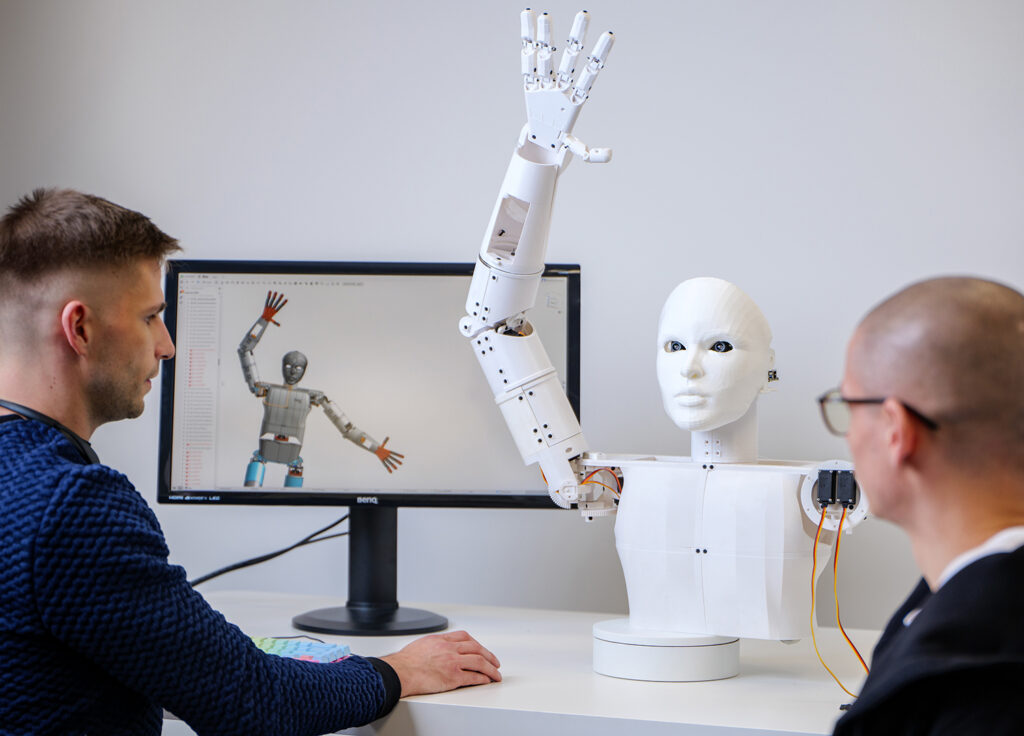
Auf der Hannover Messe 2022 stellt igus den ersten Prototypen eines humanoiden Low Cost Roboters vor
Köln, 27. Mai 2022 – Mensch, Maschine – oder beides? Humanoide Roboter sind längst nicht mehr nur Science-Fiction, sondern Realität. Auch igus forscht bereits seit einiger Zeit an humanoider Robotik und stellt nun auf der Hannover Messe einen Prototypen des motion plastics bot vor: ein humanoider Roboter, der die Vorteile von Hochleistungskunststoffen und Low Cost Automation vereint.
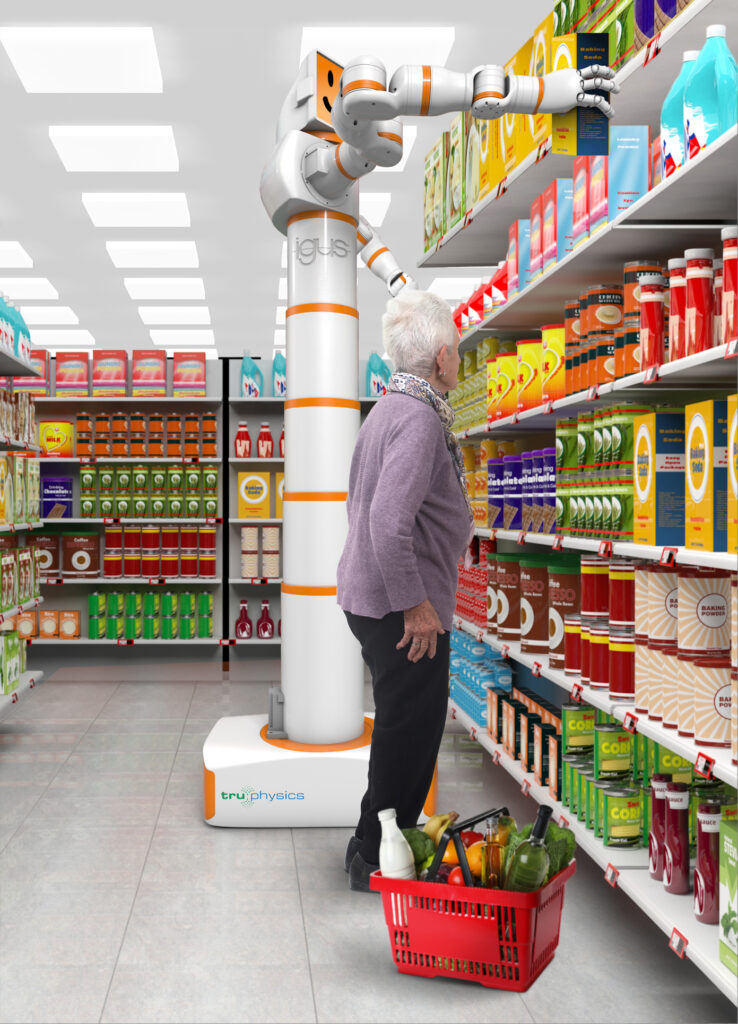

Roboter sind aus unserem Alltag nicht mehr wegzudenken. Spätestens seit dem Wandel zur Industrie 4.0 werden immer mehr Aufgaben automatisiert – und davon profitieren auch neue Formen der Robotik. Doch Roboter können nicht nur in der Industrie, sondern auch im Alltag für Erleichterung sorgen. Ein Humanoid, der nicht nur funktionell, sondern auch freundlich ist und menschliche Züge trägt, kann den Menschen nicht als Maschine, sondern als Partner begleiten. In der Forschung und Entwicklung von humanoider Robotik gibt es stetig Fortschritte. Zum Beispiel bei einem Forschungsteam der TU Chemnitz, das eine E-Skin entwickelt – eine berührungsempfindliche elektronische Haut, die humanoide Roboter noch menschenähnlicher machen könnte. Immer getrieben von der Frage, in welche Richtung sich die Robotik weiterentwickeln kann, arbeitet auch igus seit einiger Zeit an der eigenen Vision eines humanoiden Roboters – dem motion plastics bot. „Mit dem igus ReBeL und unserem drytech Angebot waren bereits passende Komponenten vorhanden, um Bewegung in einen Roboter zu bringen. Der humanoide Roboter ist ein gemeinsames Projekt mit den Robotik-Experten des Stuttgarter Start-ups TruPhysics, das den intelligenten Humanoiden aus unseren motion plastics sowie weiteren Komponenten zusammengebaut hat. Dort ist er unter dem Namen Robert M3 erhältlich”, erklärt Alexander Mühlens, Leiter Geschäftsbereich Automatisierungstechnik und Robotik bei igus. „Mit dem Bot wollen wir das Zusammenspiel von unseren Produkten aus Hochleistungskunststoffen und integrierter Intelligenz aufzeigen – und das zu einem erschwinglichen Preis.“
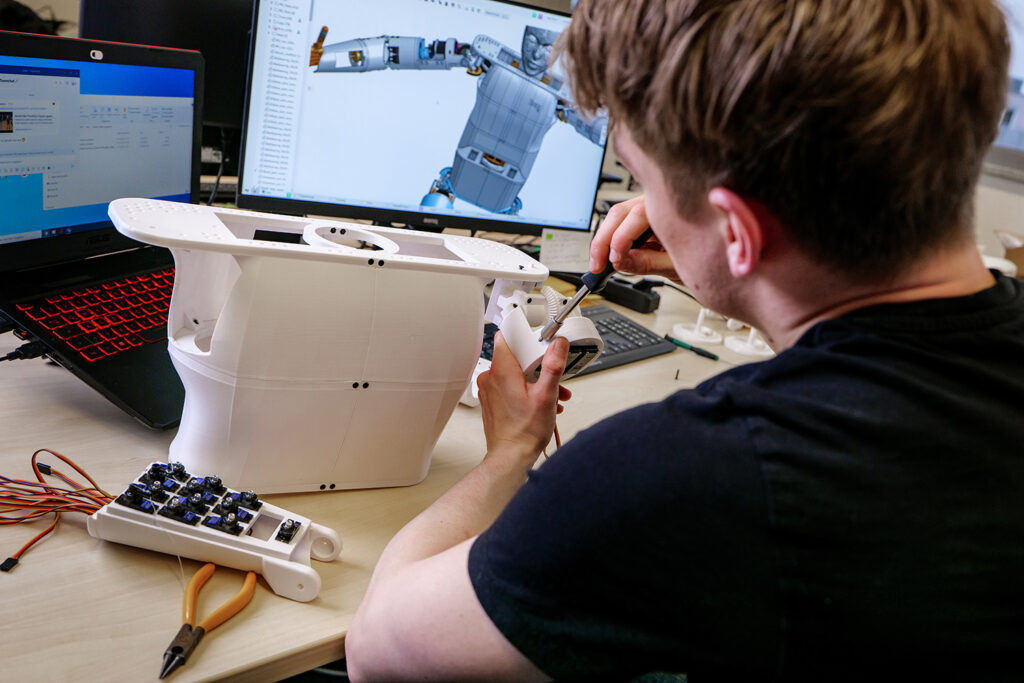
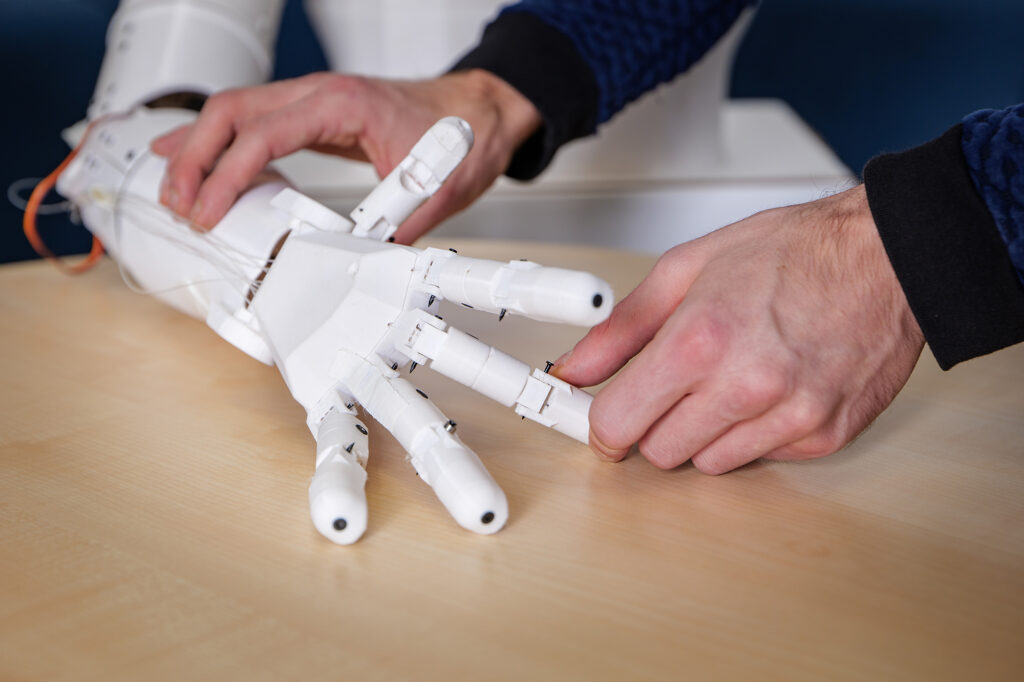
Leichter und wartungsfreier Low Cost Humanoid
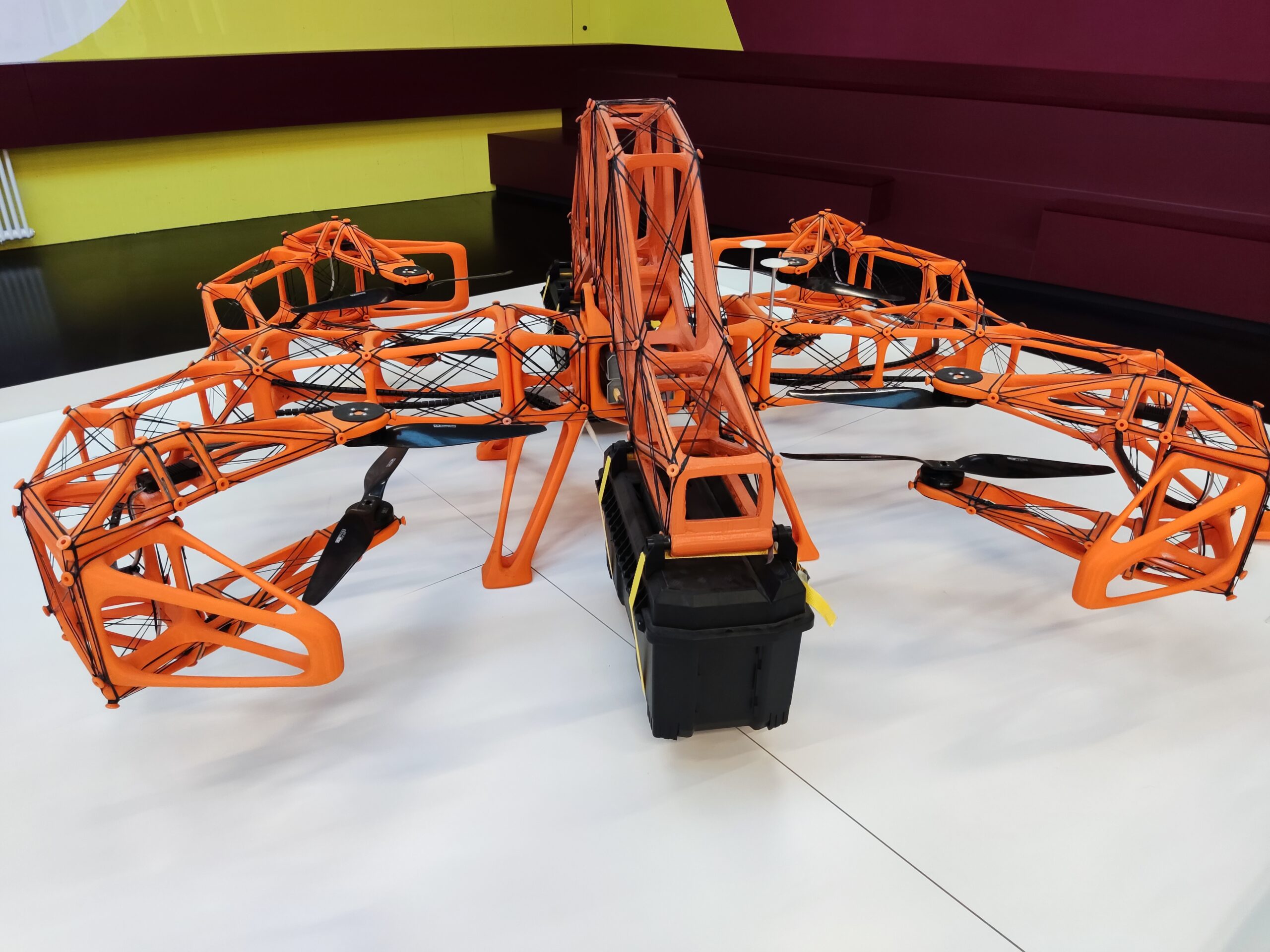
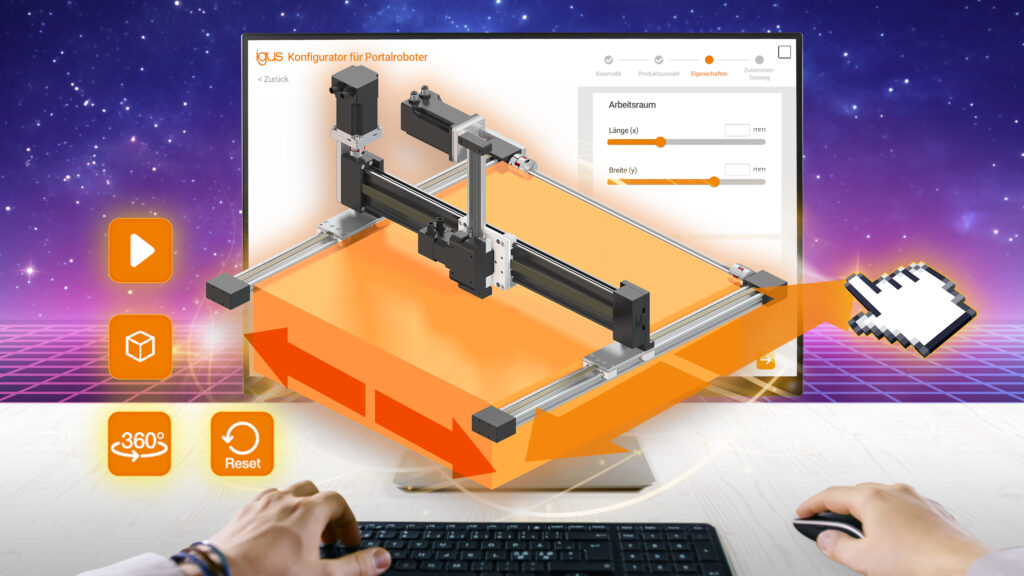
Für eine lange und störungsfreie Laufzeit ohne Wartung bieten die Tribo-Polymere von igus im motion plastics bot einen klaren Vorteil: Schmiermittelfreiheit. Gleichzeitig ermöglichen die Hochleistungskunststoffe eine leichte Bauweise. Durch ihren Einsatz bringt der motion plastics bot bei einer Höhe von bis zu 2,70 Meter lediglich 78 Kilogramm auf die Waage. Seine Spannweite beträgt 1,50 Meter. Der motion plastics bot verfügt über ein selbstfahrendes AGV (Automated Guided Vehicle), einen teleskopierbaren Körper sowie einen Kopf mit integriertem Bildschirm und Avatar für eine interaktive Kommunikation. Zentraler Bestandteil ist auch der igus ReBeL, ein Serviceroboter mit Cobot-Fähigkeiten, der als Arme des Bots zum Einsatz kommt. Das Herzstück des ReBeLs sind die vollintegrierten Tribo-Wellgetriebe aus Kunststoff mit Motor, Absolutwert-Encoder, Kraftregelung und Controller. Der motion plastics bot bewegt sich in Schrittgeschwindigkeit und verfügt über eine Traglast von 2 Kilogramm pro Arm. Angesteuert wird er als Open Source-Lösung über das Robot Operating System (ROS). Denn das gesamte Low Cost Automation-Angebot von igus lässt sich in ROS abbilden. Mit der Studie zum motion plastics bot vereint igus die Vorteile seiner Hochleistungskunststoffe für die Bewegung und sein Know-how im Bereich Low Cost Automation, um die Entwicklung der nächsten Robotergeneration weiter voranzutreiben.
Lebenslanger Begleiter statt nur Maschine
„Wir sehen viel Potenzial im Einsatz von humanoiden Robotern. Doch unsere Welt ist von Menschen für Menschen gebaut. Statt nur einzelne Automatisierungsteile zu nutzen, ist es daher sinnvoll an Humanoiden und Androiden zu forschen. Die Frage ist, wann ist der Markt soweit?“, macht Alexander Mühlens deutlich. Menschenähnliche Roboter können sowohl gefährliche als auch einfache und monotone Aufgaben übernehmen.Im beruflichen Umfeld können Arbeiten erledigt werden, die über ein bloßes Pick & Place, wie es Roboterarme verrichten, hinausgehen. Im Haushaltsbereich kann ein Bot mehrere Roboter ersetzen: Er könnte selbstständig staubsaugen, Rasen mähen, Einkäufe erledigen, kochen, Wäsche waschen und darüber hinaus alle möglichen Aufgaben erledigen – selbst die Pflege von kranken Menschen. Somit wäre er nicht nur eine Maschine, sondern ein Begleiter, der für eine Menschenleben lange Erleichterung sorgen könnte. „Der Einsatz eines solchen Roboters ist bisher noch mit hohen Kosten verbunden, berücksichtigt man jedoch die mögliche Lebensdauer, würde sich der Einsatz längerfristig amortisieren”, sagt Mühlens. „Unser Ziel ist es, mit motion plastics Komponenten kostengünstige und einfache Lösungen für humanoide Robotik aufzuzeigen.”