Künstliche Intelligenz (KI) gilt als Schlüsseltechnologie und birgt enormes wirtschaftliches Potenzial. Doch ein Blick in deutsche Produktionshallen zeigt noch ein anderes Bild: Lediglich 6,8 Prozent der Unternehmen aus den Bereichen Maschinenbau und Elektrotechnik setzen KI-Technologien ein (Stand 2019). Dabei birgt KI gerade für das produzierende Gewerbe zahlreiche Potenziale.
Künstliche Intelligenz ist ein Überbegriff, der den Ansatz beschreibt, mit Maschinen Probleme zu lösen und menschliche Intelligenz zu imitieren. Dabei spielt insbesondere ein Teilbereich, das Machine Learning (Maschinelles Lernen), in Unternehmen und Produktionen eine entscheidende Rolle. Machine Learning bedeutet, dass ein System aus Beispielen lernt und diese nach der Lernphase verallgemeinern kann.
In der Produktion kommt Machine Learning beispielsweise im Bereich Predictive Analytics zum Einsatz. Dort wird KI als Teil von Vorhersagemodellen zur Überwachung und Wartung von Produktionsanlagen eingesetzt, um frühzeitig auf kritische Zustände reagieren zu können.
Auch das Wissensmanagement greift für die Auswertung von internen Informationen und Daten auf Machine Learning zurück. Daten von Fertigungslinien, Lieferketten, aber auch von einzelnen Produkten werden für Unternehmensprozesse, die Produktentwicklung und neue Geschäftsmodelle ausgewertet. Ohne den Einsatz von KI wäre eine Analyse aufgrund der schieren Datenmenge nicht möglich.

Mit KI und Robotik Handarbeitsplätze automatisieren
Machine Learning, häufig in Kombination mit Machine Vision, kommt auch in den Bereichen Robotik und Automatisierung, Sensorik und bei fahrerlosen Transportsystemen zum Einsatz. Für die Fertigung ist dabei das Zusammenspiel von KI und Robotik ein wichtiger Schlüssel für die Zukunft.
KI-Produkte, wie beispielsweise Robotersteuerungen, ermöglichen es unter anderem, Handarbeitsplätze zu automatisieren. Ein nicht zu vernachlässigender Vorteil, denn Arbeitskräfte sind rar und der Mangel verschärft sich in den Jahren weiter, wie der Deutsche Industrie- und Handelskammertag (DIHK) prognostiziert. Übernehmen Roboter auch Aufgaben, für die es bisher die Flexibilität eines Menschen brauchte, sorgt das für die Entlastung der Stammbelegschaft, eine Auslastung der Maschinen und sichert auf lange Sicht die Wettbewerbsfähigkeit.
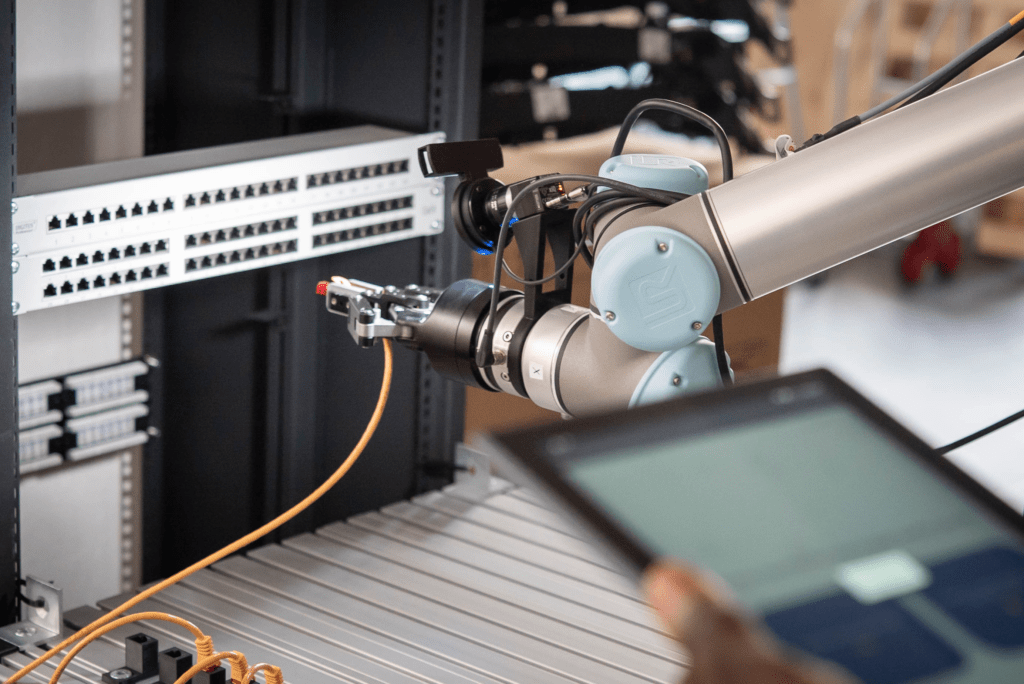
Robuster Umgang mit Varianzen
KI-Steuerungen wie MIRAI von Micropsi Industries ergänzen die native Steuerung eines Roboters. Der Roboter erhält dank einer Kamera und einem neuronalen Netzwerk die Auge-Hand-Koordination und eine vergleichbare Flexibilität wie ein Mensch. Ein solches intelligentes Robotersystem lernt bei neuen Aufgaben, bei anders geformten oder positionierten Werkteilen oder bei vergleichbaren Varianzen schnell, was es zu tun hat und passt bei Bedarf seine Bewegungen in Echtzeit eigenständig an. Ob es sich um das Picken einzelner Teile, Zustellbewegungen oder Fügen und Verfolgen handelt: Zahlreiche Tätigkeiten sind mit einer einzigen kleinen Kamera am Roboter-Handgelenk umsetzbar.
Diese Fähigkeiten lassen sich mit MIRAI durch menschliche Demonstration trainieren. Weder KI- noch Programmierkenntnisse sind erforderlich. Das Know-how bleibt selbst ohne KI-Fachkräfte im Unternehmen. Dem Roboter muss dafür das Ziel einige Male in typisch vorkommenden Varianzen mit der Kamera gezeigt werden. Die KI verallgemeinert im Anschluss die gezeigten Daten. Ein solches System kann in wenigen Stunden trainiert und sogar neu trainiert werden. Selbst eine Fertigung im High Mix-/Low-Volume lässt sich so rentabel automatisieren. Was intelligente Robotiklösungen bereits in der Praxis leisten, zeigen die folgenden Beispiele.
Intelligentes Handling-System bei ZF
Der Technologiekonzern ZF stand vor der Herausforderung, die Werkstückzufuhr einer großvolumigen Frässtation, in der Zahnräder produziert werden, zu automatisieren. Im Werkprozess werden Metallringe aus einer Kiste entnommen und auf ein Förderband gelegt, um später in die Produktion der Zahnräder einzufließen. Die Schwierigkeit: Der Produktionsschritt ist sehr variantenreich, da sich die Ringe in der angelieferten Gitterbox verschieben und dadurch zufällig angeordnet sind. Auch Platzierung und Form der Box variieren. Wechselnde Lichtverhältnisse stellen eine zusätzliche Herausforderung dar. Außerdem ist die Oberfläche der Ringe metallisch glänzend, teilweise ölverschmiert oder korrodiert, was eine klassische Automatisierung unmöglich machte.
Heute ist die KI-Steuerung MIRAI und ein Cobot vom Modell UR10e bei ZF in einer automatisierten Werkstückaufnahme im Einsatz. Mit seiner eigenen Steuerung bringt der Cobot sich über den Ringen in der Kiste in Position. Nun übernimmt das MIRAI-System die Kontrolle: Es bewegt den Roboter selbstständig zum nächsten Ring und bringt den Greifer in die korrekte dreidimensionale Greifposition. Danach übernimmt der UR10e wieder, nimmt den Ring auf und bewegt ihn zum Ablegen auf das Förderband. Das komplette Einrichten des Roboters dauerte lediglich wenige Tage – MIRAI löste in kürzester Zeit ein lang bestehendes Problem.
BSH sucht mit KI nach Kältemittellecks
An ihrem spanischen Standort stellt die BSH Hausgeräte GmbH Kühl- und Gefrierschränke her. Im Herstellungsprozess muss das Unternehmen die Kupferrohrleitungen der Kühlschränke auf Leckagen testen. Für die sogenannte Dichtheitsprüfung wird eine Schnüffelsonde entlang der Kupferrohrleitungen und Kompressoren geführt, um Lötstellen auf austretendes Gas und Kältemittel zu prüfen. Das Besondere: Jede Rückseite der hergestellten Kühlschränke ist einzigartig, was Position, Farbe und Form der Lötpunkte angeht. Für einen herkömmlichen Roboter sind solche Varianzen ein unüberwindbares Hindernis. Der monotone Prüfprozess blieb dem Menschen vorbehalten – bis jetzt.
Den Prüfprozess übernimmt bei BSH nun eine Robotik-Komplettlösung den Prüfprozess. Dank der integrierten Robotersteuerung MIRAI ist es dem Roboter möglich, alle zu prüfenden Lötstellen verlässlich zu identifizieren und die Schnüffelsonde millimetergenau heranzuführen – unabhängig von Position, Form oder Farbe. Das System reagiert in Echtzeit auf seine Umwelt und handhabt selbst unvorhergesehene Abweichungen präzise. Die Roboterfähigkeiten wurden von Mitarbeitenden bei BSH durch menschliche Demonstration in nur wenigen Stunden trainiert. Weder Programmier- noch KI-Kenntnisse waren erforderlich. BSH konnte mit der Automatisierungslösung die laufenden Betriebskosten senken und Wartungen und Fehlerbehebungen reduzieren.

Neue Technologien als Wettbewerbsvorteil
Die Beispiele zeigen, dass Unternehmen mit KI sehr viel bewirken können: KI ermöglicht mehr Flexibilität, Unabhängigkeit, Effizienz und nicht zuletzt Resilienz. Nicht unwichtig in Zeiten wie diesen. Neue Technologien sollte dabei als Türöffner zu mehr Automatisierung verstanden werden. Leistungen, die bislang von Menschen oder Maschinen erbracht wurden, können nun von einer Software geliefert werden. Das ist nicht nur vorteilhaft beim drastisch zunehmenden Arbeitskräftemangel. Es erhöht auch die Flexibilität, Nachvollziehbarkeit und Zuverlässigkeit von Produktionsprozessen und verschafft einen dauerhaften Wettbewerbsvorsprung.
Weitere Informationen unter: https://bit.ly/MicropsiIndustries