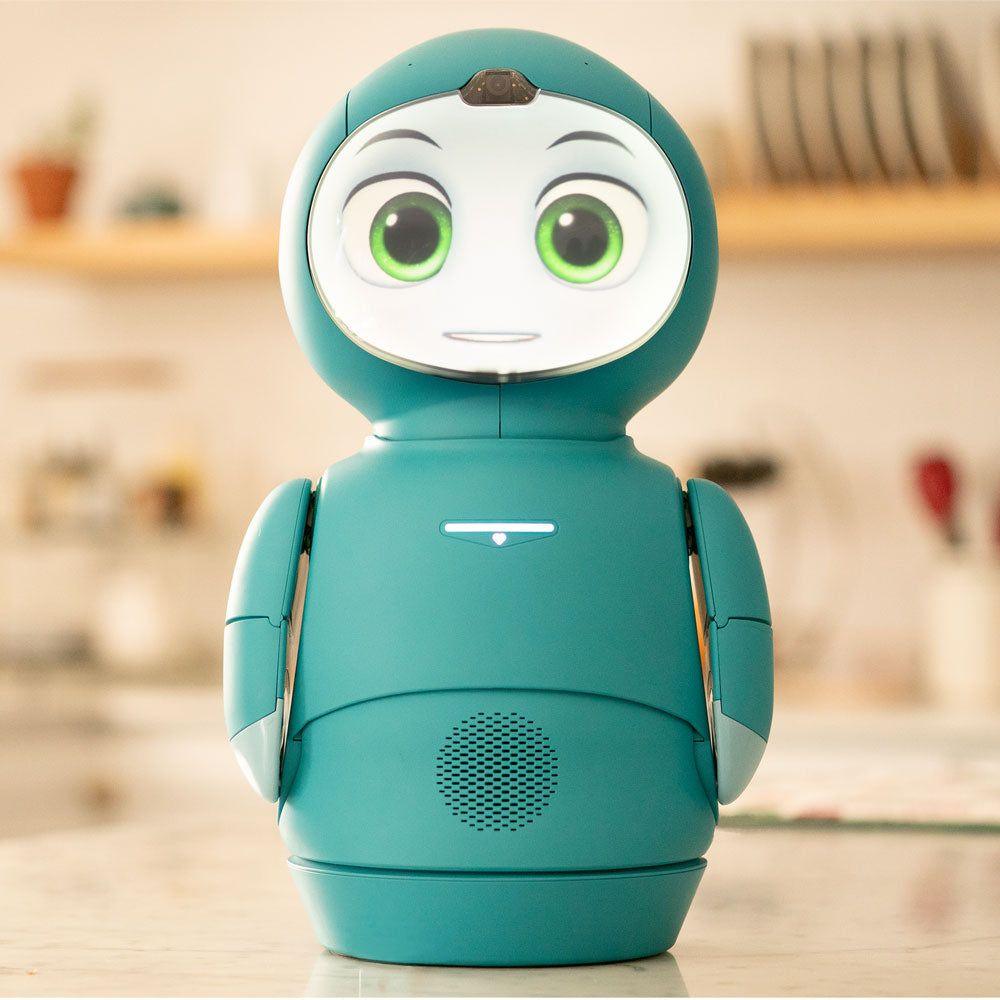
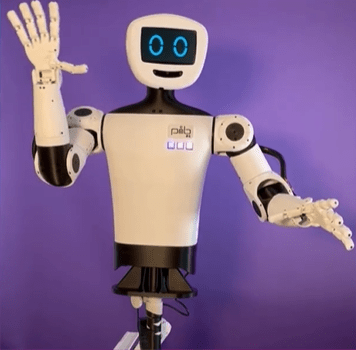
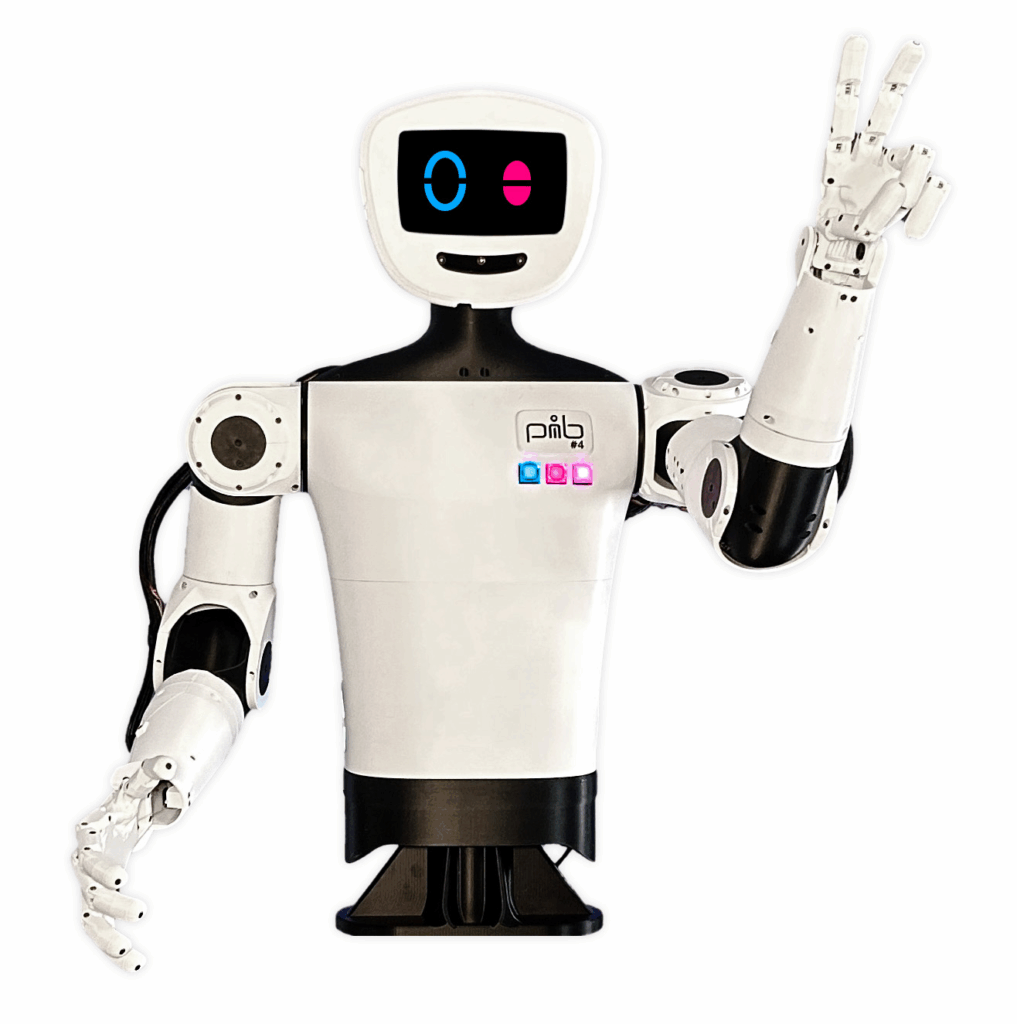
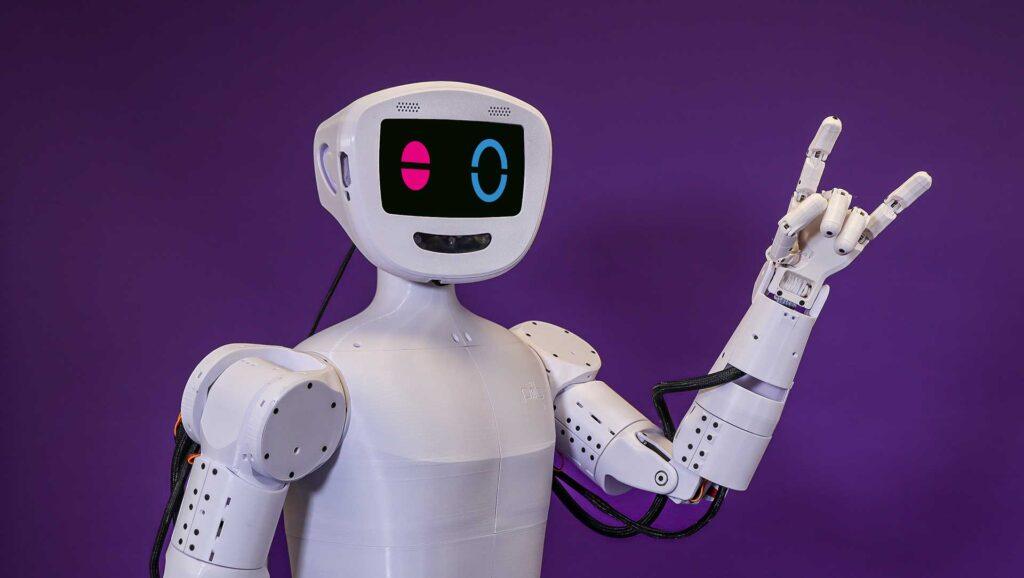
January, 2026 — M5Stack, a global leader in modular IoT and embedded development platforms, today launched StackChan, the first community-co-created open-source AI desktop robot, built on a proven ESP32 platform and designed to be endlessly hackable by makers worldwide.
Unlike closed, concept-driven AI robots, StackChan exposes its hardware, firmware, and interaction logic from day one — turning a playful desktop companion into a real development platform.
StackChan is now live on Kickstarter with a $65 Super Early Bird offer available for the first 72 hours.
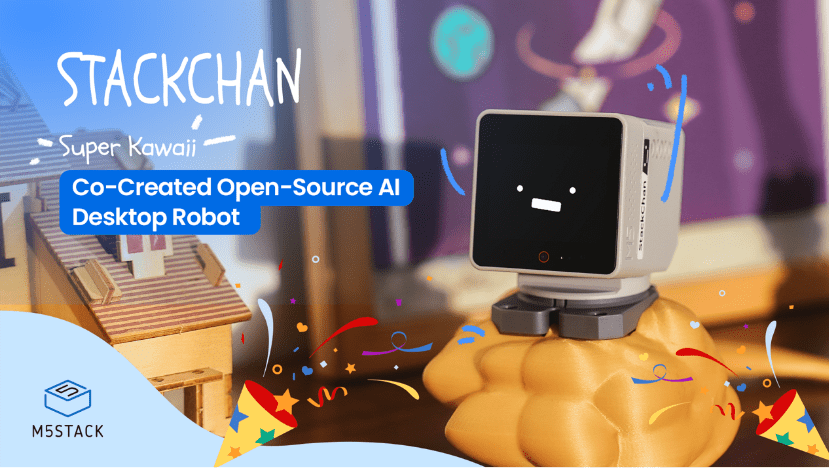
From Community to the Globe: How StackChan Was Born
Before its official launch by M5Stack, StackChan had already existed as a community-driven project since 2021. Built on M5Stack standard controller, Core series, it began as a personal open-source project by maker Shinya Ishikawa, sustained and shaped through ongoing community contributions.
As more enthusiasts joined the project, contributors like Takao, who helped popularize the DIY kits, and Robo8080, who introduced AI capabilities, played key roles in expanding StackChan beyond its original form.
Inspired by StackChan’s expandability and creative potential, M5Stack officially brought the project to life as its first ready-to-play yet endlessly hackable desktop robot—while keeping its community-driven spirit at the core.
What Remains: Core Computing & Interaction Capabilities
As with the original version, StackChan continues to use the M5Stack flagship Core Series (CoreS3) as its main controller. CoreS3 is powered by an ESP32-S3 SoC with a 240 MHz dual-core processor, 16 MB Flash, and 8 MB PSRAM, and supports both Wi-Fi and BLE connectivity.
To enable richer interactions, the main unit integrates a 2.0-inch capacitive touch display, a 0.3 MP camera, a proximity sensor, a 9-axis IMU (accelerometer + gyroscope + magnetometer). It also includes a microSD card slot, a 1W speaker, dual microphones, and power/reset buttons. Together, these hardware components form a solid foundation for StackChan’s audio-visual interactive experiences.
For more technical details, please refer to the StackChan documentation: https://docs.m5stack.com/en/StackChan
What’s New: Ready-to-Play Functions Powered by Advanced Hardware
For the robot body, several advancements have been made to make it easier to get hands-on and improve the out-of-box experience. It features:
Power & connectivity: A USB-C interface for both power and data, paired with a built-in 700 mAh battery.
Movement system: 2 feedback servos supporting 360° continuous rotation on the horizontal axis and 90° vertical tilt—enabling expressive movements with real-time position feedback.
Visual feedback: 2 rows totaling 12 RGB LEDs for expressive system and interaction feedback.
Sensors & interaction: Infrared transmission and reception, a three-zone touch panel, and a full-featured NFC module enabling touch- and identity-based interactions.
On the software side, StackChan is ready-to-play for starters with no coding required. The pre-installed factory firmware delivers:
Expressive faces and motions: Preloaded with vivid facial expressions and coordinated movements that bring personality and liveliness to StackChan.
Built-in AI agent: Integrates an AI agent for natural voice-based interaction and conversational experiences.

App-based remote interaction: Supports official iOS app for video calls, remote avatar control, and real-time interaction with StackChan.
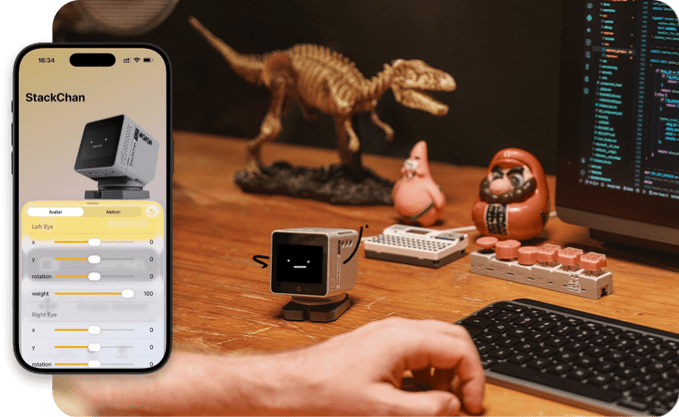

Chan-to-Chan Friends Map: Enables discovery of nearby StackChan devices, unlocking playful multi-device and social interaction scenarios.

Open for customization: While beginner-friendly by default, the firmware supports further development via Arduino and UiFlow2, making it easy to create custom applications.

100% Open-Source: Built to Be Customized and Extended
In an era filled with closed, concept-driven “AI robot” products, StackChan stands out with its open-source core. From firmware and hardware interfaces to development tools, every layer is designed to be explored, modified, and extended by users.
Beyond code, StackChan also encourages physical customization. With 3D printing and creative accessories, users can personalize their StackChan’s appearance and turn it into a unique desktop companion.
Open-source repository: https://github.com/m5stack/StackChan
Fun with Global Community: Share, Extend, and Evolve Together
Since its birth, StackChan has grown into a vibrant global community of makers, developers, and enthusiasts. From sharing projects and source code online to hosting meetups and anniversary events offline, the community continues to expand what StackChan can be.
Owning a StackChan is not just about building a robot—it’s about being part of an open ecosystem where ideas and creativity evolve together.
StackChan is not built to its end at launch. It is built to grow—through open technology, creative experimentation, and a global community that continues to redefine what a desktop robot can be.
Discover your StackChan on Kickstarter now: https://www.kickstarter.com/projects/m5stack/stackchan-the-first-co-created-open-source-ai-desktop-robot?ref=d5iznw&utm_source=PR