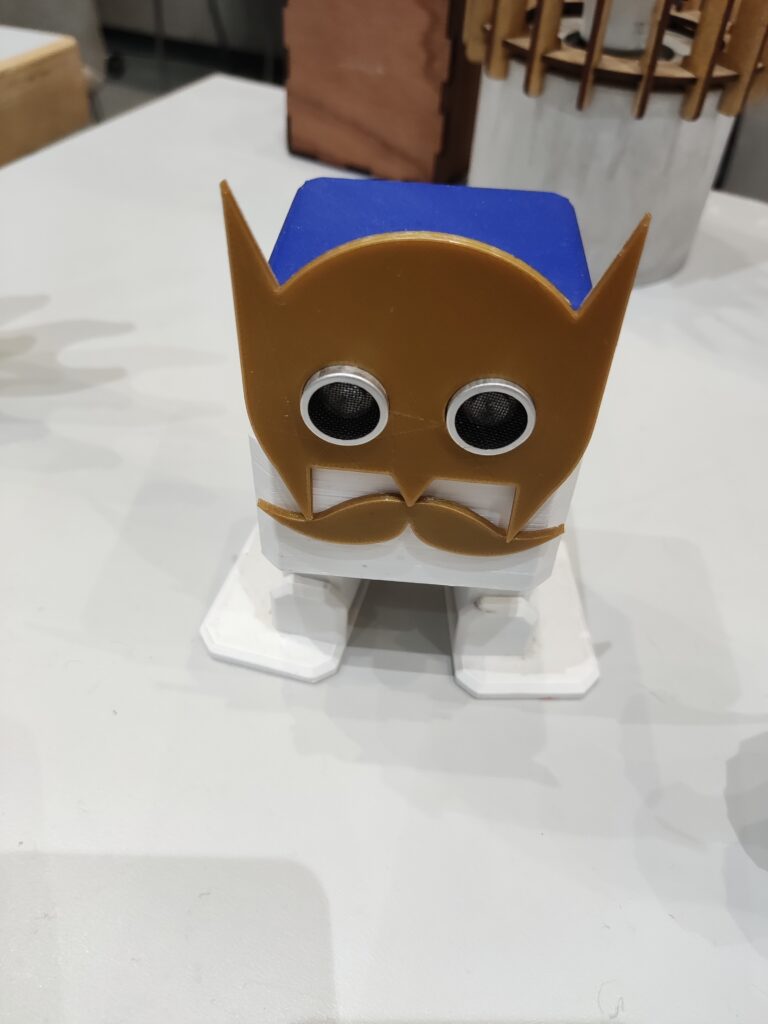
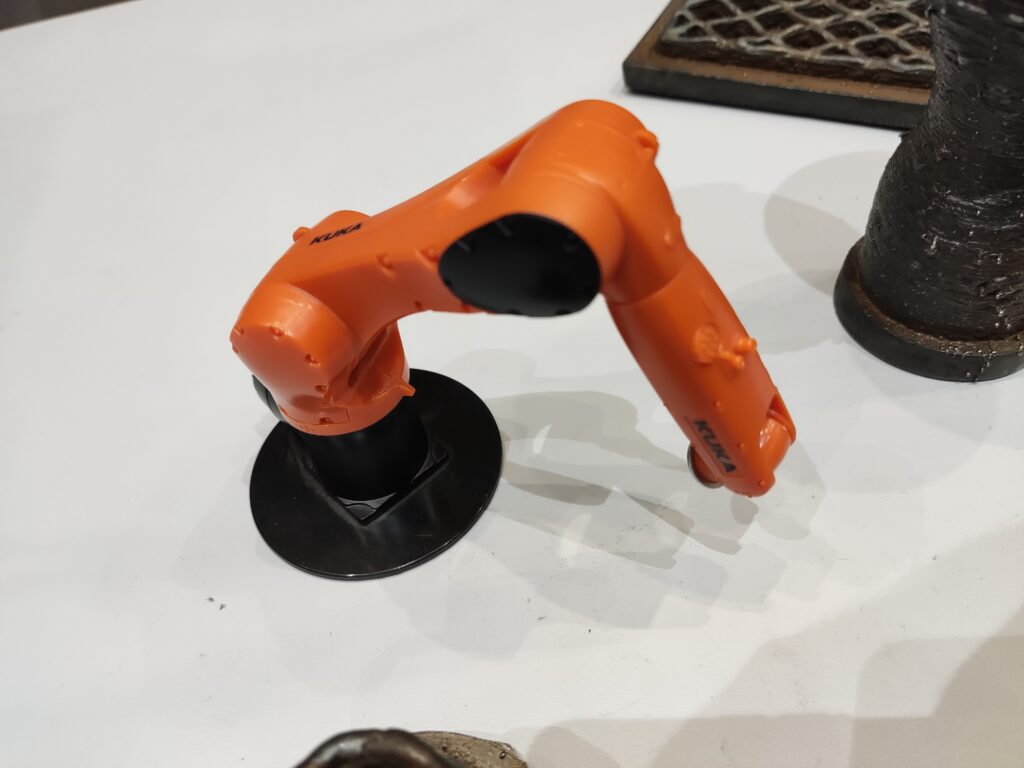
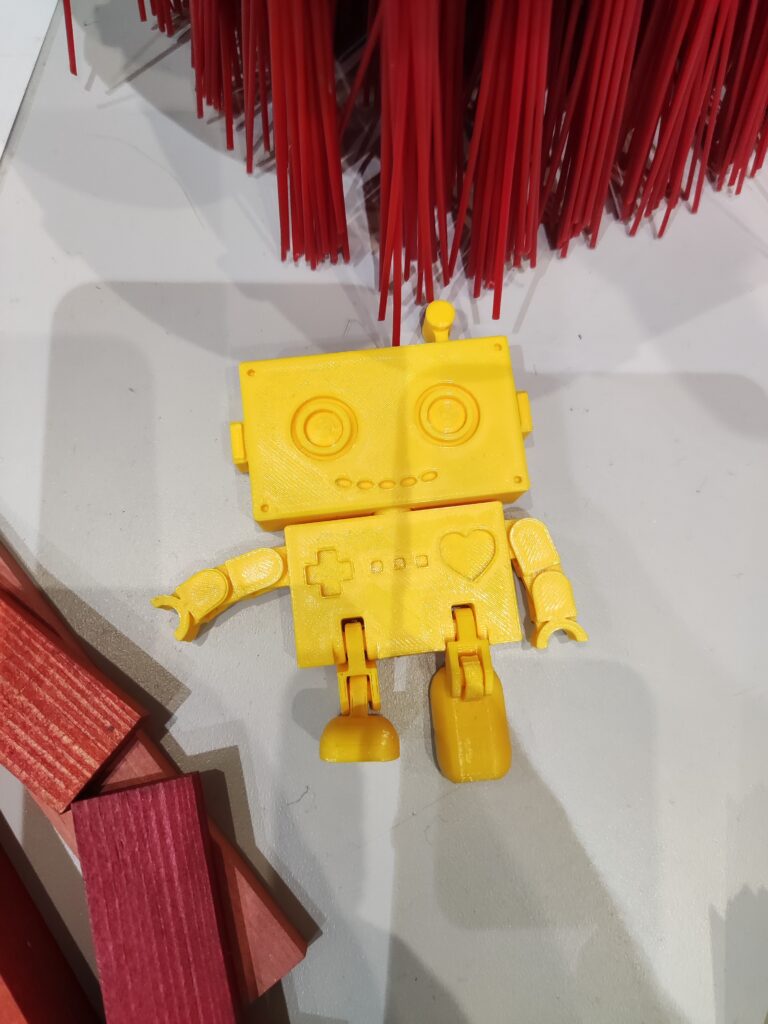
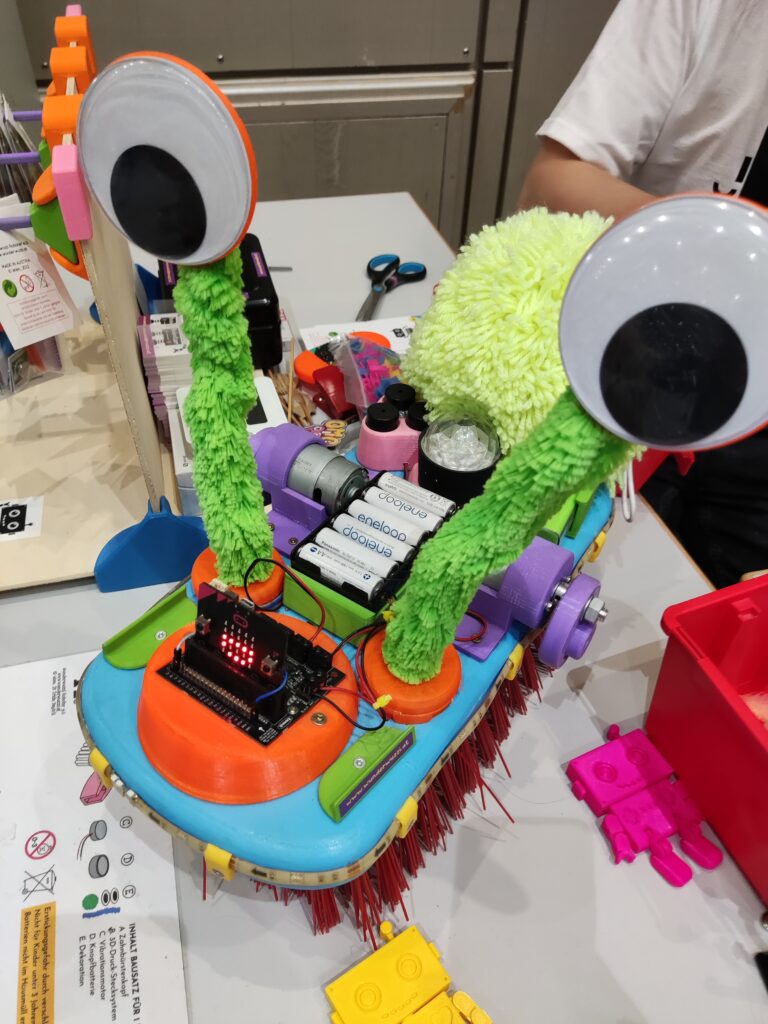
























































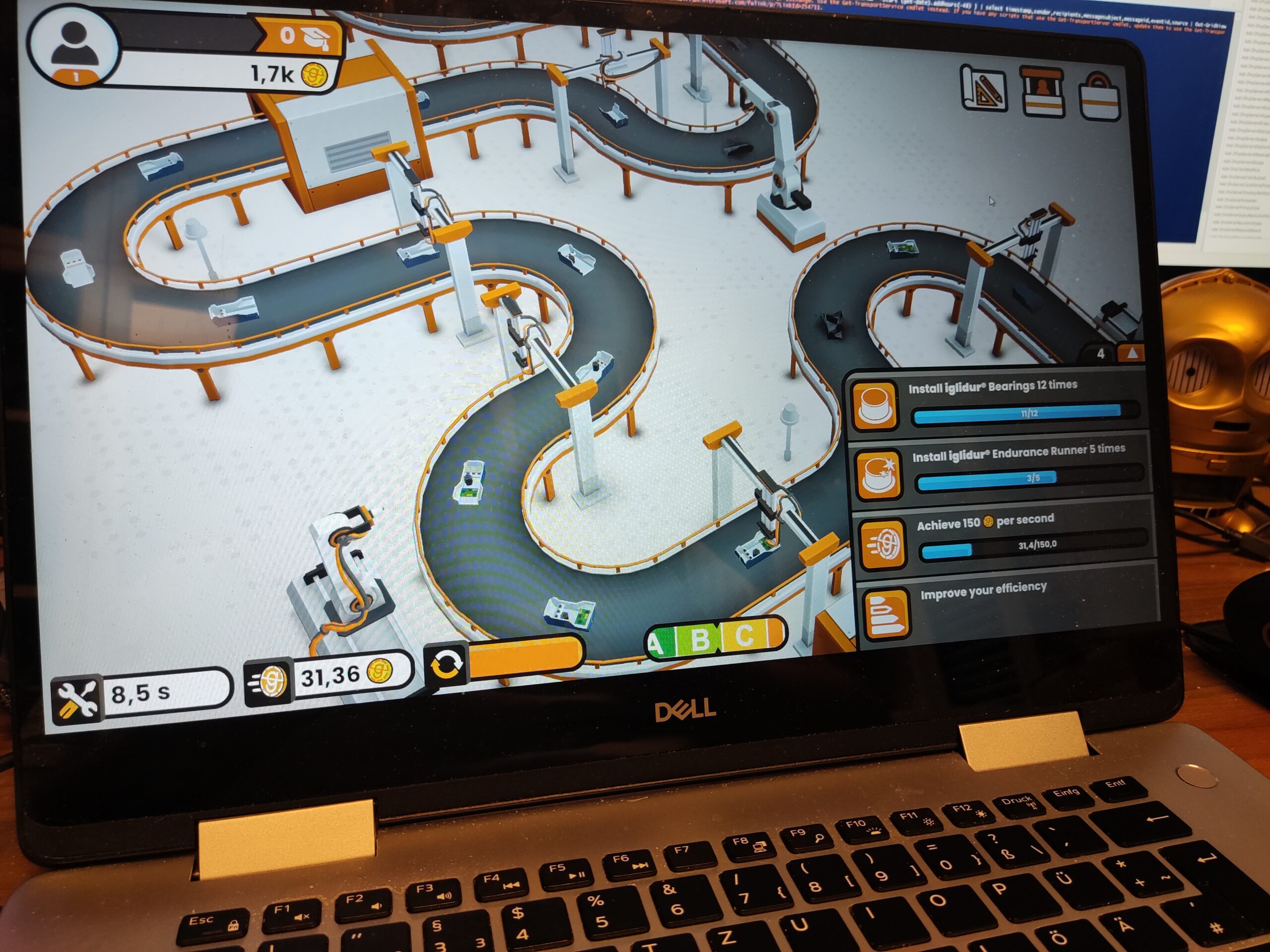
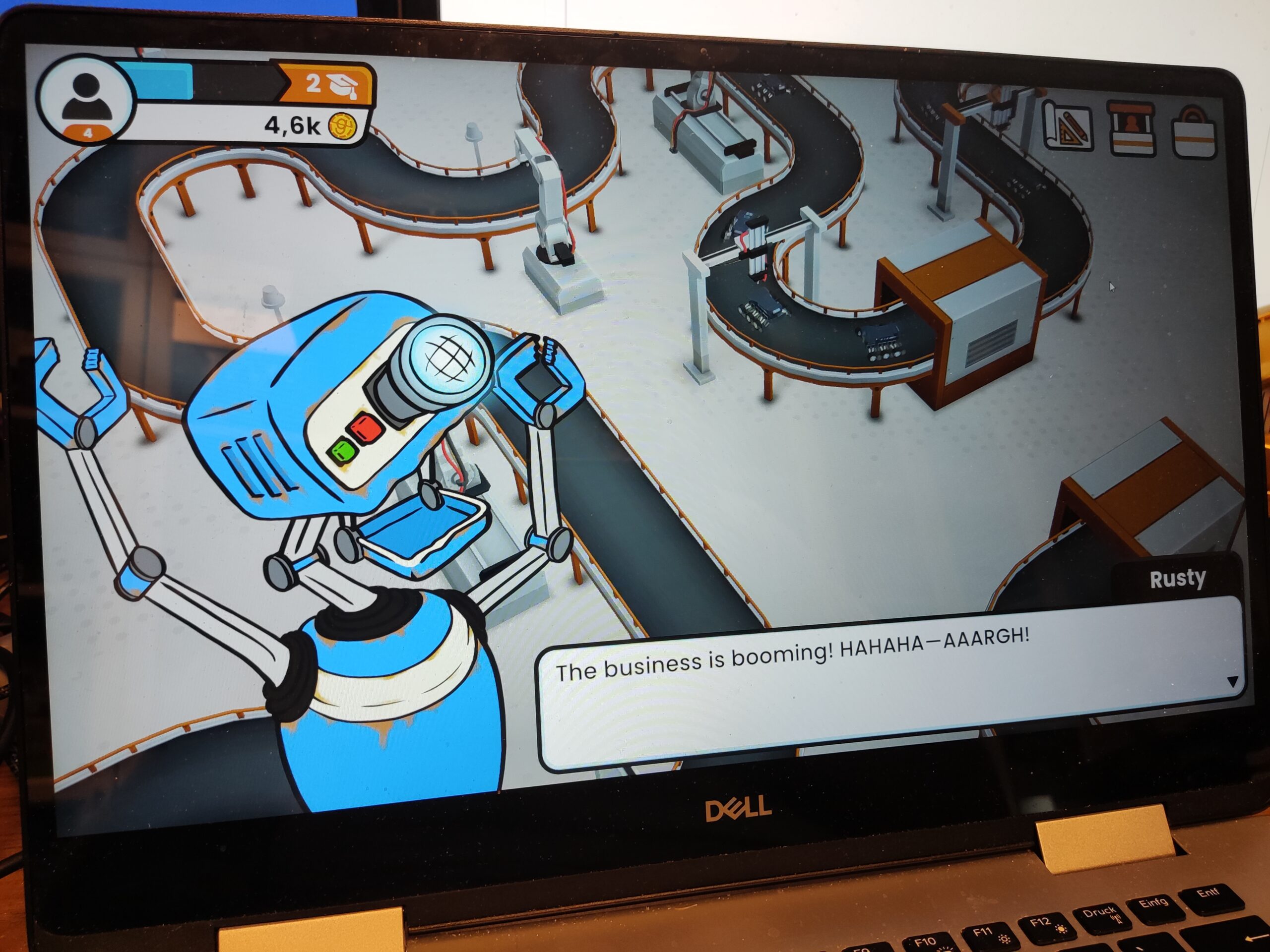
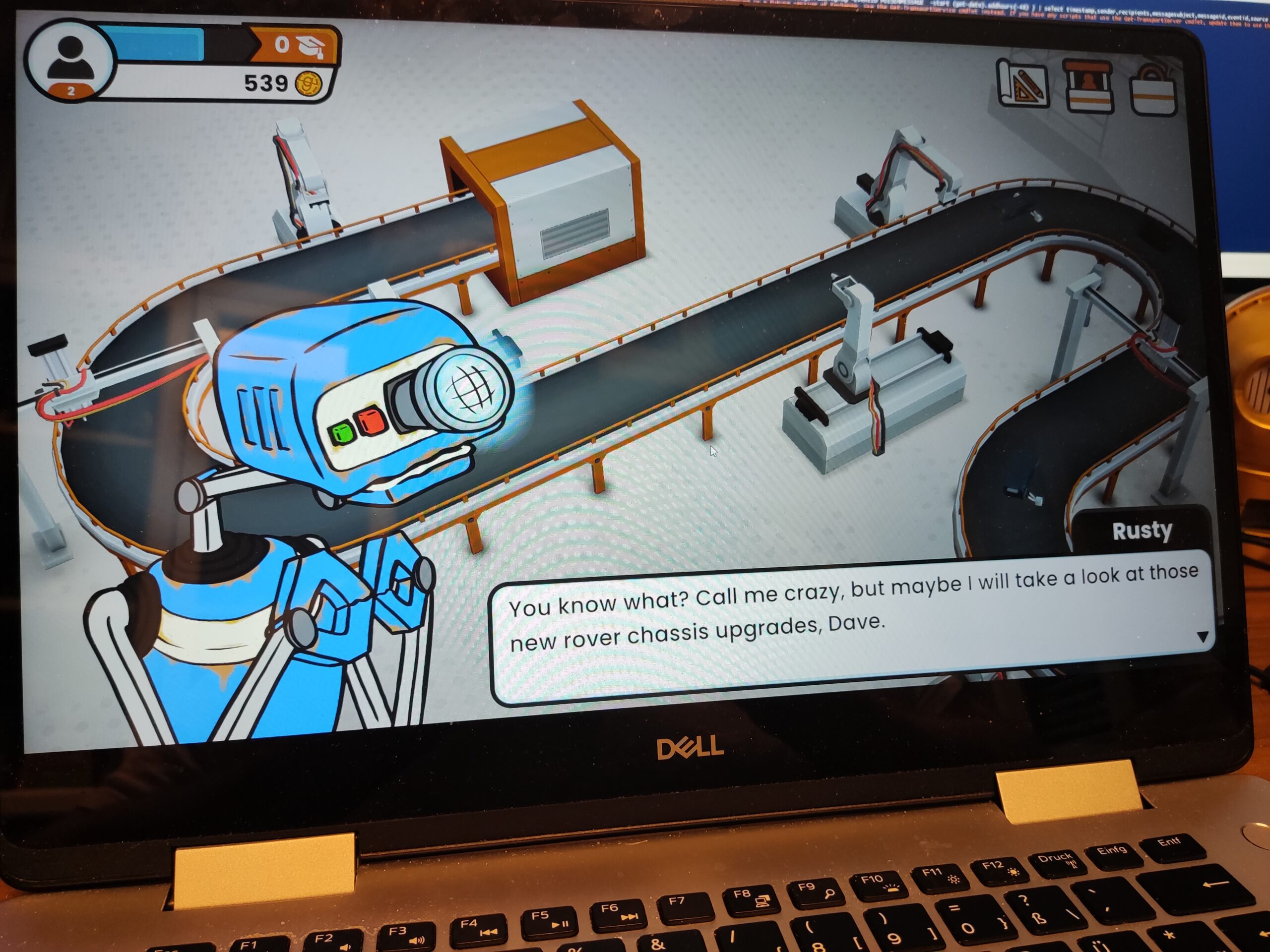
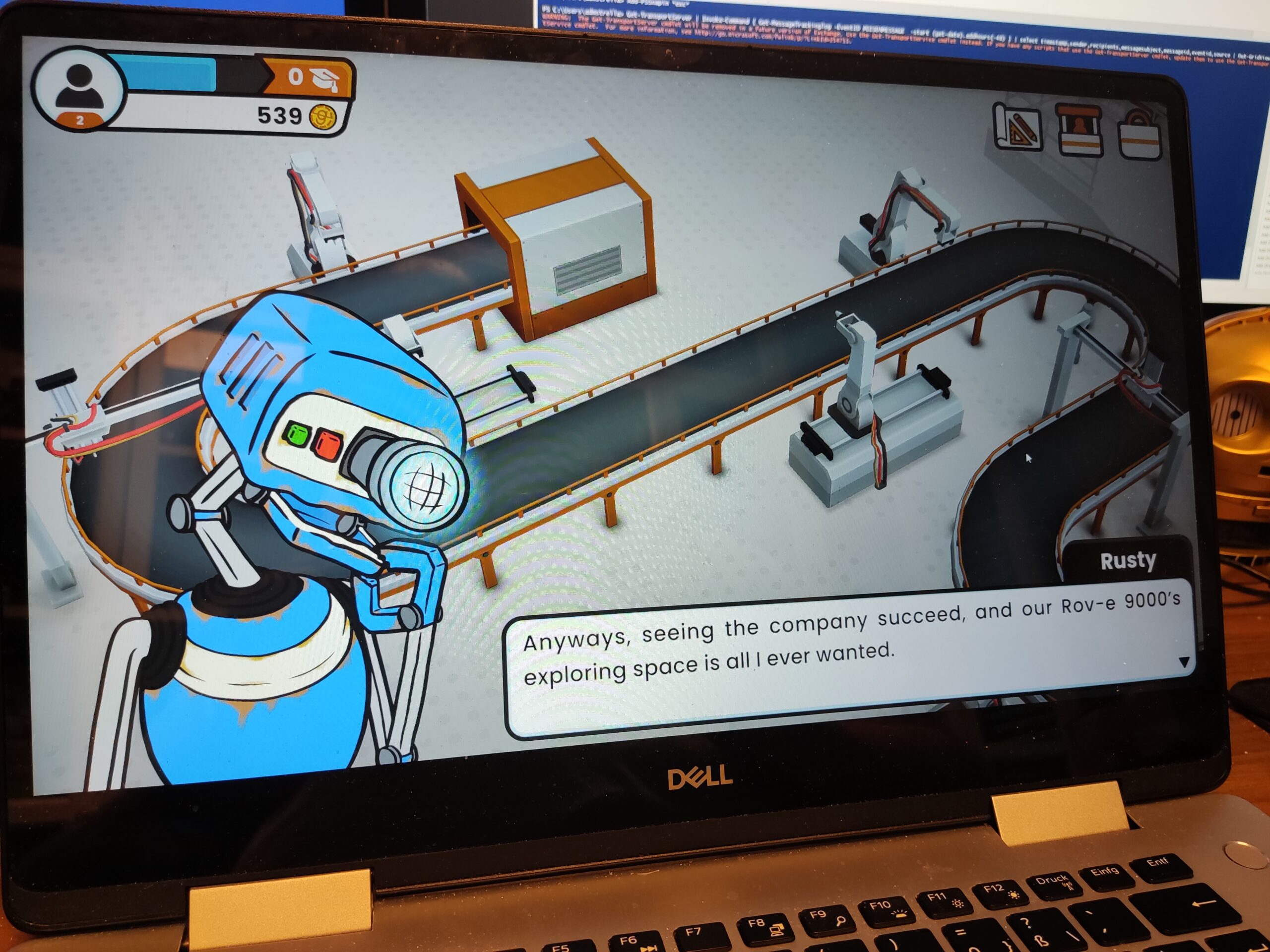
Igus igumania game. Build your own Mars Rover assembling automation factory and improve it with @igusgmbh products. Enjoy this new game soon in your Webbrowser and on other plattforms. Get to know Rusty the robot and Dave the igus employee while learning about igus smart plastics products and low cost Automation. I really enjoyed playing this game, mainly for one reason: robots 😉



Veo Robotics’ 2022 Manufacturing Automation Outlook finds that human-robot collaboration has risen for 6 out of 10 manufacturers in the last year, as facilities turn to automation to supplement workers
WALTHAM, MASS. (PRWEB) JULY 12, 2022
57% of global manufacturers believe that robots are not replacing human workers in their facilities, but rather working alongside humans to supplement their work. This is one of the significant findings from Veo Robotics’ 2022 Manufacturing Automation Outlook, released today by the industrial automation company that created FreeMove®, a comprehensive 3D safeguarding system for industrial robots that powers dynamic human-robot collaboration.
The Outlook also found that 61% of manufacturers say that human-robot interaction within their facilities has increased over the last year. The data point highlights how humans increasingly work alongside robot co-workers post-pandemic as manufacturers grapple with inflation, ongoing supply chain issues, and unprecedented labor shortages. Nearly all manufacturers are looking to automate more operations, including turning to robots to handle mundane, repetitive, or overly risky tasks.
With North American robot purchases reaching a record high in 2021, and global sales expected to increase to $31B by 2028, Veo Robotics surveyed more than 500 manufacturers across the US, UK, and Japan to inform the Outlook and explore how these organizations are integrating robots into their workforce, as well as the resulting impacts on facilities and their human workers. As speculation about the effect of robots on local jobs markets continues to contribute to mixed public opinion, Veo Robotics’ data suggests most manufacturing professionals do not believe that their jobs are at risk due to the increased adoption of robots.
“Our findings highlight that the majority of manufacturers are increasing automation with the goal of robots working alongside human co-workers rather than directly replacing them,” said Patrick Sobalvarro, CEO and co-founder of Veo Robotics. “We find that using robots increases the productivity and the value of human workers, freeing them to use their intelligence, judgment, and dexterity in their work.”
The rise in interactions between human and machine co-workers also necessitates new safeguarding methods that don’t hinder productivity. Although 63% of manufacturers told Veo Robotics that they were at least “moderately satisfied” with their safety when interacting with robots, most (41%) say they keep their robots in fully-fenced, caged environments to prevent injury or harm to human workers. This reliance on fully caged robots often hinders modern manufacturing facilities‘ speed, efficiency, and flexibility.
In fact, 44% of manufacturers note that their workers need to enter workcells at least every 1-2 hours, making it unsurprising that 63% also report that their current workcell safeguarding solutions pose challenges in the form of limiting flexibility, increasing human workloads, constraining space, and slowing down production time.
Additional highlights from Veo Robotics’ 2022 Manufacturing Automation Outlook include:
“Innovation being embraced within industrial processes is a great sign. But as the machine workforce evolves, so must the work environment,“ added Sobalvarro. “Modern manufacturing facilities and warehouses do not have the time to halt production in every situation where a human worker needs to enter a cage. A much more efficient and flexible safeguarding method is Speed & Separation Monitoring (SSM), which enables workers to interact safely with robots without entering the caged work environment. With SSM, manufacturers can prioritize safety and productivity without sacrificing one for the other.”
Read the full Veo Robotics 2022 Manufacturing Automation Outlook here.
About Veo Robotics
Veo Robotics is an industrial automation company building comprehensive sensing and intelligence for robots to collaborate with humans safely. It is the creator of FreeMove®, a comprehensive 3D safeguarding system for industrial robots that powers dynamic human-robot interactions. FreeMove enables fluid, efficient, and flexible production lines. Veo currently partners with the world’s four major robot manufacturers FANUC, Yaskawa, ABB, and Kuka. To learn more, please visit http://www.veobot.com.
Künstliche Intelligenz (KI) gilt als Schlüsseltechnologie und birgt enormes wirtschaftliches Potenzial. Doch ein Blick in deutsche Produktionshallen zeigt noch ein anderes Bild: Lediglich 6,8 Prozent der Unternehmen aus den Bereichen Maschinenbau und Elektrotechnik setzen KI-Technologien ein (Stand 2019). Dabei birgt KI gerade für das produzierende Gewerbe zahlreiche Potenziale.
Künstliche Intelligenz ist ein Überbegriff, der den Ansatz beschreibt, mit Maschinen Probleme zu lösen und menschliche Intelligenz zu imitieren. Dabei spielt insbesondere ein Teilbereich, das Machine Learning (Maschinelles Lernen), in Unternehmen und Produktionen eine entscheidende Rolle. Machine Learning bedeutet, dass ein System aus Beispielen lernt und diese nach der Lernphase verallgemeinern kann.
In der Produktion kommt Machine Learning beispielsweise im Bereich Predictive Analytics zum Einsatz. Dort wird KI als Teil von Vorhersagemodellen zur Überwachung und Wartung von Produktionsanlagen eingesetzt, um frühzeitig auf kritische Zustände reagieren zu können.
Auch das Wissensmanagement greift für die Auswertung von internen Informationen und Daten auf Machine Learning zurück. Daten von Fertigungslinien, Lieferketten, aber auch von einzelnen Produkten werden für Unternehmensprozesse, die Produktentwicklung und neue Geschäftsmodelle ausgewertet. Ohne den Einsatz von KI wäre eine Analyse aufgrund der schieren Datenmenge nicht möglich.

Mit KI und Robotik Handarbeitsplätze automatisieren
Machine Learning, häufig in Kombination mit Machine Vision, kommt auch in den Bereichen Robotik und Automatisierung, Sensorik und bei fahrerlosen Transportsystemen zum Einsatz. Für die Fertigung ist dabei das Zusammenspiel von KI und Robotik ein wichtiger Schlüssel für die Zukunft.
KI-Produkte, wie beispielsweise Robotersteuerungen, ermöglichen es unter anderem, Handarbeitsplätze zu automatisieren. Ein nicht zu vernachlässigender Vorteil, denn Arbeitskräfte sind rar und der Mangel verschärft sich in den Jahren weiter, wie der Deutsche Industrie- und Handelskammertag (DIHK) prognostiziert. Übernehmen Roboter auch Aufgaben, für die es bisher die Flexibilität eines Menschen brauchte, sorgt das für die Entlastung der Stammbelegschaft, eine Auslastung der Maschinen und sichert auf lange Sicht die Wettbewerbsfähigkeit.
Robuster Umgang mit Varianzen
KI-Steuerungen wie MIRAI von Micropsi Industries ergänzen die native Steuerung eines Roboters. Der Roboter erhält dank einer Kamera und einem neuronalen Netzwerk die Auge-Hand-Koordination und eine vergleichbare Flexibilität wie ein Mensch. Ein solches intelligentes Robotersystem lernt bei neuen Aufgaben, bei anders geformten oder positionierten Werkteilen oder bei vergleichbaren Varianzen schnell, was es zu tun hat und passt bei Bedarf seine Bewegungen in Echtzeit eigenständig an. Ob es sich um das Picken einzelner Teile, Zustellbewegungen oder Fügen und Verfolgen handelt: Zahlreiche Tätigkeiten sind mit einer einzigen kleinen Kamera am Roboter-Handgelenk umsetzbar.
Diese Fähigkeiten lassen sich mit MIRAI durch menschliche Demonstration trainieren. Weder KI- noch Programmierkenntnisse sind erforderlich. Das Know-how bleibt selbst ohne KI-Fachkräfte im Unternehmen. Dem Roboter muss dafür das Ziel einige Male in typisch vorkommenden Varianzen mit der Kamera gezeigt werden. Die KI verallgemeinert im Anschluss die gezeigten Daten. Ein solches System kann in wenigen Stunden trainiert und sogar neu trainiert werden. Selbst eine Fertigung im High Mix-/Low-Volume lässt sich so rentabel automatisieren. Was intelligente Robotiklösungen bereits in der Praxis leisten, zeigen die folgenden Beispiele.
Intelligentes Handling-System bei ZF
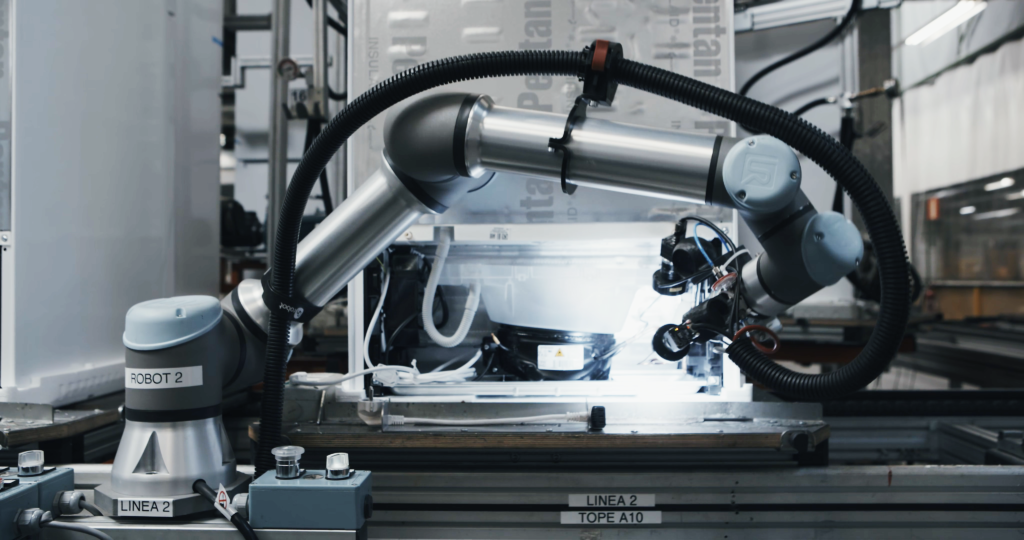
Der Technologiekonzern ZF stand vor der Herausforderung, die Werkstückzufuhr einer großvolumigen Frässtation, in der Zahnräder produziert werden, zu automatisieren. Im Werkprozess werden Metallringe aus einer Kiste entnommen und auf ein Förderband gelegt, um später in die Produktion der Zahnräder einzufließen. Die Schwierigkeit: Der Produktionsschritt ist sehr variantenreich, da sich die Ringe in der angelieferten Gitterbox verschieben und dadurch zufällig angeordnet sind. Auch Platzierung und Form der Box variieren. Wechselnde Lichtverhältnisse stellen eine zusätzliche Herausforderung dar. Außerdem ist die Oberfläche der Ringe metallisch glänzend, teilweise ölverschmiert oder korrodiert, was eine klassische Automatisierung unmöglich machte.
Heute ist die KI-Steuerung MIRAI und ein Cobot vom Modell UR10e bei ZF in einer automatisierten Werkstückaufnahme im Einsatz. Mit seiner eigenen Steuerung bringt der Cobot sich über den Ringen in der Kiste in Position. Nun übernimmt das MIRAI-System die Kontrolle: Es bewegt den Roboter selbstständig zum nächsten Ring und bringt den Greifer in die korrekte dreidimensionale Greifposition. Danach übernimmt der UR10e wieder, nimmt den Ring auf und bewegt ihn zum Ablegen auf das Förderband. Das komplette Einrichten des Roboters dauerte lediglich wenige Tage – MIRAI löste in kürzester Zeit ein lang bestehendes Problem.
BSH sucht mit KI nach Kältemittellecks
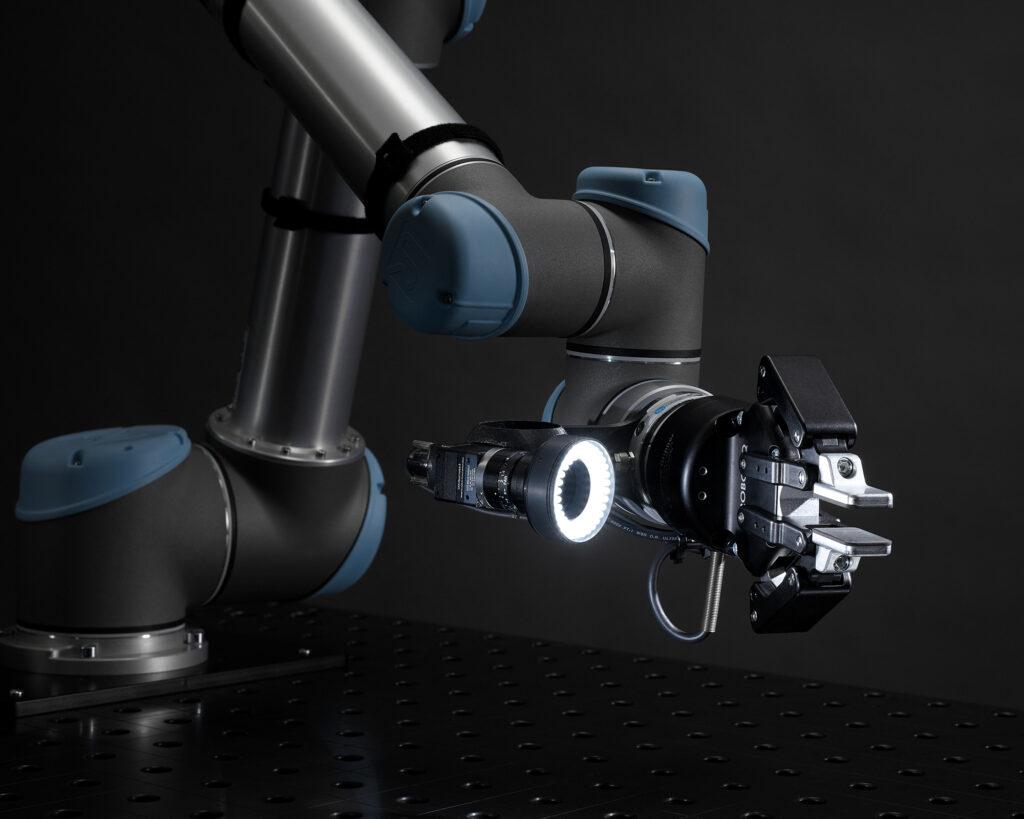
An ihrem spanischen Standort stellt die BSH Hausgeräte GmbH Kühl- und Gefrierschränke her. Im Herstellungsprozess muss das Unternehmen die Kupferrohrleitungen der Kühlschränke auf Leckagen testen. Für die sogenannte Dichtheitsprüfung wird eine Schnüffelsonde entlang der Kupferrohrleitungen und Kompressoren geführt, um Lötstellen auf austretendes Gas und Kältemittel zu prüfen. Das Besondere: Jede Rückseite der hergestellten Kühlschränke ist einzigartig, was Position, Farbe und Form der Lötpunkte angeht. Für einen herkömmlichen Roboter sind solche Varianzen ein unüberwindbares Hindernis. Der monotone Prüfprozess blieb dem Menschen vorbehalten – bis jetzt.
Den Prüfprozess übernimmt bei BSH nun eine Robotik-Komplettlösung den Prüfprozess. Dank der integrierten Robotersteuerung MIRAI ist es dem Roboter möglich, alle zu prüfenden Lötstellen verlässlich zu identifizieren und die Schnüffelsonde millimetergenau heranzuführen – unabhängig von Position, Form oder Farbe. Das System reagiert in Echtzeit auf seine Umwelt und handhabt selbst unvorhergesehene Abweichungen präzise. Die Roboterfähigkeiten wurden von Mitarbeitenden bei BSH durch menschliche Demonstration in nur wenigen Stunden trainiert. Weder Programmier- noch KI-Kenntnisse waren erforderlich. BSH konnte mit der Automatisierungslösung die laufenden Betriebskosten senken und Wartungen und Fehlerbehebungen reduzieren.

Neue Technologien als Wettbewerbsvorteil
Die Beispiele zeigen, dass Unternehmen mit KI sehr viel bewirken können: KI ermöglicht mehr Flexibilität, Unabhängigkeit, Effizienz und nicht zuletzt Resilienz. Nicht unwichtig in Zeiten wie diesen. Neue Technologien sollte dabei als Türöffner zu mehr Automatisierung verstanden werden. Leistungen, die bislang von Menschen oder Maschinen erbracht wurden, können nun von einer Software geliefert werden. Das ist nicht nur vorteilhaft beim drastisch zunehmenden Arbeitskräftemangel. Es erhöht auch die Flexibilität, Nachvollziehbarkeit und Zuverlässigkeit von Produktionsprozessen und verschafft einen dauerhaften Wettbewerbsvorsprung.
Weitere Informationen unter: https://bit.ly/MicropsiIndustries