Communication & Safety Challenges Facing Mobile Robots Manufacturers
Mobile robots are everywhere, from warehouses to hospitals and even on the street. Their popularity is easy to understand; they’re cheaper, safer, easier to find, and more productive than actual workers. They’re easy to scale or combine with other machines. As mobile robots collect a lot of real-time data, companies can use mobile robots to start their IIoT journey.
But to work efficiently, mobile robots need safe and reliable communication. This article outlines the main communication and safety challenges facing mobile robot manufacturers and provides an easy way to overcome these challenges to keep mobile robots moving.

What are Mobile Robots?
Before we begin, let’s define what we mean by mobile robots.
Mobile robots transport materials from one location to another and come in two types, automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and autonomous mobile robots (AMRs). AGVs use guiding infrastructure (wires reflectors, reflectors, or magnetic strips) to follow predetermined routes. If an object blocks an AGV’s path, the AGV stops and waits until the object is removed.
AMRs are more dynamic. They navigate via maps and use data from cameras, built-in sensors, or laser scanners to detect their surroundings and choose the most efficient route. If an object blocks an AMR’s planned route, it selects another route. As AMRs are not reliant on guiding infrastructure, they’re quicker to install and can adapt to logistical changes.
What are the Communication and Safety Challenges Facing Mobile Robot Manufacturers?
1. Establish a Wireless Connection
The first challenge for mobile robot manufacturers is to select the most suitable wireless technology. The usual advice is to establish the requirements, evaluate the standards, and choose the best match. Unfortunately, this isn’t always possible for mobile robot manufacturers as often they don’t know where the machine will be located or the exact details of the target application.
Sometimes a Bluetooth connection will be ideal as it offers a stable non-congested connection, while other applications will require a high-speed, secure cellular connection. What would be useful for mobile robot manufacturers is to have a networking technology that’s easy to change to meet specific requirements.
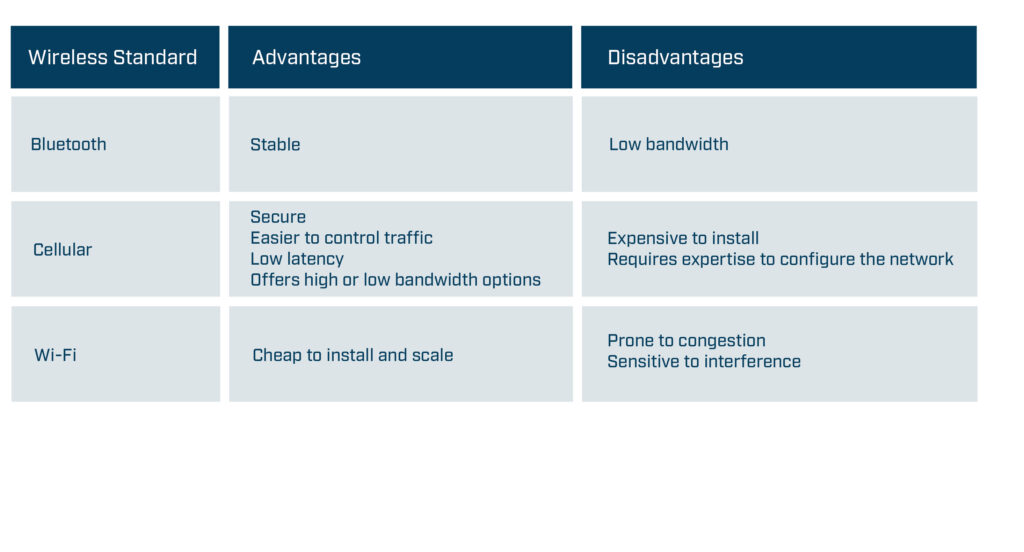
Wireless standard -high-level advantages and disadvantages
The second challenge is to ensure that the installation works as planned. Before installing a wireless solution, complete a predictive site survey based on facility drawings to ensure the mobile robots have sufficient signal coverage throughout the location. The site survey should identify the optimal location for the Access Points, the correct antenna type, the optimal antenna angle, and how to mitigate interference. After the installation, use wireless sniffer tools to check the design and adjust APs or antenna as required.
2. Connecting Mobile Robots to Industrial Networks
Mobile robots need to communicate with controllers at the relevant site even though the mobile robots and controllers are often using different industrial protocols. For example, an AGV might use CANopen while the controller might use PROFINET. Furthermore, mobile robot manufacturers may want to use the same AGV model on a different site where the controller uses another industrial network, such as EtherCAT.
Mobile robot manufacturers also need to ensure that their mobile robots have sufficient capacity to process the required amount of data. The required amount of data will vary depending on the size and type of installation. Large installations may use more data as the routing algorithms need to cover a larger area, more vehicles, and more potential routes. Navigation systems such as vision navigation process images and therefore require more processing power than installations using other navigation systems such as reflectors. As a result, mobile robot manufacturers must solve the following challenges:
- They need a networking technology that supports all major fieldbus and industrial Ethernet networks.
- It needs to be easy to change the networking technology to enable the mobile robot to communicate on the same industrial network as the controller without changing the hardware design.
- They need to ensure that the networking technology has sufficient capacity and functionality to process the required data.
3. Creating a Safe System
Creating a system where mobile robots can safely transport material is a critical but challenging task. Mobile robot manufacturers need to create a system that considers all the diverse types of mobile robots, structures, and people in the environment. They need to ensure that the mobile robots react to outside actions, such as someone opening a safety door or pushing an emergency stop button, and that the networking solution can process different safety protocols and interfaces. They need to consider that AMRs move freely and manage the risk of collisions accordingly. The technology used in sensors is constantly evolving, and mobile robot manufacturers need to follow the developments to ensure their products remain as efficient as possible.
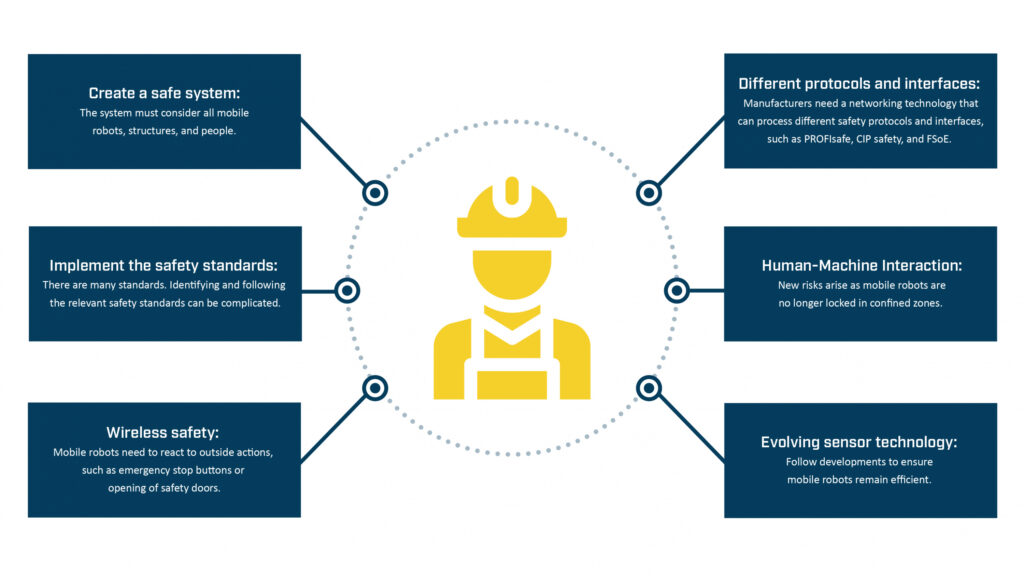
Overview of Safety Challenges for Mobile Robot Manufacturers
Safety Standards
The safety standards provide guidelines on implementing safety-related components, preparing the environment, and maintaining machines or equipment.
While compliance with the different safety standards (ISO, DIN, IEC, ANSI, etc.) is mostly voluntary, machine builders in the European Union are legally required to follow the safety standards in the machinery directives. Machinery directive 2006/42/EC is always applicable for mobile robot manufacturers, and in some applications, directive 2014/30/EU might also be relevant as it regulates the electromagnetic compatibility of equipment. Machinery directive 2006/42/EC describes the requirements for the design and construction of safe machines introduced into the European market. Manufacturers can only affix a CE label and deliver the machine to their customers if they can prove in the declaration of conformity that they have fulfilled the directive’s requirements.
Although the other safety standards are not mandatory, manufacturers should still follow them as they help to fulfill the requirements in machinery directive 2006/42/EC. For example, manufacturers can follow the guidance in ISO 12100 to reduce identified risks to an acceptable residual risk. They can use ISO 13849 or IEC 62061 to find the required safety level for each risk and ensure that the corresponding safety-related function meets the defined requirements. Mobile robot manufacturers decide how they achieve a certain safety level. For example, they can decrease the speed of the mobile robot to lower the risk of collisions and severity of injuries to an acceptable level. Or they can ensure that mobile robots only operate in separated zones where human access is prohibited (defined as confined zones in ISO 3691-4).
Identifying the correct standards and implementing the requirements is the best way mobile manufacturers can create a safe system. But as this summary suggests, it’s a complicated and time-consuming process.
4. Ensuring a Reliable CAN Communication
A reliable and easy-to-implement standard since the 1980s, communication-based on CAN technology is still growing in popularity, mainly due to its use in various booming industries, such as E-Mobility and Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS). CAN is simple, energy and cost-efficient. All the devices on the network can access all the information, and it’s an open standard, meaning that users can adapt and extend the messages to meet their needs.
For mobile robot manufacturers, establishing a CAN connection is becoming even more vital as it enables them to monitor the lithium-ion batteries increasingly used in mobile robot drive systems, either in retrofit systems or in new installations. Mobile robot manufacturers need to do the following:
1.Establish a reliable connection to the CAN or CANopen communication standards to enable them to check their devices, such as monitoring the battery’s status and performance.
2. Protect systems from electromagnetic interference (EMI), as EMI can destroy a system’s electronics. The risk of EMI is significant in retrofits as adding new components, such as batteries next to the communication cable, results in the introduction of high-frequency electromagnetic disturbances.
5. Accessing Mobile Robots Remotely
The ability to remotely access a machine’s control system can enable mobile robot vendors or engineers to troubleshoot and resolve most problems without traveling to the site.
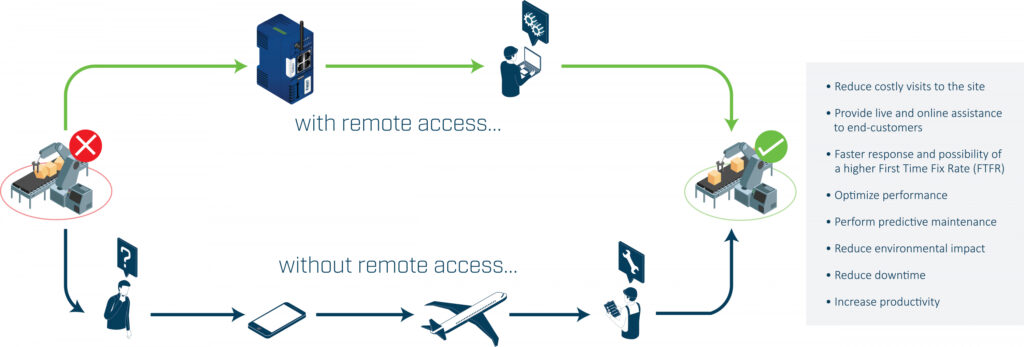
Benefits of Remote Access
The challenge is to create a remote access solution that balances the needs of the IT department with the needs of the engineer or vendor.
The IT department wants to ensure that the network remains secure, reliable, and retains integrity. As a result, the remote access solution should include the following security measures:
- Use outbound connections rather than inbound connections to keep the impact on the firewall to a minimum.
- Separate the relevant traffic from the rest of the network.
- Encrypt and protect all traffic to ensure its confidentiality and integrity.
- Ensure that vendors work in line with or are certified to relevant security standards such as ISO 27001
- Ensure that suppliers complete regular security audits.
The engineer or vendor wants an easy-to-use and dependable system. It should be easy for users to connect to the mobile robots and access the required information. If the installation might change, it should be easy to scale the number of robots as required. If the mobile robots are in a different country from the vendors or engineers, the networking infrastructure must have sufficient coverage and redundancy to guarantee availability worldwide.
Conclusion
As we’ve seen, mobile robot manufacturers must solve many communication and safety challenges. They must establish a wireless connection, send data over different networks, ensure safety, connect to CAN systems, and securely access the robots remotely. And to make it more complicated, each installation must be re-assessed and adapted to meet the on-site requirements.
Best practice to implement mobile robot communication
Mobile robot manufacturers are rarely communication or safety experts. Subsequently, they can find it time-consuming and expensive to try and develop the required communication technology in-house. Enlisting purpose-built third-party communication solutions not only solves the communication challenges at hand, it also provides other benefits.
Modern communication solutions have a modular design enabling mobile robot manufacturers to remove one networking product designed for one standard or protocol and replace it with a product designed for a different standard or protocol without impacting any other part of the machine. For example, Bluetooth may be the most suitable wireless standard in one installation, while Wi-Fi may provide better coverage in another installation. Similarly, one site may use the PROFINET and PROFIsafe protocols, while another may use different industrial and safety protocols. In both scenarios, mobile robot manufacturers can use communication products to change the networking technology to meet the local requirements without making any changes to the hardware design.
Authors:
Mark Crossley, Daniel Heinzler, Fredrik Brynolf, Thomas Carlsson
HMS Networks
HMS Networks is an industrial communication expert based in Sweden, providing several solutions for AGV communication. Read more on www.hms-networks.com/agv