Schlagwort-Archiv: Cobot
Volker Spanier präsentiert neuen Epson 6-Achs-Roboter Cobot AX6 im Robots-Blog Interview auf automatica 2025
Spielerische Robotik-Ausbildung: igus Low-Cost-Automation bewährt sich im Schulalltag
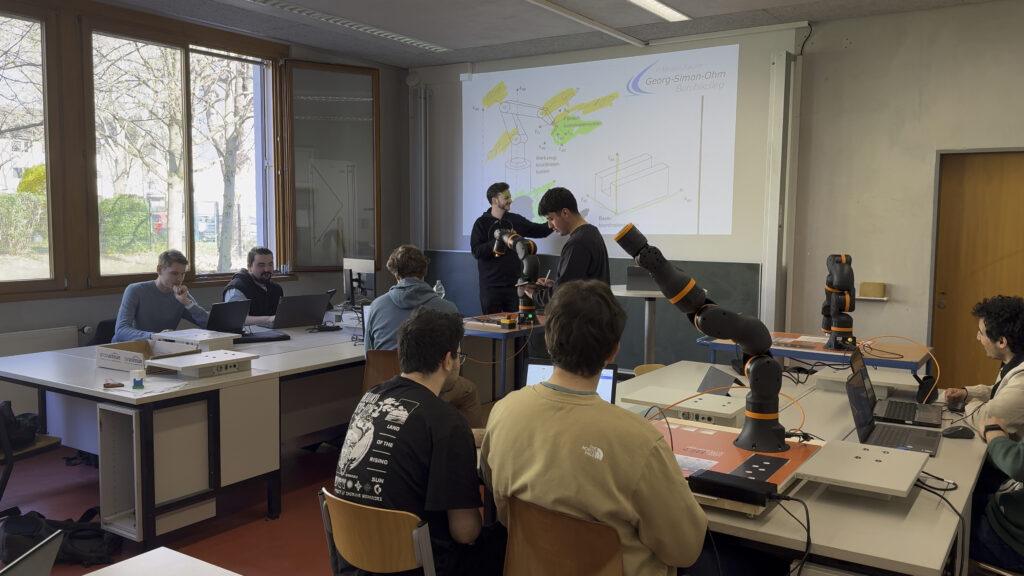

Georg-Simon-Ohm-Berufskolleg setzt auf ReBeL Cobots und Education Kits von igus, um Schülern einen einfachen Einstieg in die Roboter-Programmierung zu ermöglichen
Köln, 17. Juni 2025 – Junge Menschen für Technik begeistern: Dieses Ziel verfolgt der Kunststoffspezialist und Robotikhersteller igus mit seinen Bildungsangeboten speziell für Schulen, Hochschulen und Universitäten. Dazu zählt auch das ReBeL Education Kit: Ein Lernpaket, das Schülern und Studierenden den spielerischen Einstieg in die Robotik mithilfe des ReBeL Cobots ermöglichen soll. Zum Einsatz kommen die Education Kits unter anderem am Georg-Simon-Ohm-Berufskolleg in Köln. So bekommen die Schüler die Möglichkeit, erste Programmierkenntnisse zu erwerben und praxisnahe Anwendungen zu erproben.
Von Elektrotechnik über Datenbankwissen bis hin zur Softwareentwicklung: Die Ausbildung zum Informationstechnischen Assistenten am Georg-Simon-Ohm-Berufskolleg in Köln umfasst ein vielseitiges Lehrprogramm. Dazu gehört auch das Programmieren von Robotern, um den Schülern besondere Qualifikationen in der Automatisierungstechnik zu vermitteln. „Für unsere Robotik-Klasse kamen bisher humanoide Robotiksysteme zum Einsatz, die jedoch mit der Zeit störungsanfällig geworden sind“, erklärt Kevin Meyer, Lehrer für Elektrotechnik und Robotik am Georg-Simon-Ohm-Berufskolleg. „Daher brauchten wir Ersatz für die alten Systeme und haben uns gezielt auf die Suche nach Roboterarmen gemacht, die einfach zu bedienen sind und realitätsnahe Anwendungsszenarien ermöglichen.“ Fündig wurde das Berufskolleg schließlich beim Kölner Kunststoffspezialisten igus.
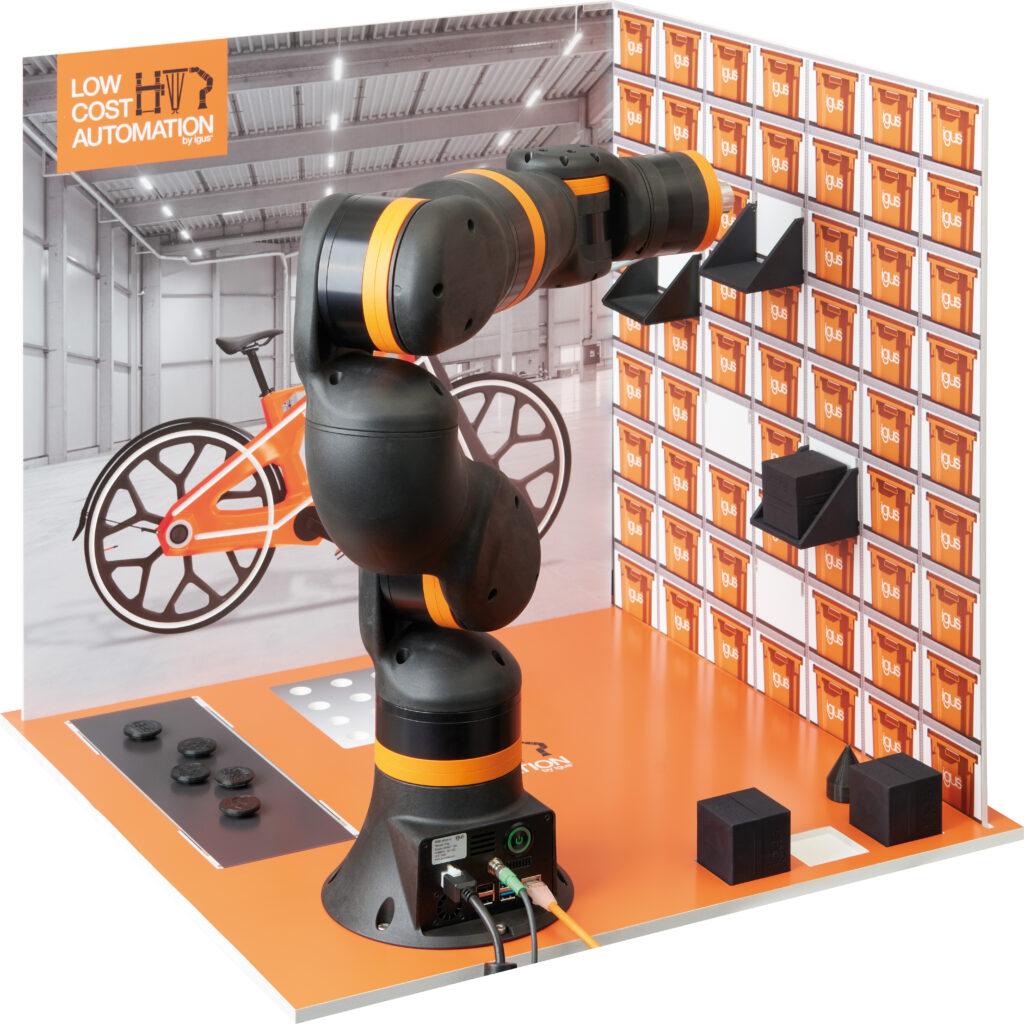

Programmieren lernen mit realitätsnahen Anwendungsbeispielen
„igus war uns bereits für seine Energieketten bekannt, doch bei unserer Suche sind wir dann auch auf das Low-Cost-Automation-Angebot gestoßen und haben gleich einen Beratungstermin vor Ort ausgemacht“, erzählt Kevin Meyer. Auf der 400 Quadratmeter großen Customer Test Area können Kunden zahlreiche Automationslösungen aus der Praxis in Aktion sehen und gemeinsam mit den Robotik-Experten von igus die Machbarkeit ihrer geplanten Anwendung testen. Die Wahl fiel schließlich auf zehn ReBeL Cobots mit sechs Achsen inklusive Education Kits. „Roboter gibt es auf dem Markt zwar viele, aber die Alternativen waren für unsere Zwecke entweder zu klein oder zu teuer. Zudem war für uns auch eine leichte Bedienbarkeit wichtig.“ Der ReBeL Cobot mit einem Gewicht von nur 8,2 Kilogramm, einer Traglast von zwei Kilogramm und einer Reichweite von 664 Millimetern ist in der vollausgestatteten Plug-and-Play-Variante bereits für 4.970 Euro erhältlich. Im Education Kit enthalten sind über 100 Stunden Lernmaterial und Projektplatten, die auf eine Arbeitsfläche montiert werden. Anhand derer lassen sich unterschiedliche Szenarien mit Realitätsbezug programmieren: ob Behälter in ein Hochregal sortieren, Bauteile eines Fahrrads vom Förderband nehmen und an der entsprechenden Stelle einsetzen oder die Qualitätskontrolle am Fahrrad. Die kostenlose und lizenzfreie igus Robot Control Software ermöglicht zudem eine einfache Bedienbarkeit und erleichtert den Einstieg in die Roboterprogrammierung.
Lernende gezielt auf die moderne Arbeitswelt vorbereiten
Die ReBeL Cobots und Education Kits sind inzwischen seit einem Jahr in vier Robotik-Klassen des Berufskollegs im Einsatz. „Die meisten Schüler arbeiten sehr gerne mit den Robotern. Die Bedienung war am Anfang für manche noch eine Herausforderung, aber am Ende haben es alle geschafft“, erzählt Kevin Meyer. Die Software sei visuell sehr anschaulich und ermögliche den Schülern, schnell kleine Fortschritte zu machen. Alexander Mühlens, Leiter Geschäftsbereich Low-Cost-Automation bei igus betont: „Uns liegt die Förderung des Roboternachwuchses sehr am Herzen, daher freuen uns solche Projekte immer besonders. Mit unserem breiten Bildungsangebot möchten wir Schulen, Hochschulen und Universitäten dabei unterstützen, theoretisches Wissen praxisnah zu vermitteln und Lernende gezielt auf die moderne Arbeitswelt vorzubereiten.“
Mehr Informationen zum Robotik-Bildungsangebot von igus finden Sie hier:
automatica 2025: erster kollaborativer Roboter von Epson
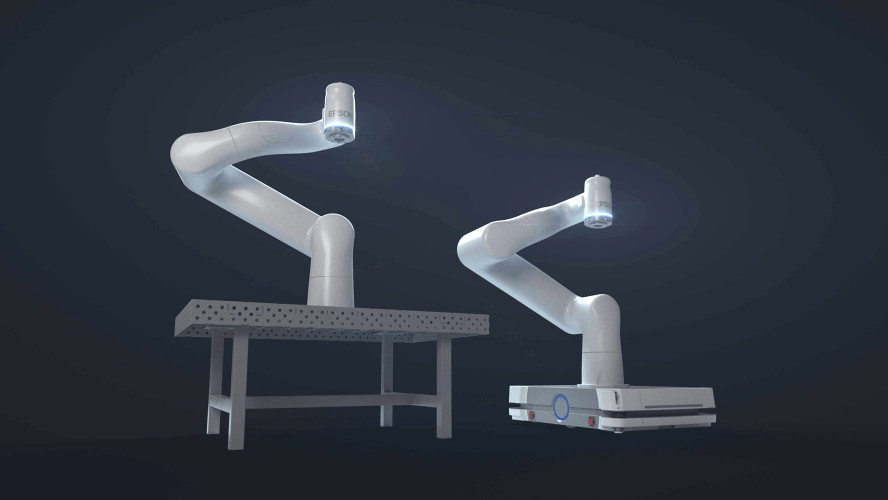
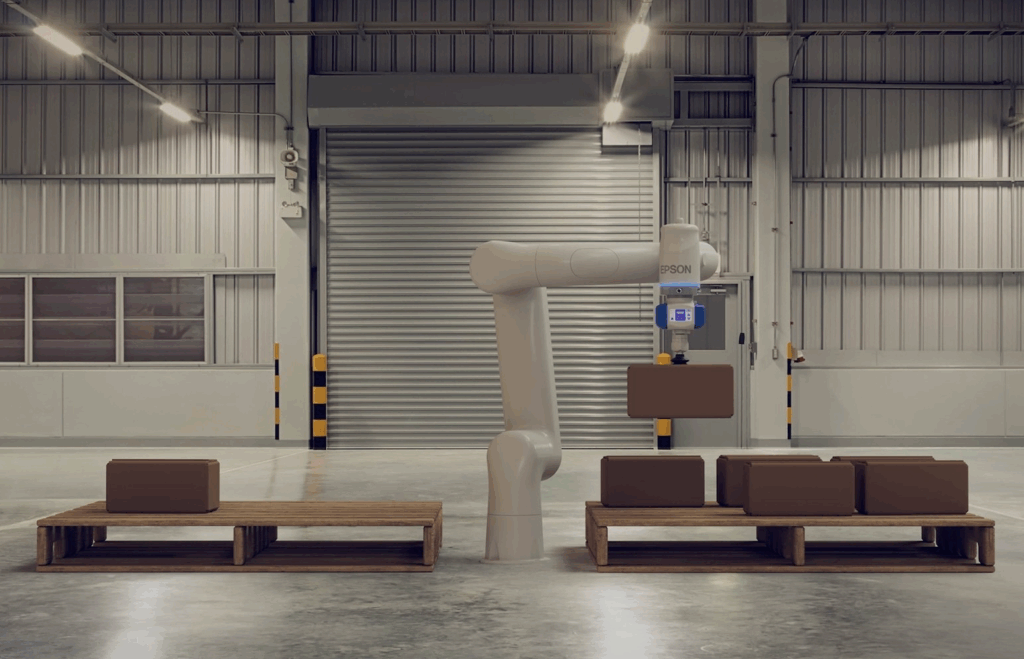
Düsseldorf, 10. Juni 2025 – Epson, ein führender Anbieter von Roboter- und Automatisierungstechnik, stellt auf der automatica 2025 seine erste kollaborative Industrieroboterlösung vor. Diese ermöglicht in Branchen wie Fertigung, Logistik und dem sich schnell entwickelnden Life-Science-Sektor eine wirkungsvolle Interaktion zwischen Mensch und Maschine und steigert so die Effizienz und Produktivität. Die Lösung wird ab Herbst 2025 als erstes kollaboratives Roboter-Komplettpaket von Epson angeboten, welches den neuen, aus Carbon-Leichtbau bestehenden 6-Achs-Roboter AX6-A901S sowie die kompakte Epson RC-A101-Steuerung inklusive dem Programmiersystem AX-Portal umfasst.
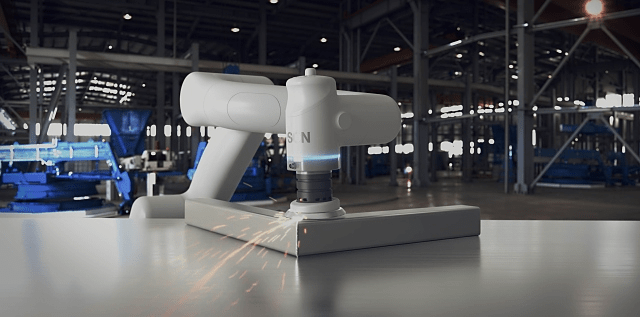
„In den stark wachsenden Bereichen Biowissenschaften und pharmazeutische Industrie sind präzise Arbeitsabläufe und ein strenges Hygienemanagement von größter Bedeutung“, erklärt Volker Spanier, Head of Manufacturing Solutions von Epson. „Um auch diese Anforderungen zu erfüllen, ist der neue kollaborative Roboter von Epson reinraumtauglich. Dank seiner präzisen Bewegungen erlaubt die Maschine daher auch in Laboren und pharmazeutischen Einrichtungen die Verrichtung selbst komplizierter Aufgaben.“
Wichtige Produktmerkmale des kollaborativen Roboters AX6-A901S von Epson:
- Ausbalanciertes Design: Der AX6-A901S bewegt eine Nutzlast von bis zu 6 kg bei einer Armlänge von 900 mm. Er besitzt ein besonders leichtes und kompaktes Design, sodass sowohl sein Transport als auch seine Integration in bestehende Produktionslinien sehr einfach sind. Dank der kompakten Abmessungen lässt er sich auch in beengten Umgebungen einsetzen.
- Kompakter und leichter Controller: Der Epson RC-A101-Controller ist für die Installation auf fahrerlosen Transportfahrzeugen (AGVs) und autonomen, mobilen Robotern (AMRs) geeignet. Er hat die Abmessungen B 440 x T 205 x H 135 mm und wiegt weniger als 6 kg. Auch dieses kompakte Design ermöglicht eine sehr platzsparende Installation.
- Kompatibel zu verschiedenen Stromquellen: Der kollaborative Roboter ist mit Stromquellen von 100 bis 230 VAC bzw. 48 VDC kompatibel, sodass er in Umgebungen mit verschiedenen Stromquellen installiert werden kann.
- Reinraumkompatibilität: Der AX6-A901S besitzt die Reinraumklasse 5 nach ISO 14644-1 und die Schutzart IP54. Das glatte Gehäusedesign ohne Schraubenlöcher und scharfe Kanten minimiert die Staubansammlung und damit das Kontaminationsrisiko in Reinraumumgebungen.
- Python-Programmierung: Die Programmierumgebung unterstützt die weit verbreitete Programmiersprache Python. Diese Kompatibilität vereinfacht die Integration in alle F&E-Umgebungen und die Inbetriebnahme. Auch wird so das Erlernen einer neuen Programmiersprache unnötig.

Spanier fasst zusammen: „Epsons Engagement für die Weiterentwicklung der Robotik resultiert in diesem kollaborativen Roboter, der auch sehr komplexe Aufgaben sicher ausführt. Damit erfüllen wir die wachsende Nachfrage der Labor- und Pharmaindustrie und weiteren Branchen. Diese Maschine stellt einen bedeutenden Fortschritt auf dem Weg zur Verbesserung des Epson Angebotes im Bereich der industriellen Automatisierung dar. Unsere Roboter erfüllen dabei auch die strikten Anforderungen des Life-Science-Sektors und gewährleisten Sicherheit und Präzision bei jeder Interaktion zwischen Mensch und Maschine.“
Zu den neuen Robotern gibt es am 24. Juni eine Pressekonferenz am Epson Stand 311 in Halle B5
Weitere Informationen zu den Robotiklösungen von Epson:
automatica 2025 | Epson Europe
ReBeL Move: Autonomes Logistik-Fahrzeug von igus für 29.838 Euro
Einfach installiert und schnell amortisiert ermöglicht der mobile Roboter den kostengünstigen Einstieg in die Automatisierung von Logistikprozessen
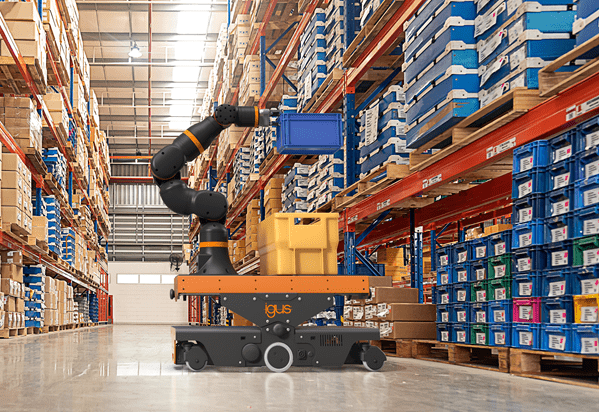

Stuttgart/Köln, 8. Oktober 2024 – Dass die Automatisierung von Intralogistikprozessen weder teuer noch kompliziert sein muss, beweist igus mit dem neuen ReBeL Move, den der Kölner motion plastics Spezialist auf der Motek 2024 präsentiert. Der mobile Roboter bewegt sich autonom durch Fabrikhallen und transportiert Produkte von A nach B – und kann dafür auch mit dem ReBeL Cobot aus Hochleistungskunststoff kombiniert werden. Es lässt sich schon mit einfachsten IT-Kenntnissen innerhalb einer Stunde in Betrieb nehmen und ist inklusive ReBeL Cobot für 34.808 Euro erhältlich.
Fahrerlose Transportsysteme (FTS) vereinfachen den Alltag in Industriebetrieben: Mitarbeiter an Maschinen müssen beispielsweise nicht länger Werkzeuge und Materialien zu Fuß aus dem Lager holen, sondern lassen sich von autonomen Fahrzeugen unterstützen. Dass eine solche Automatisierung in Zeiten von Kostendruck und Personalmangel die Produktivität steigert und Kosten senkt, erkennen auch immer mehr kleine und mittelständische Betriebe mit niedrigem Automatisierungsgrad. „Dennoch gibt es oft Berührungsängste, weil die Erfahrung fehlt und stattdessen die Angst vor Fehlinvestitionen überwiegt“, sagt Alexander Mühlens, Prokurist und Leiter Geschäftsbereich Low-Cost-Automation bei igus. „Um diesen Betrieben einen barrierefreien und risikoarmen Einstieg in die Automatisierung von Intralogistikprozessen zu ermöglichen, haben wir ein kostengünstiges und intuitiv bedienbares FTS mit einem integrierten Cobot zum Greifen von Gegenständen entwickelt: den ReBeL Move.“
Investition amortisiert sich unter 12 Monaten
Das autonome Transportfahrzeug kann Kleinladungsträger (KLT) mit den Maßen 60×40 Zentimeter und 30×40 Zentimeter und einer Zuladung von bis zu 35 Kilogramm transportieren. Es fährt mit einer Geschwindigkeit von bis zu 1,5 m/s, hat eine Batterielaufzeit von über acht Stunden und eine Ladezeit von unter zwei Stunden. An Bord ist optional der ReBeL, ein Cobot, den igus fast vollständig aus robustem und kostengünstigem Hochleistungskunststoff fertigt. Der Gelenkarmroboter ist mit einem Einzelpreis von nur 4.970 Euro für die vollausgestattete Variante fünfmal günstiger als vergleichbare Modelle aus Metall. Er hat ein Eigengewicht von 8,2 Kilogramm, eine Traglast von 2 Kilogramm und eine Reichweite von 664 Millimetern. „Mit einem Preis von nur 34.808 Euro kostet der ReBeL Move nur einen Bruchteil herkömmlicher FTS, sodass sich die Investition innerhalb von 12 Monaten amortisiert“, so Alexander Mühlens.
ReBeL Move lässt sich innerhalb einer Stunde in Betrieb nehmen
Das neue FTS-System ist nicht nur kostengünstiger als vergleichbare Lösungen, sondern auch besonders leicht in Betrieb zu nehmen – ähnlich schnell wie ein Rasenmähroboter. In weniger digitalisierten Unternehmen funktioniert das FTS als eigenständiges System, das lediglich eine WLAN-Verbindung benötigt. Für die Konfiguration bewegt der Betreiber das Fahrzeug mit einem Handcontroller entlang der zukünftigen Arbeitsbereiche. Der ReBeL Move verfügt über eine 360-Grad-Kamera und erstellt mithilfe der sogenannten Slam-Technologie während der Rundfahrt automatisch eine Digitalkarte. Auf dem Tablet kann der Betreiber nach dieser ersten Kartierungsfahrt dann einzelne Stationen zum Arbeiten, Warten und Aufladen festlegen. Ebenso No-go-Areas wie Bereiche rund um Treppen und Fahrstühle oder Zonen, in denen der Roboter mit reduzierter Geschwindigkeit fahren soll, um Mitarbeiter nicht zu stören. In der physischen Realität erkennt der mobile Roboter die Zielorte dann mithilfe einer Kamera und Reflektoren an den einzelnen Stationen, ohne dass der Betreiber aufwendig Leitlinien oder Spuren auf dem Boden installieren müsste.
Kinderleicht festlegen lassen sich über das Tablet zudem die Jobs, die der ReBeL Move in der Intralogistik erledigen soll, etwa mit dem ReBeL Cobot an Station A Produkte aus einem Gebinde entnehmen und zu Station B transportieren. Teil der Lösung ist darüber hinaus eine Software, die ein intelligentes Flottenmanagement ermöglicht, sodass mehrere FTS effizient zusammenarbeiten können. „Die gesamte Inbetriebnahme ist so leicht, dass Anwender innerhalb von 15 Minuten einfache Jobs programmieren können“, sagt Mühlens. Auch die Einbindung in gewachsene IT-Landschaften, die beispielsweise ein synchronisiertes Zusammenspiel von Robotern und automatischen Rolltoren ermöglicht, ist dank Schnittstellen wie IoT, VDA 5050, REST, SAP und ERP kein Problem. Mühlens: „Da die Inbetriebnahme so schnell funktioniert, können wir bei interessierten Kunden jederzeit vor Ort kleine Automationslösungen simulieren und ihnen somit die Berührungsangst mit der Technologie nehmen. Zum Kaufmodell haben wir zusätzlich auch ein Mietmodell im Angebot.“
Vention and ABB collaborate to make cobot automation accessible to SMBs
Montreal/Berlin, September 10, 2024 – Vention, the company behind the cloud-based Manufacturing Automation Platform (MAP), announces its collaboration with ABB Robotics, confirming the compatibility between the Vention platform and the ABB GoFa™ family of cobots. Vention and ABB customers benefit from a seamless integration of both companies‘ technologies, from the design phase of the robot cells to the processes on the factory floor.
As part of the Vention ecosystem, ABB will gain access to a wider range of do-it-yourself automation customers, while Vention will expand its offering with ABB’s robotic solutions. The mutually beneficial relationship will expand market reach and innovation for both companies.

Enhanced automation capabilities with the ABB GoFa™ CRB15000 Series
The ABB GoFa™ robots, now available on the Vention marketplace, offer manufacturers proven cobots with a payload of 5 kg, 10 kg and 12 kg. Known for their safety, ease of use and performance, ABB GoFa™ robots are designed to work side-by-side with humans in various applications, from assembly and welding to material handling and inspection.
ABB GoFa™ robots, enhanced by the power of the Vention Manufacturing Automation Platform
ABB GoFa™ robots are now compatible with the entire Vention platform, including MachineBuilder (design), MachineLogic (robot programming), MachineAnalytics (operational monitoring and data) and Remote Support (on-demand support). This compatibility provides ABB customers with an intuitive user experience, from the design to the operation of robot cells. In addition, ABB GoFa™ robots will be available for Vention’s innovative Rapid Series application line during 2025.
„We are very pleased to welcome ABB to the Vention ecosystem. This collaboration enhances our ability to deliver democratized and powerful automation solutions“ says Etienne Lacroix, Founder and CEO of Vention.
„The partnership with Vention represents a significant step forward for both companies. This collaboration combines ABB’s advanced cobot portfolio with Vention’s expertise in application design and delivery. By bringing together our hardware and software capabilities, we’re making robot automation more accessible and easier to integrate for businesses of all sizes. „Our joint efforts will address key industry trends and help companies improve their operations and make workplaces safer and more efficient,“ said Andrea Cassoni, Head of Collaborative Robotics at ABB Robotics.
About Vention
Vention helps companies automate their production areas in just a few days through a democratized user experience. Vention’s digital manufacturing automation platform allows customers to design, automate, order, and deploy automated equipment directly from their web browser. Vention is headquartered in Montreal, Canada, with offices in Berlin and Boston. Its more than 300 employees serve more than 4,000 customers on five continents and in 25 manufacturing industries. For more information, see vention.com or follow us on LinkedIn. *MachineMotion, MachineLogic, MachineCloud and Vention are trademarks of Vention Inc.
About ABB Robotics
ABB (ABBN: SIX Swiss Ex) ABB is a technology leader in electrification and automation, enabling a more sustainable and resource-efficient future. The company’s solutions combine technical expertise and software to optimize the manufacturing, movement, power, and operation of things. Building on more than 140 years of excellence, ABB’s more than 105,000 employees are committed to driving innovation that accelerates industrial transformation. www.abb.com
ABB Robotics & Discrete Automation, as one of the world’s leading providers of robotics and machine automation, is the only company with a comprehensive and integrated portfolio that includes robots, autonomous mobile robots and machine automation solutions developed and orchestrated by our value-added software. We help companies of all sizes and industries – from automotive to electronics to logistics – to become more resilient, flexible and efficient. ABB Robotics & Discrete Automation is helping customers transition to the connected and collaborative factory of the future. The business unit employs around 11,000 people at over 100 locations in around 53 countries. go.abb/robotics
Vention und ABB arbeiten zusammen, um Cobot Automatisierung für KMU zugänglich zu machen
Montreal/Berlin, 10. September 2024 – Vention, das Unternehmen hinter der cloudbasierten Manufacturing Automation Platform (MAP), gibt seine Zusammenarbeit mit ABB Robotics bekannt und bestätigt die Kompatibilität zwischen der Vention-Plattform und der Cobot-Familie ABB GoFa™. Kunden von Vention und ABB profitieren von einer nahtlosen Integration der Technologien beider Unternehmen, von der Entwurfsphase der Roboterzellen bis hin zu den Abläufen in der Fabrikhalle.
Als Teil des Vention-Ökosystems erhält ABB Zugang zu einem breiteren Spektrum von Do-it-yourself-Automatisierungskunden, während Vention sein Angebot mit den Roboterlösungen von ABB erweitern wird. Die für beide Seiten vorteilhafte Beziehung wird die Marktreichweite und Innovation für beide Unternehmen erweitern.

Verbesserte Automatisierungsfunktionen mit der ABB GoFa™ CRB15000-Serie
Die ABB GoFa™-Roboter, die jetzt auf dem Vention-Marktplatz erhältlich sind, bieten Herstellern bewährte Cobots mit einer Nutzlast von 5 kg, 10 kg und 12 kg. ABB GoFa™- Roboter sind für ihre Sicherheit, Benutzerfreundlichkeit und Leistung bekannt und wurden entwickelt, um in verschiedenen Anwendungen, von der Montage und dem Schweißen bis hin zur Materialhandhabung und Inspektion, Seite an Seite mit Menschen zu arbeiten.
ABB GoFa™-Roboter, verbessert durch die Leistung der Vention Manufacturing Automation Platform
ABB GoFa™-Roboter sind jetzt mit der gesamten Vention-Plattform kompatibel, einschließlich MachineBuilder (Design), MachineLogic (Roboterprogrammierung), MachineAnalytics (Betriebsüberwachung und -daten) und Remote Support (On-Demand Support). Diese Kompatibilität bietet ABB-Kunden ein intuitives Benutzererlebnis, vom Design bis zum Betrieb von Roboterzellen. Darüber hinaus werden die ABB GoFa™-Roboter im Laufe des Jahres 2025 für die innovative Rapid Series-Anwendungslinie von Vention verfügbar sein.
„Wir freuen uns sehr, ABB im Vention-Ökosystem begrüßen zu dürfen. Diese Zusammenarbeit verbessert unsere Fähigkeit, demokratisierte und leistungsstarke Automatisierungslösungen bereitzustellen“ – Etienne Lacroix, Gründer und CEO von Vention.
„Die Partnerschaft mit Vention stellt für beide Unternehmen einen bedeutenden Schritt nach vorne dar. Diese Zusammenarbeit kombiniert das fortschrittliche Cobot-Portfolio von ABB mit der Expertise von Vention in Anwendungsdesign und -bereitstellung. Durch die Zusammenführung unserer Hardware- und Softwarefähigkeiten machen wir die Roboterautomatisierung für Unternehmen jeder Größe zugänglicher und einfacher zu integrieren. „Unsere gemeinsamen Anstrengungen werden wichtige Branchentrends ansprechen und Unternehmen dabei helfen, ihre Betriebsabläufe zu verbessern und Arbeitsplätze sicherer und effizienter zu machen“, sagt Andrea Cassoni, Leiter von Collaborative Robotics bei ABB Robotics.
Über Vention
Vention hilft Unternehmen, ihre Produktionsbereiche durch eine demokratisierte Benutzererfahrung in nur wenigen Tagen zu automatisieren. Mit der digitalen Fertigungsautomatisierungsplattform von Vention können Kunden automatisierte Geräte direkt über ihren Webbrowser entwerfen, automatisieren, bestellen und bereitstellen. Vention hat seinen Hauptsitz in Montreal, Kanada, und Niederlassungen in Berlin und Boston. Die über 300 Mitarbeiter betreuen mehr als 4.000 Kunden auf fünf Kontinenten und in 25 Fertigungsindustrien. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter vention.com oder folgen Sie uns auf LinkedIn. *MachineMotion, MachineLogic, MachineCloud und Vention sind Marken von Vention Inc.
Über ABB Robotics
ABB (ABBN: SIX Swiss Ex) ABB ist ein Technologieführer in den Bereichen Elektrifizierung und Automatisierung und ermöglicht eine nachhaltigere und ressourceneffizientere Zukunft. Die Lösungen des Unternehmens verbinden technisches Know-how und Software, um die Herstellung, Bewegung, Stromversorgung und Bedienung von Dingen zu optimieren. Aufbauend auf über 140 Jahren Spitzenleistung engagieren sich die mehr als 105.000 Mitarbeiter von ABB dafür, Innovationen voranzutreiben, die den industriellen Wandel beschleunigen. www.abb.com
ABB Robotics & Discrete Automation ist als einer der weltweit führenden Anbieter von Robotik und Maschinenautomatisierung das einzige Unternehmen mit einem umfassenden und integrierten Portfolio, das Roboter, autonome mobile Roboter und Maschinenautomatisierungslösungen umfasst, die von unserer wertschöpfenden Software entwickelt und orchestriert werden. Wir helfen Unternehmen aller Größen und Branchen – von der Automobilindustrie über die Elektronik bis hin zur Logistik –, widerstandsfähiger, flexibler und effizienter zu werden. ABB Robotics & Discrete Automation unterstützt Kunden beim Übergang zur vernetzten und kollaborativen Fabrik der Zukunft. Der Geschäftsbereich beschäftigt rund 11.000 Mitarbeiter an über 100 Standorten in etwa 53 Ländern. go.abb/robotics
Große Unternehmen holen bei DIY-Automatisierung auf
Montreal/Berlin, 5. Juni 2024. Das Technologieunternehmen Vention hat in einer Studie analysiert, wie Unternehmen ihre Produktion selbstständig automatisieren. Kleine Unternehmen sind Trendsetter in der Do-it-yourself (DIY)-Automatisierung, doch große Unternehmen holen auf. Die Studie basiert auf anonymisierten Daten von weltweit über 1.400 Firmennutzern der Manufacturing Automation Platform (MAP) von Vention.
Zum zweiten Mal veröffentlicht Vention die jährliche Studie „The State of DIY Industrial Automation“. Der Fokus liegt auf der Do-it-yourself (DIY)-Automatisierung, die es Herstellern unterschiedlicher Größe ermöglicht, ihre Produktion mithilfe modernster Technologien selbstständig zu automatisieren.

Für die Studie hat Vention das Nutzerverhalten seiner Firmenkunden auf der Vention Cloud Plattform MAP von Januar bis Dezember 2023 ausgewertet. Ziel war es, den aktuellen Stand der DIY-Automatisierung in Unternehmen zu erfassen und zu erläutern, wie sie den DIY Ansatz für die Konzeption, Integration und den Betrieb von Automatisierungskomponenten, wie z.B. Roboterzellen oder Cobot-Palettierern, nutzen.
„Der Trend zur DIY-Automatisierung setzt sich in diesem Jahr fort“, sagt Etienne Lacroix, CEO von Vention. „Ein Treiber ist der Fachkräftemangel, der sich zunehmend bemerkbar macht. Die Frage, wie die Produktion schnell und kostengünstig automatisiert werden kann, beschäftigt aktuell viele Unternehmen. Wir sehen, dass insbesondere kleine Unternehmen selbstständig automatisieren. Doch im Vergleich zum letzten Jahr steigt die Zahl der großen Unternehmen, die DIY-Automatisierung einsetzen, deutlich.“
Die wichtigsten Erkenntnisse der Studie:
1. Kleine („Small“, < 200 Mitarbeiter (MA)) und mittlere Unternehmen („Medium“, < 2.000 MA) waren im Jahr 2023 mit einem Anteil von 48 % bzw. 17 % die führenden Nutzer von Automatisierungssystemen auf MAP. Allerdings sahen sich kleine Unternehmen im Jahr 2023 mit schwierigeren wirtschaftlichen Bedingungen konfrontiert. Infolgedessen kam es in diesem Segment zu einem Rückgang von 12 % im Vergleich zum Vorjahr (s. Studie, S. 8).
2. Große Unternehmen („Large“, < 10.000 MA) sowie der akademische und staatliche Forschungssektor („Academia & Gov Research“) haben bei der Nutzung des DIY-Ansatzes auf MAP deutlich zugelegt (+ 10 % bzw. + 4 %). Die Plattformtechnologie machte im vergangenen Jahr erhebliche Fortschritte und bietet dadurch mehr Möglichkeiten für Hochdurchsatzprojekte, die herkömmlicherweise mit größeren Herstellern bzw. Nutzern verbunden sind (s. Studie, S. 8).
3. Im Jahr 2023 haben sehr große Unternehmen („Enterprise“, > 10.000 MA) den DIY-Ansatz häufiger in ihren Fabrikhallen genutzt als jeder andere Sektor. Entsprechend ist die Anzahl der mit MAP realisierten Projekte in diesem Segment gestiegen – von durchschnittlich 4,1 im Jahr 2022 auf 4,9 Projekte im Jahr 2023 (s. Studie, S. 11).
4. Projekte mit Maschinenbedienungsanwendungen wurden im Jahr 2023 auf MAP am schnellsten realisiert. Dies ist wahrscheinlich darauf zurückzuführen, dass es angesichts des anhaltenden Arbeitskräftemangels für die Unternehmen schwierig ist, Personal zu rekrutieren. Da die CNC-Integration durch die jüngsten Innovationen leichter zugänglich geworden ist, sind Hersteller mehr denn je bestrebt, schnell automatisierte Maschinenbedienungsanwendungen einzuführen (s. Studie, S. 24).
5. Nach zwei Jahren mit Rekordverkäufen (2021 und 2022) meldete die Association for Advancing Automation (A3) für 2023 einen deutlichen Rückgang der Roboterverkäufe in Nordamerika um 30 %. Demgegenüber verzeichneten die Robotereinsätze auf MAP sowohl 2022 als auch 2023 einen bemerkenswerten Anstieg. Im Jahr 2023 wuchsen die Robotereinsätze auf MAP um etwa 40 % (s. Studie, S. 26).
Die vollständige Studie in Englisch finden Sie hier.
United Robotics Group presents new modular uLink series for retail, warehouse logistics and production
- At VivaTech 2024, the United Robitics Group (URG) will be showing the new product in action – together with other robots from the URG fleet, which are fully adapted to the needs of retailers.
- uLink is a highly flexible, versatile platform for rapid adaptation and support in logistics and automation.
- uLink is the first URG solution with an open API for seamless integration with operating systems and greater operational flexibility.
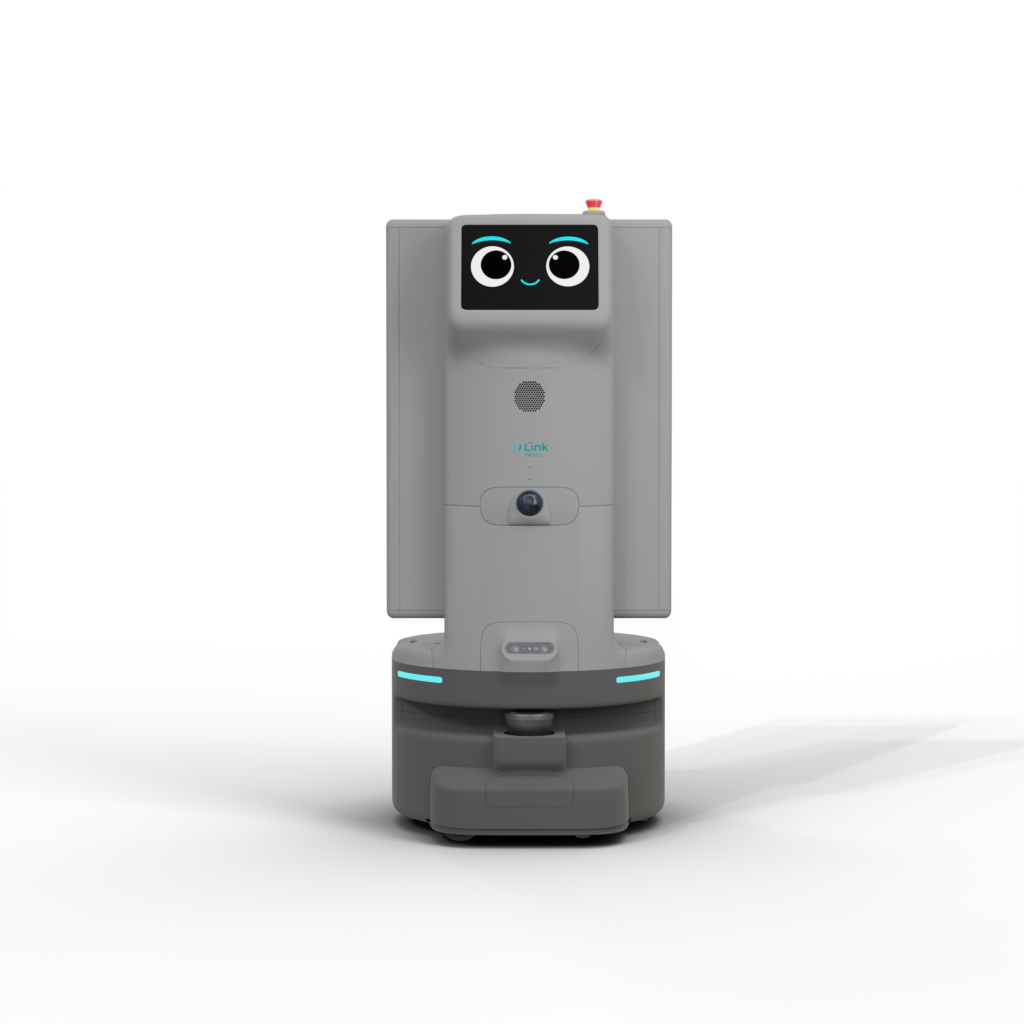

Paris/Bochum, May 22, 2024 – At VivaTech in Paris, the United Robotics Group will be presenting its new service robots from the uLink series for the first time, which are characterized by easy integration, flexible customization and individual extensions. They are suitable for use in retail, warehouse logistics and manufacturing. As the European market leader for service robotics solutions, URG is expanding its CobiotX portfolio worldwide with the latest Cobiot for integrated workflows in the aforementioned segments. The modular platform fits seamlessly into the respective workflows and can be expanded with industry-standard accessories. uLink is designed to simplify operations and increase safety and efficiency in various environments. The unique combination of features sets new standards in the industry – from modular design and open API to 3D LiDAR-based navigation and real-time operational data visualization.
uLink is equipped with IDE, SDK and fleet management tools and allows the seamless integration and control of various components such as LiDARS, engines or sensors. Thanks to powerful software functions for configuring and managing robot applications, as well as sensors and accessories, the robot can easily handle various logistics challenges in trade and warehousing, which vary depending on the industry, company size and automation requirements. The uLink accessory interface is also modular, so that the usable area can carry a payload of up to 60 kg. The SEER navigation control allows deliveries in a predefined area of up to 400,000 m².
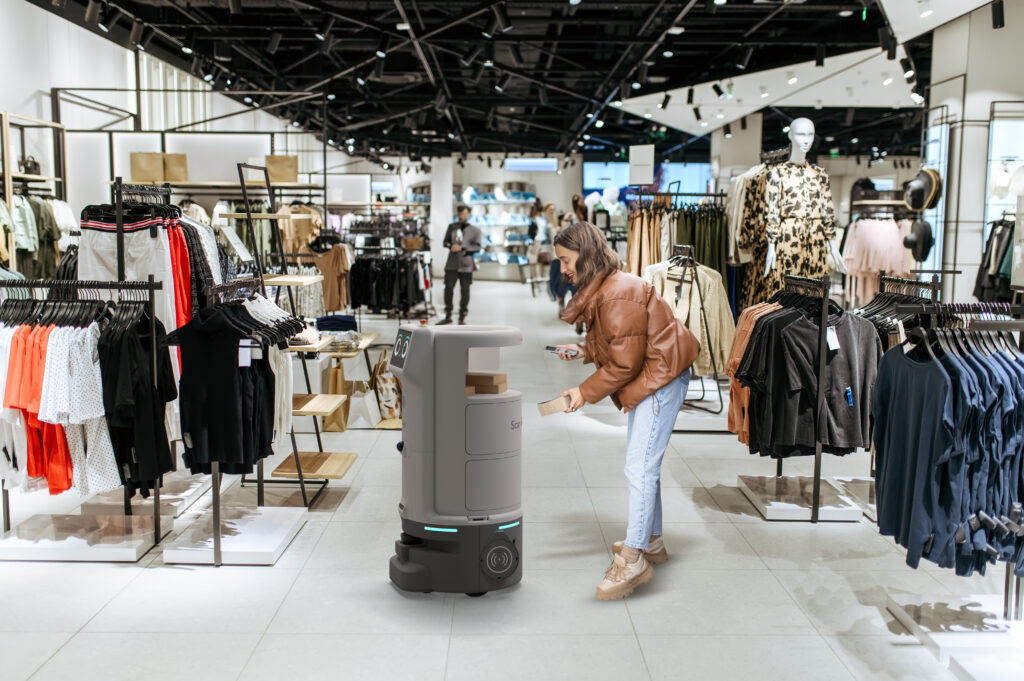

With the help of the plug-and-play mechanism, other accessories such as a locker for Click & Collect or confidential deliveries, a pegboard for the delivery of tools and spare parts, and trays for transporting stock can be integrated into the platform. In addition, partner integrators can develop new accessories to meet specific requirements.
„The retail and logistics sector has been undergoing a profound transformation for years, related to the growth of e-commerce, automation and the shortage of skilled workers in the value chain. Whether it’s shelf replenishers or water-spiders, i.e. those responsible for inventory in warehouses or production: it is important to support the players and offer solutions that meet their specific needs,“ explains Thomas Linkenheil, Co-CEO of the United Robotics Group. „In a highly competitive sector, consumers want a fast and personalized service. Our new logistics solution enables service providers to offer up-to-date customer service without long searches in the warehouse or tedious processes that can cost time and affect customer business.“
First Cobiot with an open API for connectivity and flexibility
Like all CobiotX solutions from the United Robotics Group, uLink is also equipped with a particularly user-friendly user interface. It is based on the no-code principle and enables users without robotics knowledge to quickly integrate into daily operations. In addition, uLink has an open API platform. This allows the solution to communicate with existing operations and other connected systems such as automatic doors or elevators, and also work with other robots and automated guided vehicles such as AMRs and AGVs.
With the launch of uLink, United Robotics Group is expanding its range of robotics solutions for logistics, warehouse management and industrial manufacturing. The robot is intended to be used in retail and logistics environments such as department stores, supermarkets, warehouses and fulfillment centers, but also factories and production facilities as well as airports and healthcare facilities.
The robot is equipped with 3D LiDAR and PL LiDAR systems for maximum precision in mobility. The platform can immediately register changes in the environment such as certain movements or people or machines and react accordingly. It is connected to an online dashboard that facilitates both workflow management and quick decisions between front- and back-of-house teams.
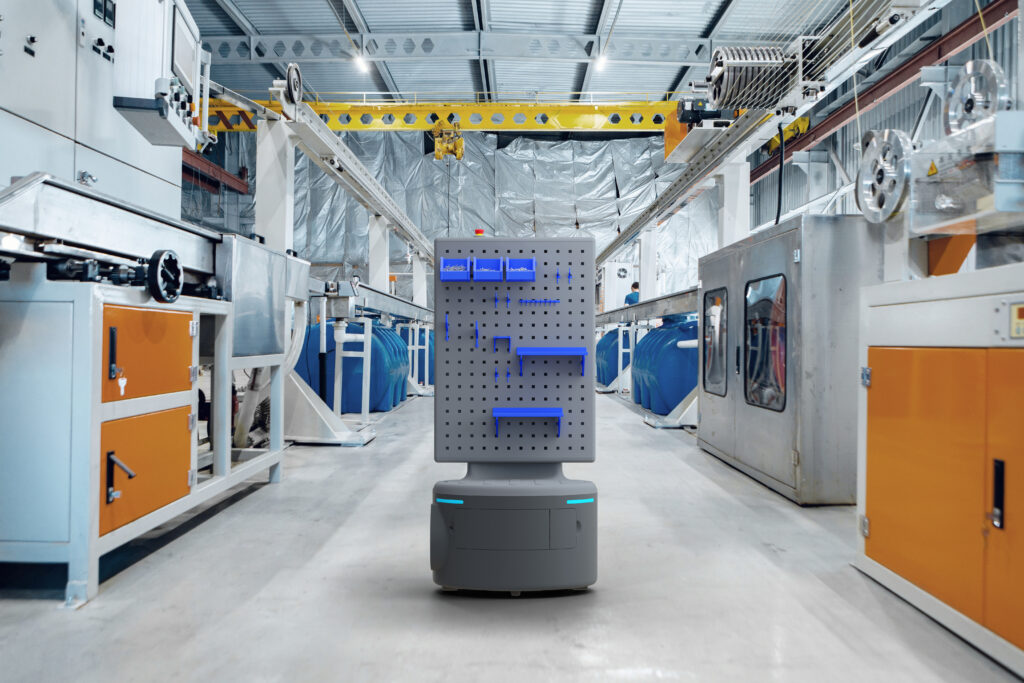

uLink has a long battery life of up to 14 hours on a single charge. In addition, the solution has an intelligent, wireless charging function that was developed with a well-known German battery manufacturer. This allows it to automatically return to the charging station between individual operations. The robot complies with the highest security and privacy standards, including the EU’s Performance Level D Machinery Directive and GDPR regulations.
uLink, along with United Robotics Group’s logistics and warehouse management fleet, including RBWatcher and MobilePalletizer, will be on display at the company’s VivaTech booth (Hall 1, Booth G18) in Paris from May 22-25.
uLink can be rented via the RaaS (Robot as a Service) model of the United Robotics Group from 699 euros / month or purchased for 19,900 euros.

Exploring Elephant Robotics LIMO Cobot
1. Introduction:
This article primarily introduces the practical application of LIMO Cobot by Elephant Robotics in a simulated scenario. You may have seen previous posts about LIMO Cobot’s technical cases, A[LINK], B[LINK]. The reason for writing another related article is that the original testing environment, while demonstrating basic functionality, often appears overly idealized and simplified when simulating real-world applications. Therefore, we aim to use it in a more operationally consistent environment and share some of the issues that arose at that time.
2. Comparing the Old and New Scenarios:
First, let’s look at what the old and new scenarios are like.
Old Scenario: A simple setup with a few obstacles, relatively regular objects, and a field enclosed by barriers, approximately 1.5m*2m in size.
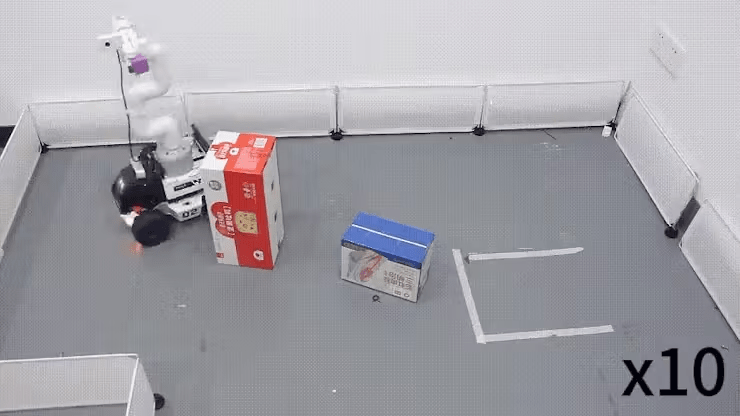
New Scenario: The new scenario contains a wider variety of obstacles of different shapes, including a hollowed-out object in the middle, simulating a real environment with road guidance markers, parking spaces, and more. The size of the field is 3m*3m.
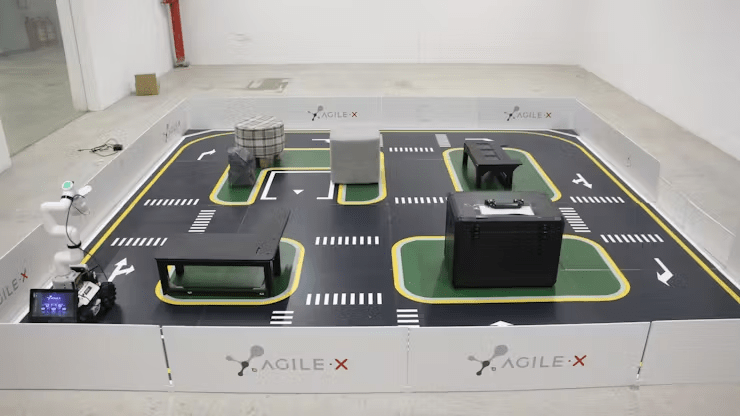
The change in environment is significant for testing and demonstrating the comprehensiveness and applicability of our product.
3. Analysis of Practical Cases:
Next, let’s briefly introduce the overall process.
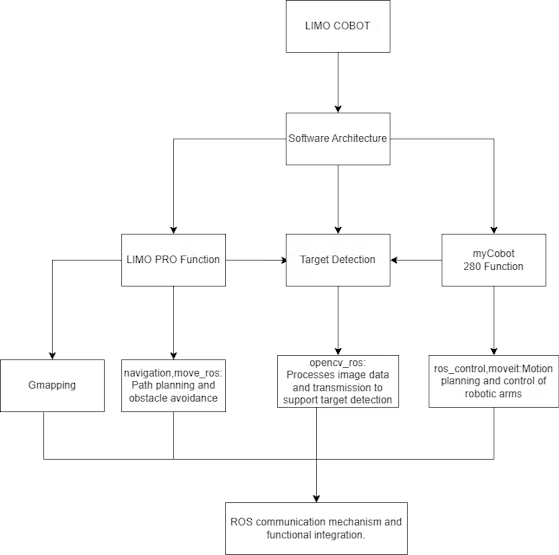
The process is mainly divided into three modules: one is the functionality of LIMO PRO, the second is machine vision processing, and the third is the functionality of the robotic arm. (For a more detailed introduction, please see the previous article [link].)
LIMO PRO is mainly responsible for SLAM mapping, using the gmapping algorithm to map the terrain, navigate, and ultimately achieve the function of fixed-point patrol.
myCobot 280 M5 is primarily responsible for the task of grasping objects. A camera and a suction pump actuator are installed at the end of the robotic arm. The camera captures the real scene, and the image is processed by the OpenCV algorithm to find the coordinates of the target object and perform the grasping operation.
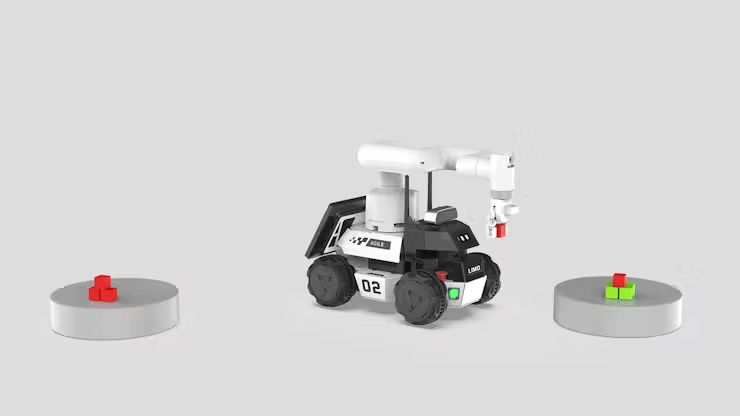
Overall process:
1. LIMO performs mapping.⇛
2. Run the fixed-point cruising program.⇛
3. LIMO goes to point A ⇛ myCobot 280 performs the grasping operation ⇒ goes to point B ⇛ myCobot 280 performs the placing operation.
4. ↺ Repeat step 3 until there are no target objects, then terminate the program.
Next, let’s follow the practical execution process.
Mapping:
First, you need to start the radar by opening a new terminal and entering the following command:
roslaunch limo_bringup limo_start.launch pub_odom_tf:=falseThen, start the gmapping mapping algorithm by opening another new terminal and entering the command:
roslaunch limo_bringup limo_gmapping.launchAfter successful startup, the rviz visualization tool will open, and you will see the interface as shown in the figure.
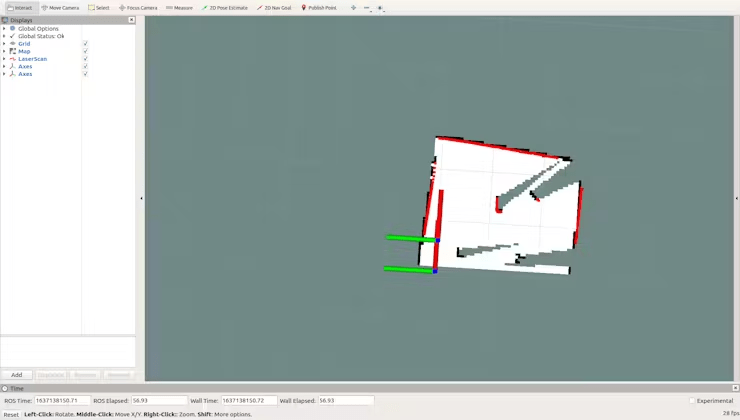
At this point, you can switch the controller to remote control mode to control the LIMO for mapping.
After constructing the map, you need to run the following commands to save the map to a specified directory:
1. Switch to the directory where you want to save the map. Here, save the map to `~/agilex_ws/src/limo_ros/limo_bringup/maps/`. Enter the command in the terminal:
cd ~/agilex_ws/src/limo_ros/limo_bringup/maps/2. After switching to `/agilex_ws/limo_bringup/maps`, continue to enter the command in the terminal:
rosrun map_server map_saver -f map1
This process went very smoothly. Let’s continue by testing the navigation function from point A to point B.
Navigation:
1. First, start the radar by entering the following command in the terminal:
roslaunch limo_bringup limo_start.launch pub_odom_tf:=false2. Start the navigation function by entering the following command in the terminal:
roslaunch limo_bringup limo_navigation_diff.launchUpon success, this interface will open, displaying the map we just created.
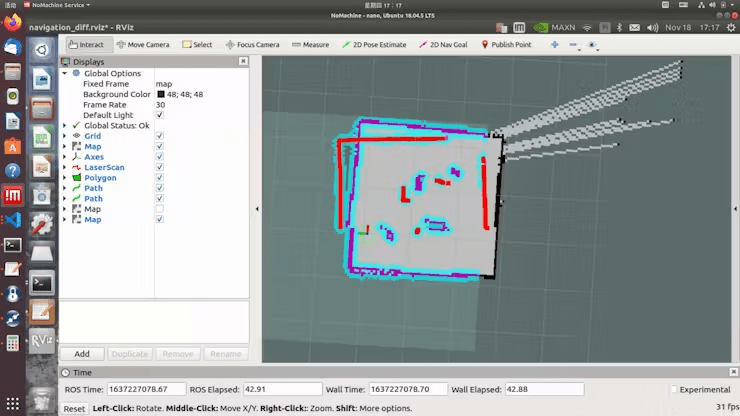
Click on „2D Pose Estimate, “ then click on the location where LIMO is on the map. After starting navigation, you will find that the shape scanned by the laser does not overlap with the map. You need to manually correct this by adjusting the actual position of the chassis in the scene on the map displayed in rviz. Use the tools in rviz to publish an approximate position for LIMO. Then, use the controller to rotate LIMO, allowing it to auto-correct. When the shape of the laser scan overlaps with the shapes in the map’s scene, the correction is complete, as shown in the figure where the scanned shape and the map overlap.
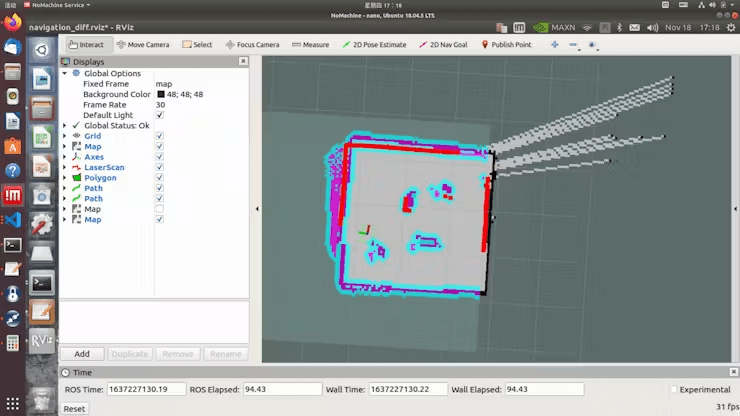
Click on „2D Nav Goal“ and select the destination on the map for navigation.
The navigation test also proceeds smoothly.
Next, we will move on to the part about the static robotic arm’s grasping function.
Identifying and Acquiring the Pose of Aruco Codes
To precisely identify objects and obtain the position of the target object, we processed Aruco codes. Before starting, ensure the specific parameters of the camera are set.
Initialize the camera parameters based on the camera being used.
def __init__(self, mtx: np.ndarray, dist: np.ndarray, marker_size: int):
self.mtx = mtx
self.dist = dist
self.marker_size = marker_size
self.aruco_dict = cv2.aruco.Dictionary_get(cv2.aruco.DICT_6X6_250)
self.parameters = cv2.aruco.DetectorParameters_create()Then, identify the object and estimate its pose to obtain the 3D position of the object and output the position information.
def estimatePoseSingleMarkers(self, corners):
"""
This will estimate the rvec and tvec for each of the marker corners detected by:
corners, ids, rejectedImgPoints = detector.detectMarkers(image)
corners - is an array of detected corners for each detected marker in the image
marker_size - is the size of the detected markers
mtx - is the camera matrix
distortion - is the camera distortion matrix
RETURN list of rvecs, tvecs, and trash (so that it corresponds to the old estimatePoseSingleMarkers())
"""
marker_points = np.array([[-self.marker_size / 2, self.marker_size / 2, 0],
[self.marker_size / 2, self.marker_size / 2, 0],
[self.marker_size / 2, -self.marker_size / 2, 0],
[-self.marker_size / 2, -self.marker_size / 2, 0]], dtype=np.float32)
rvecs = []
tvecs = []
for corner in corners:
retval, rvec, tvec = cv2.solvePnP(marker_points, corner, self.mtx, self.dist, False,
cv2.SOLVEPNP_IPPE_SQUARE)
if retval:
rvecs.append(rvec)
tvecs.append(tvec)
rvecs = np.array(rvecs)
tvecs = np.array(tvecs)
(rvecs - tvecs).any()
return rvecs, tvecsThe steps above complete the identification and acquisition of the object’s information, and finally, the object’s coordinates are returned to the robotic arm to execute the grasping.
Robotic Arm Movement and Grasping Operation
Based on the position of the Aruco marker, calculate the target coordinates the robotic arm needs to move to and convert the position into a coordinate system suitable for the robotic arm.
def homo_transform_matrix(x, y, z, rx, ry, rz, order="ZYX"):
rot_mat = rotation_matrix(rx, ry, rz, order=order)
trans_vec = np.array([[x, y, z, 1]]).T
mat = np.vstack([rot_mat, np.zeros((1, 3))])
mat = np.hstack([mat, trans_vec])
return matIf the Z-axis position is detected as too high, it will be corrected:
if end_effector_z_height is not None:
p_base[2] = end_effector_z_heightAfter the coordinate correction is completed, the robotic arm will move to the target position.
# Concatenate x, y, z, and the current posture into a new array
new_coords = np.concatenate([p_base, curr_rotation[3:]])
xy_coords = new_coords.copy()Then, control the end effector’s API to suction the object.
The above completes the respective functions of the two robots. Next, they will be integrated into the ROS environment.
#Initialize the coordinates of point A and B
goal_1 = [(2.060220241546631,-2.2297520637512207,0.009794792000444471,0.9999520298742676)] #B
goal_2 = [(1.1215190887451172,-0.002757132053375244,-0.7129997613218174,0.7011642748707548)] #A
#Start navigation and link the robotic arm
map_navigation = MapNavigation()
arm = VisualGrasping("10.42.0.203",9000)
print("connect successful")
arm.perform_visual_grasp(1,-89)
# Navigate to location A and perform the task
for goal in goal_1:
x_goal, y_goal, orientation_z, orientation_w = goal
flag_feed_goalReached = map_navigation.moveToGoal(x_goal, y_goal, orientation_z, orientation_w)
if flag_feed_goalReached:
time.sleep(1)
# executing 1 grab and setting the end effector's Z-axis height to -93.
arm.unload()
print("command completed")
else:
print("failed")
4. Problems Encountered
Mapping Situation:
When we initially tried mapping without enclosing the field, frequent errors occurred during navigation and localization, and it failed to meet our requirements for a simulated scenario.
Navigation Situation:
In the new scenario, one of the obstacles has a hollow structure.

During navigation from point A to point B, LIMO may fail to detect this obstacle and assume it can pass through, damaging the original obstacle. This issue arises because LIMO’s radar is positioned low, scanning only the empty space. Possible solutions include adjusting the radar’s scanning range, which requires extensive testing for fine-tuning, or adjusting the radar’s height to ensure the obstacle is recognized as impassable.
Robotic Arm Grasping Situation:
In the video, it’s evident that our target object is placed on a flat surface. The grasping did not consider obstacle avoidance for the object. In the future, when setting special positions for grasping, this situation needs to be considered.
5. Conclusion
Overall, LIMO Cobot performed excellently in this scenario, successfully meeting the requirements. The entire simulated scenario covered multiple core areas of robotics, including motion control of the robotic arm, path planning, machine vision recognition and grasping, and radar mapping navigation and fixed-point cruising functions of the mobile chassis. By integrating these functional modules in ROS, we built an efficient automated process, showcasing LIMO Cobot’s broad adaptability and advanced capabilities in complex environments.
Credits

