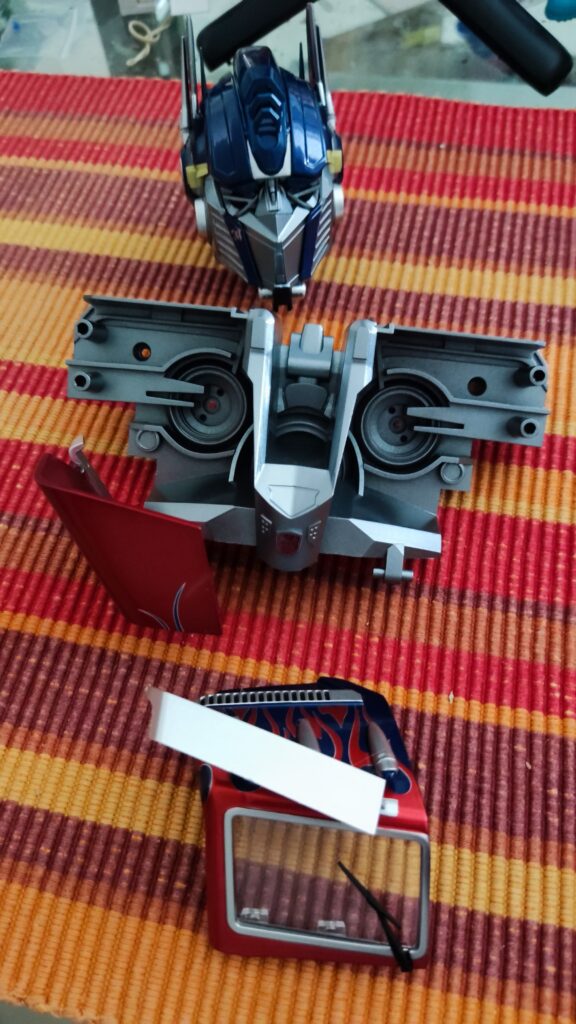
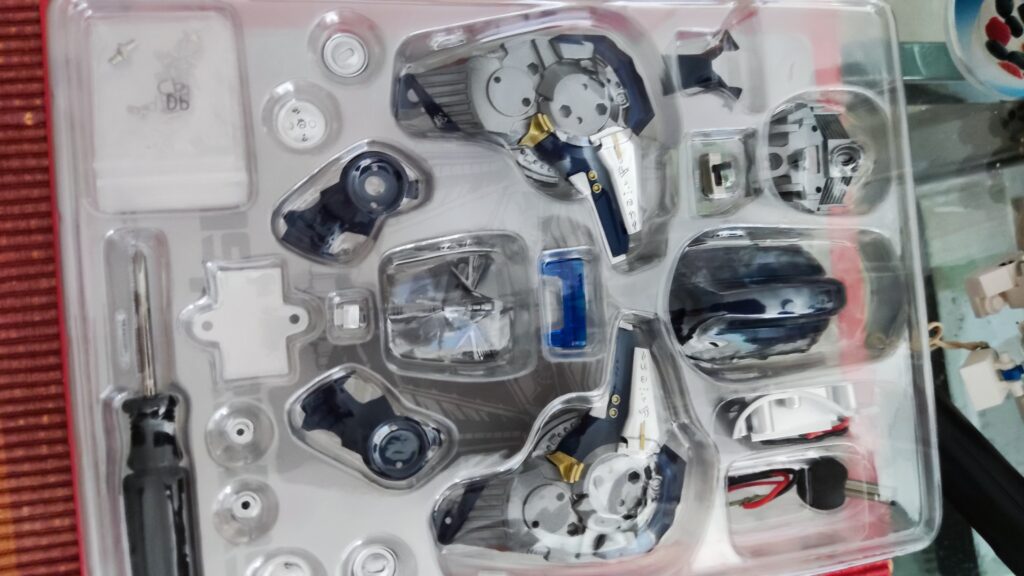
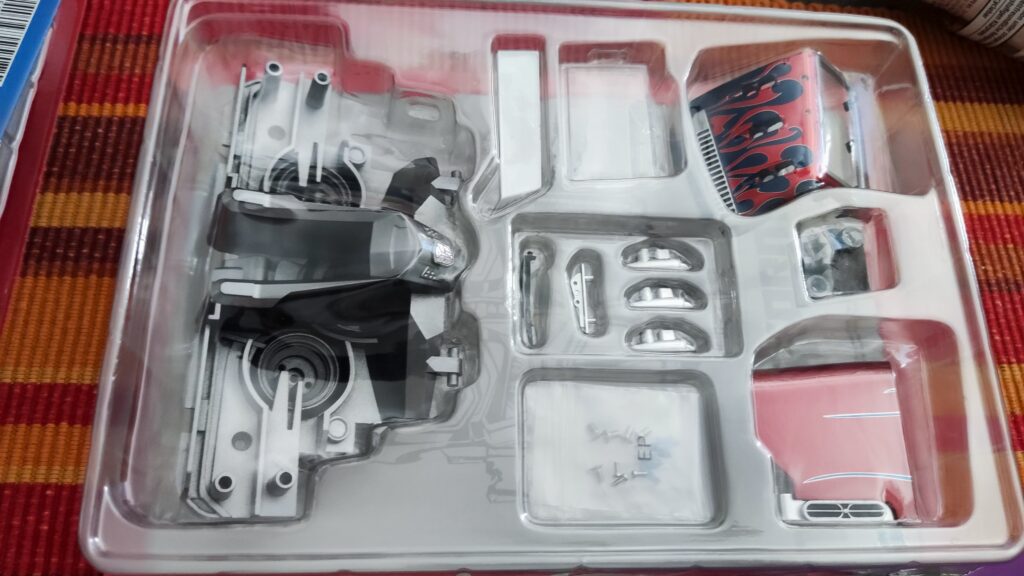
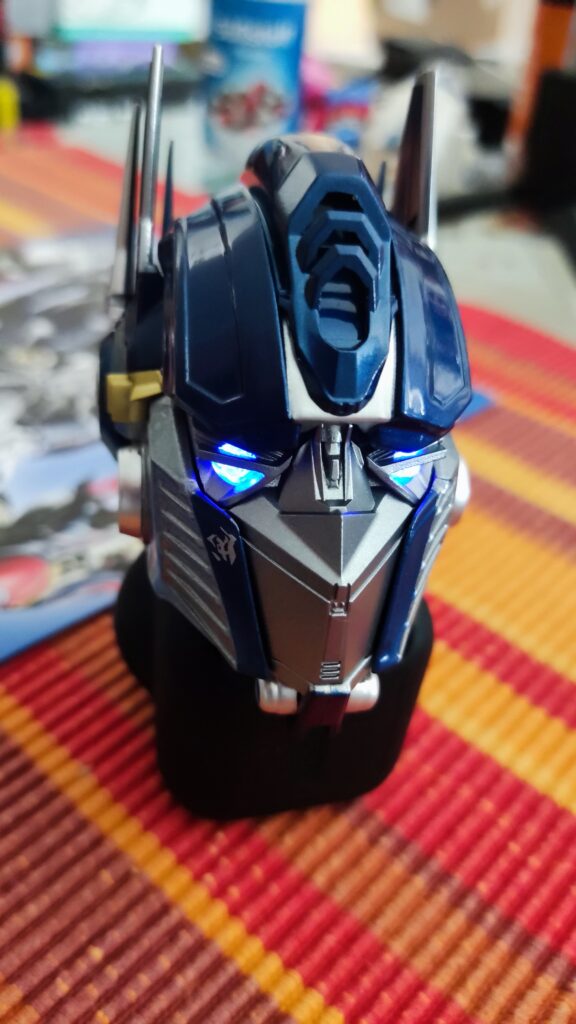
This sophisticated robotic toy is created remarkably to follow lines seamlessly. For kids above 10 years, the Kosmos Line-Follow Robot provides an exciting chance to construct their robot and experience its remarkable line-following skills firsthand. Different branches of science, including physics and mathematics, are all brought together in one convenient experiment kit. Let’s investigate what makes this fascinating instructional tool so effective.
Simplifying Robotics
The Kosmos Line-Follow Robot is an attempt to simplify the complex field of robotics so that it may be understood by and appealing to young people. Despite the common perception that robots are too complicated or only useful for highly specialised tasks, it is crucial to learn the basics of robotics as these devices become increasingly commonplace in everyday life. Involving yourself with the Kosmos Line-Follow Robot is an excellent way for students to get their feet wet in the fascinating field of robotics.
Applied Physics and Logical Thinking
Students need a foundation in physics and the ability to think critically to control the line-follow robot properly. Students may learn the basics of simple circuits using the Kosmos robot’s helpful visual representations. Through hands-on assembly, students create a flow of electricity between electrical components, guaranteeing the vehicle’s functionality and conformity with input and line specifications. This method improves one’s capacity to comprehend logic and circuits.
Line Following and Steering
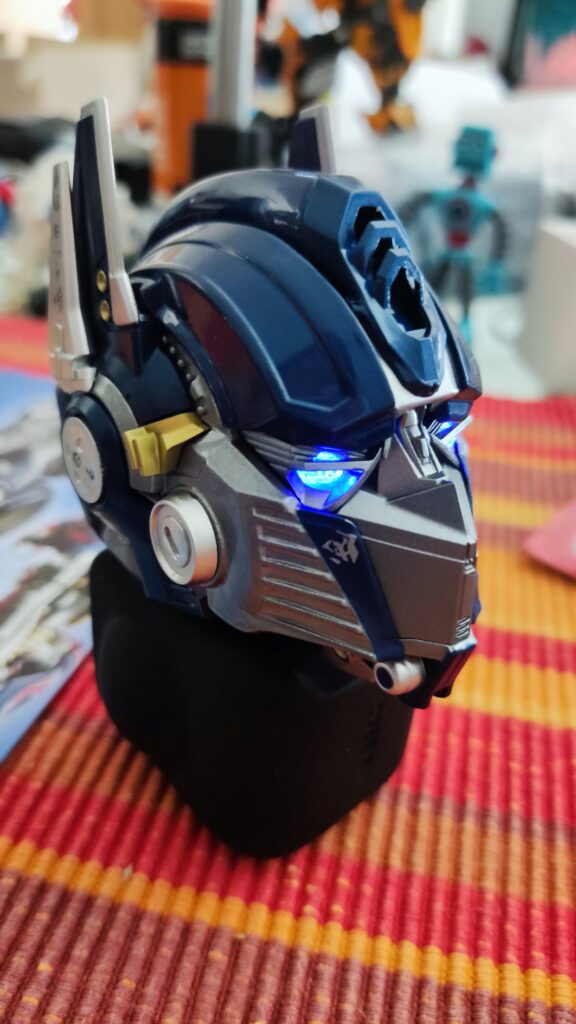
The robot’s fundamental goal is always the same: it must follow a black line, either one that has been physically put out or one that has been painted on a surface. . The Kosmos Line-Follow Robot shows how robots may independently traverse their environment with the help of sensors.
Components and Reusability
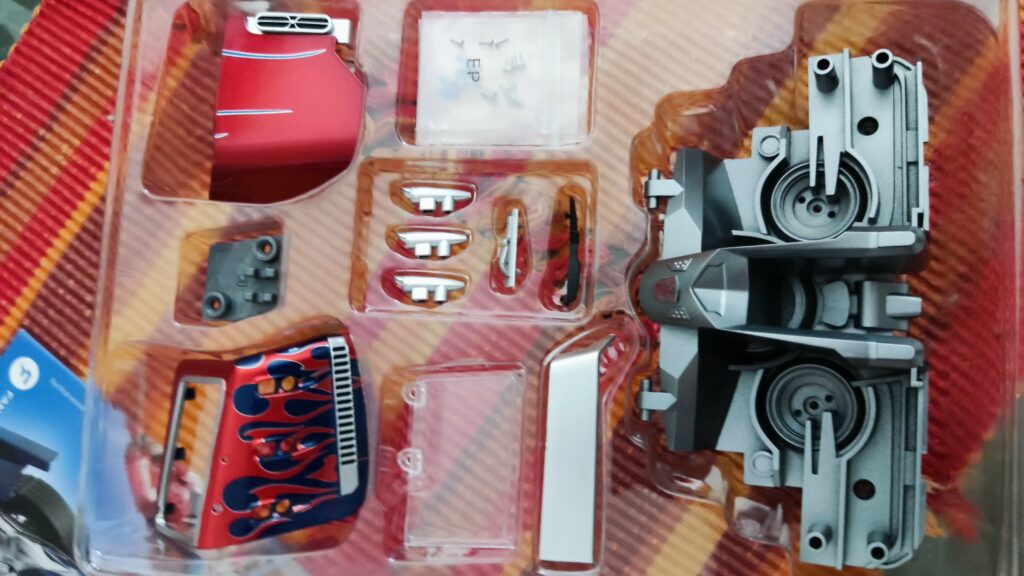
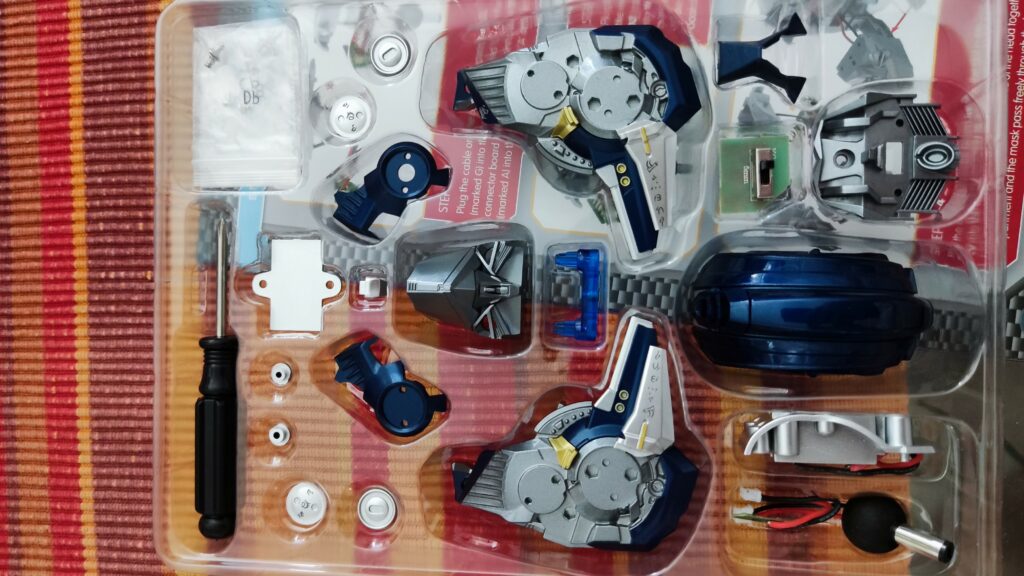
Electrical components with cables, motors, wheels, tires, printed robot decorations, and in-depth instructions are all included in the Kosmos experiment kit. The kit’s target audience was children in grades 4 through 8, however, it may be used with any age group for demonstration. After the first construction is complete, the robot may be used as a helpful teaching tool in physics classes, concretizing theoretical concepts about circuits. The fact that the robot can be assembled and disassembled several times means it may serve as a durable and adaptable teaching tool.
Learning Outcomes
During its construction, the Kosmos Line-Follow Robot relied heavily on principles of physics and mechanics, two fields that are deeply intertwined. Students may learn how to operate the robot by following detailed instructions that walk them through each procedure. Students learn important information that may be used in the classroom and built upon in other ways, such as via experimentation and independent study.
Hands-On Experience and Practical Understanding
The line-following robot facilitates experiential learning and real-world comprehension via the use of a potentiometer for detecting electrical resistance and LEDs for providing visual feedback. By taking the robot apart and putting it back together, students may better understand the interdependencies between its parts. The robot’s behaviour can be changed by tinkering with the black line, opening the door to experimentation and a deeper knowledge of cause and effect.
Conclusion
The Kosmos Line-Follow Robot is an excellent approach to introduce children to robotics. This teaching aid gives students a firm footing on which to explore the potential of robotics by giving them hands-on experience, encouraging logical thought, and incorporating fundamental principles from physics and mechanics. The Kosmos Line-Follow Robot sets the path for the next generation of robotics experts by arousing their natural curiosities, encouraging them to try new things.