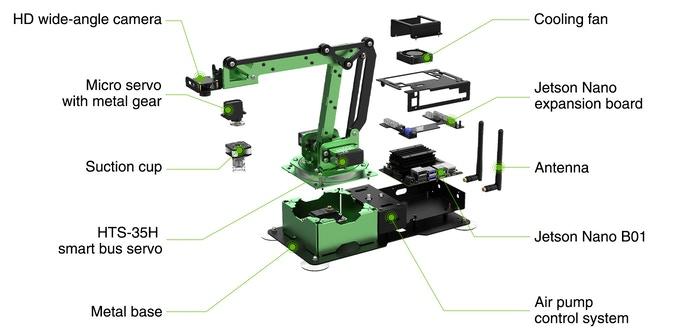
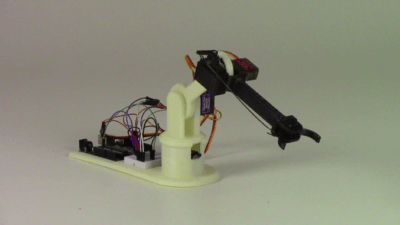
I just received this information from the blinkgogo team:
“Wireless program Arduino & Fun Robotic Learning Platform. Designed for STEM education, Open Source! APP controlled, based on Arduino, supports Scratch. Let kids Play and Learn! ”
Blinkgogo is a open source fun STEM robotic learning platform based on Arduino. Blinkgogo supports wireless Bluetooth upload, APP controlled, Scratch.
This robot kit has everything you need to get started. You can demonstrate many standard robot functions right out of the box. It’s simple, easy to use and fun.
With Blinkgogo, you can build many standard robots for example Line Following robot, Light Seeking robot, Edge Detection robot, APP control robot.
It comes with 3D printed shell and compatible with LEGO blocks.
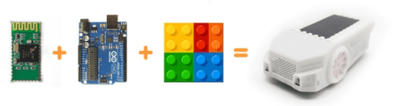
Blinkgogo also comes with a hardware expansion board for those who really want to go wild when it comes to trying new things and developing new robotics systems.
Blinkgogo comes with three step-by-step tutorials to help you learn programming.
- Binkgogo play right out of the box Tutorial: Blinkgogo works right out of the box. You can demonstrate many standard robot functions. You can drive it by controlling it with your phone through it’s Bluetooth capability. Or have it follow a black line.
- Blinkgogo for Beginners Tutorial:Blinkgogo comes with a number of step-by-step tutorials. It is easy to program with the scratch graphical programming language. For the more extreme programmers it also works with C++. And the Arduino IDE programming environment
- Blinkgogo for Advanced Users Tutorial:Blinkgogo offers a lot for advanced users. Blinkgogo comes with a hardware expansion prototyping plate where you can mount servos and many other sensors.

It’s perfect for STEM education:
In the home
Perhaps your home has many toys already. However we believe to prepare for the future children need toys that are made to be modified and programmed. Children need to learn not just to be consumers but to actively participate in the building and modifying of things around them.
In school
Everybody knows that STEM education is important however most robotics platforms do not come with enough easy to use tutorials out of the box to be used by most non-engineers and still have enough flexibility to be still useful to those who excel in programming.
Why we made this kit?
Ever since I was a child I have always wanted to learn how to make electronics. Now that I am an electrical engineer my dreams are now a reality. However in the past when friends and asked if they could do electronics, my only answer was you need to go to school to be an electrical engineer.
Luckily time to change. Thanks to Arduino and other open-source platforms it’s not only possible for my friends to start their own hobby electronics products I can now start teaching my two children Harry and Tina. I have selfishly developed Blinkgogo specifically to teach my children electronics. But due to enthusiasm from my neighbors I have developed Blinkgogo into a product to share with the world. I hope you have as much fun with Blinkgogo as I did developing it and share it with my children.
We are on kickstarter now!
We are now crowdfunding on kickstarter now. We got over 60% funds within 24 hours. Please support us and let more kids can enjoy this all-in-one robotic learning platform!
Website: www.blinkgogo.com
Video: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCgj2axca16VY3bHaIBzzzuQ
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/blinkgogorobot/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/BlinkgogoRobot
Google+: https://plus.google.com/u/0/111819239969740793655
Kickstarter link: https://www.kickstarter.com/projects/makerstudio/blinkgogo-wireless-arduino-and-fun-robotics-learni?ref=4a4oio