Schlagwort-Archive: Robotics
Men in Blech statt Mann am Band: Ambitionierte Ziele für die Massenfertigung von Humanoiden
Die Entwicklung im Bereich humanoider Roboter schreitet mit einer beeindruckenden Dynamik voran. Das Kräftemessen zwischen den USA und China sowie Fortschritte im Bereich der KI, der Batterieentwicklung und der Mechanik befeuern die Performance der Men in Blech. Auf der automatica wird deutlich werden, wie weit diese Entwicklung bereits fortgeschritten ist.
Was die Humanoiden im Reich der Mitte zu leisten im Stande sind, konnten sie jüngst bei einem Halbmarathon in Peking unter Beweis stellen. Auf der gut 21 Kilometer langen Laufstrecke traten rund 20 humanoide Roboter erfolgreich gegen Menschen an. Mit dem Wettlauf hat die Volksrepublik ihr Ziel erreicht, sich als einer der führenden Anbieter menschenähnlicher Roboter zu präsentieren.
Zwei Beine ermöglichen maximale Flexibilität und Mobilität
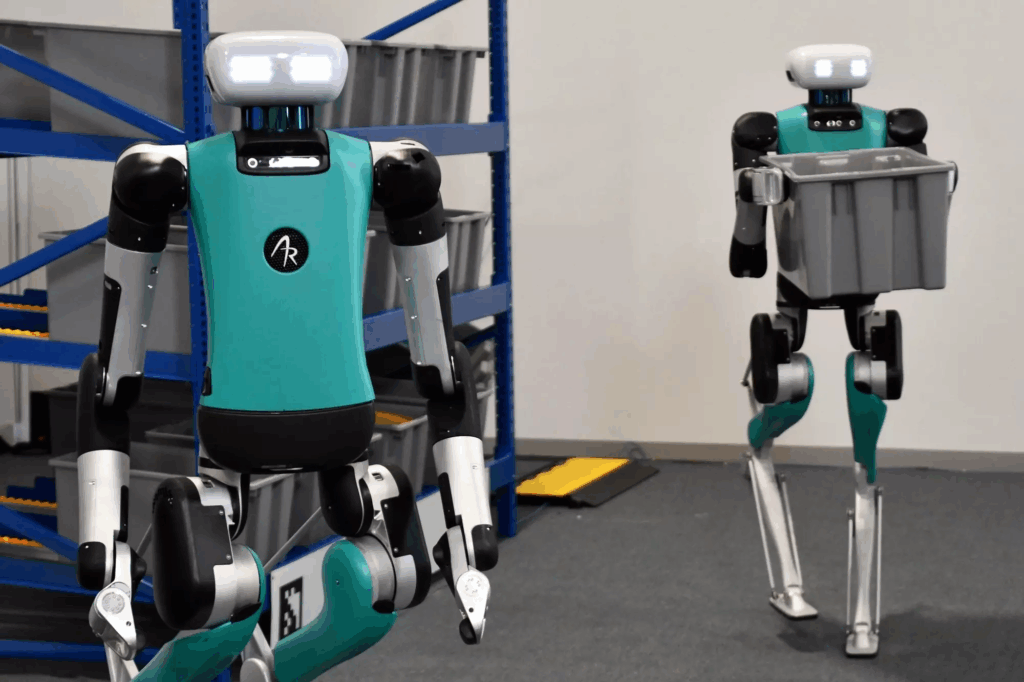
Aber gerade ein Halbmarathon führt zwangsläufig zu einer oft gestellten Frage: Warum haben Humanoide Beine? Wäre es nicht effizienter, Radantriebe zu nutzen? Weshalb die meisten Humanoiden dennoch mit zwei Beinen ausgestattet sind, erklärt Jonathan Hurst, Chief Robot Officer bei Agility Robotics: „Zweibeinige Roboter sind für die Koexistenz mit dem Menschen konzipiert und bieten eine Vielseitigkeit und Mobilität, die über das hinausgeht, was Radantriebe leisten können. Durch den Einsatz von Beinen können sich Humanoide an komplexe Umgebungen anpassen, Treppen steigen, Bordsteine überwinden und ein breites Aufgabenspektrum erfüllen.“ Digit, der Humanoide von Agility, ist bereits in vielen Applikationen vorwiegend in Logistikzentren im Einsatz wie beispielsweise bei amazon und GXO Logistics. Mit einer Körpergröße von 1,75 m und einem Gewicht von etwa 64 kg kann Digit komplexe Aufgaben wie das Heben von Lasten mit einem Gewicht von bis zu 16 kg ausführen. Und dank fortschrittlicher Sensorik, darunter LIDAR und Kameras, kann er auch selbstständig navigieren. Über Digit und die Frage, wie Humanoide Lücken in der Automatisierungskette schließen können, spricht auch Melonee Wise, Chief Product Officer bei Agility Robotics, auf dem automatica Forum in Halle A5. Anwendungsorientiert referiert direkt im Anschluss Carolin Richter, Head of Next Generation Robotics bei der BMW Group, über die Erfahrungen des Unternehmens mit konkreten Praxiseinsätzen von Humanoiden.
USA mit Vorreiterrolle in der Technologieentwicklung
Wie Digit kommen weitere hochentwickelte Humanoide aus den USA, darunter Atlas von Boston Dynamics, Optimus von Tesla, Figure 01 und 02 von Figure AI und Apollo von Apptronik. Sie alle arbeiten bereits in Piloteinsätzen in der Automobilindustrie. „Wir entwickeln die fortschrittlichsten und leistungsfähigsten humanoiden Roboter der Welt, die den Menschen auf sinnvolle und revolutionäre Weise zur Seite stehen“, sagt Jeff Cardenas, CEO und Mitbegründer von Apptronik. Aber viel Kapital und potente Mitstreiter sind nötig, um diese Entwicklungen voranzutreiben. Gerade konnte Apptronik eine Finanzierungsrunde von mehr als 350 Millionen Dollar abschließen. Kooperationen mit der NASA, NVIDIA, Google DeepMind und auf der Anwenderseite mit Mercedes-Benz und GXO Logistics sollen sicherstellen, dass Apptronik in diesem Zukunftsmarkt weiter ganz vorne mitspielen wird.
Deutschland mit Aufholbedarf bei humanoider Robotik
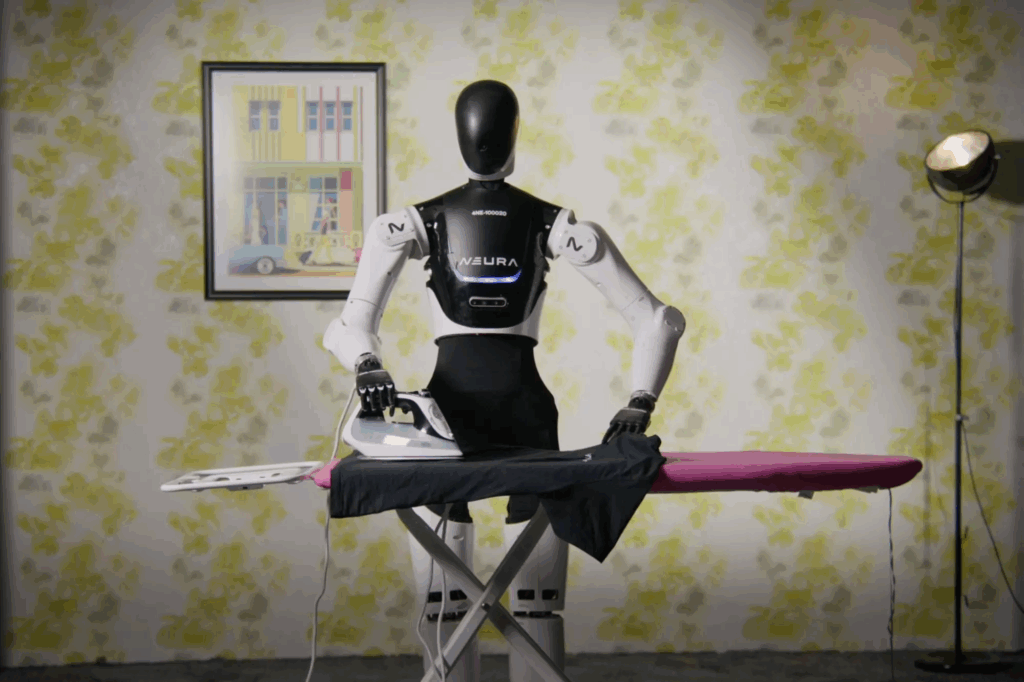
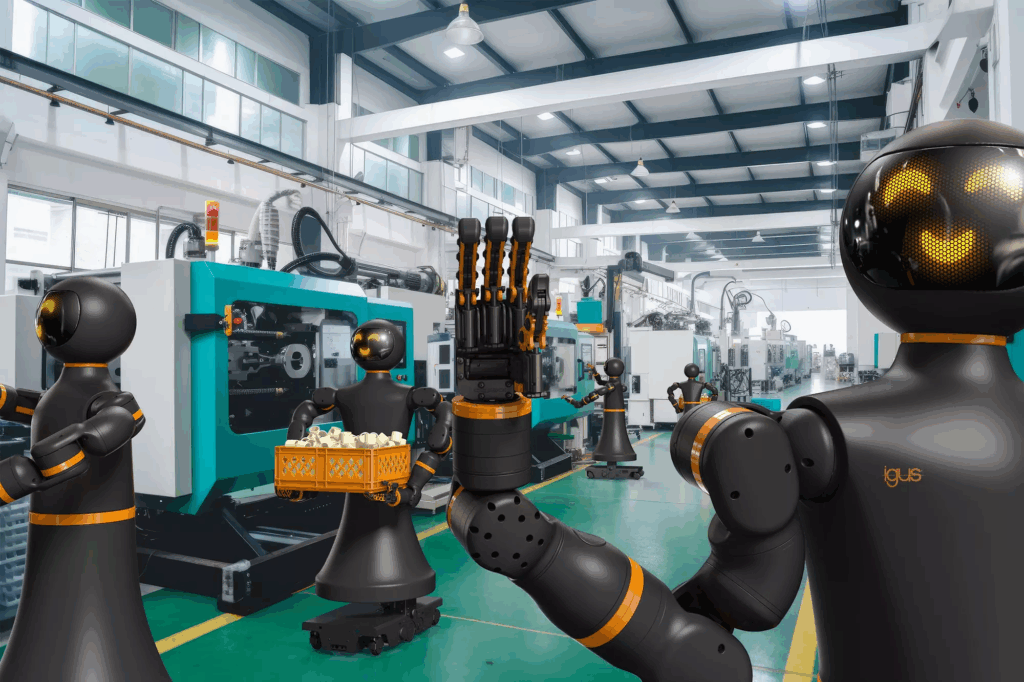
Zwar spielt Deutschland auf dem Weltmarkt für Humanoide keine Schlüsselrolle, dennoch belegt die automatica, dass es auch hier vielversprechende Entwicklungen gibt. Denn neben dem 4NE-1 von Neura Robotics, der bereits 2023 auf der automatica debütierte, werden dieses Jahr weitere Humanoide den Weg nach München finden. Einer von ihnen kommt aus Köln und hört auf den Namen „Iggy Rob“. Igus bietet seinen ersten humanoiden Roboter für knapp unter 50.000 Euro an. Möglich wird dies nach Herstellerangaben durch die Kombination aus hauseigenen Komponenten wie den ReBeL Cobots für die Roboterarme und der mobilen Basis ReBeL Move. Sein Einsatzspektrum reicht von der Assistenzrobotik über Fabrikautomation bis hin zu Bildung und Forschung. Igus will Iggy Rob im eigenen Unternehmen für die Automation von Spritzgießmaschinen nutzen.
© Messe München GmbH
Mit Spannung erwartet wird auch der Messeauftritt des Instituts für Robotik und Mechatronik des Deutschen Zentrums für Luft- und Raumfahrt. Hier forscht man intensiv an der Weiterentwicklung in der humanoiden Robotik. Die jüngsten Ergebnisse werden auf der automatica zu sehen sein. Aufhorchen lässt auch die jüngst geschlossene Kooperation des Instituts mit Siemens. „Diese strategische Partnerschaft ist ein weiteres Beispiel für Transfer von Robotiktechnologien aus der Raumfahrt in industrielle Anwendungen“, sagt Institutsleiter Alin Albu-Schäffer. „Die enge Vernetzung mit führenden deutschen Industriepartnern wie Siemens ist essenziell, um die Wettbewerbsfähigkeit der europäischen Robotik auch in der Zukunft, angesichts der rasanten Entwicklungen in USA und China, zu sichern.“
Humanoide Roboter: ein gigantischer Wachstumsmarkt
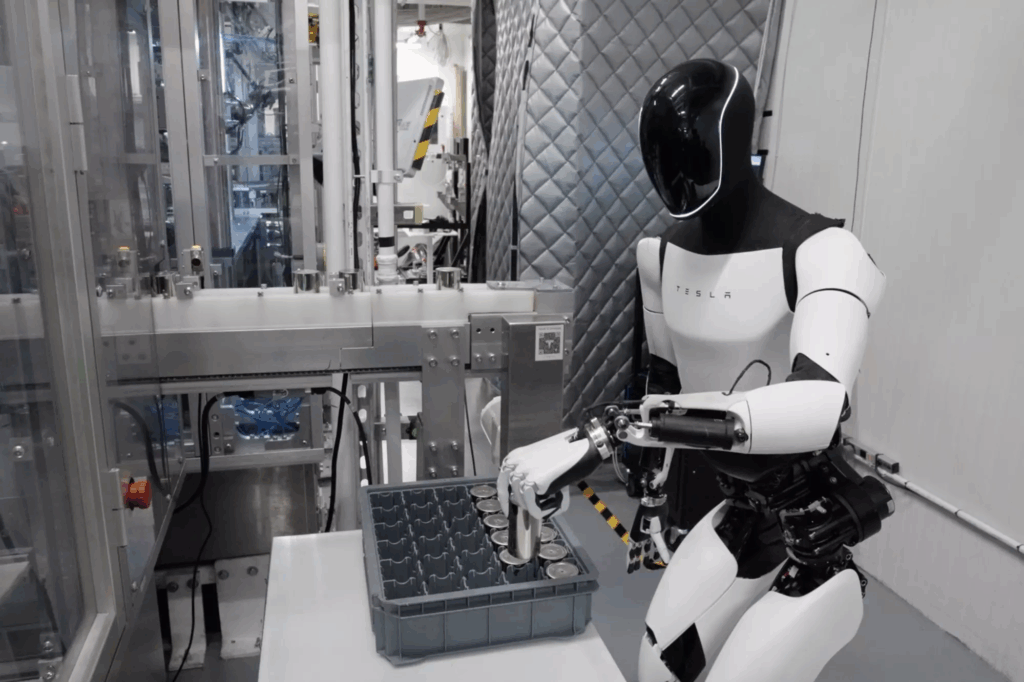
Tesla sieht sich mit seinem humanoiden Roboter Optimus als Technologieführer. Dieser bewegt sich elegant, ist schnell und besitzt eine hochflexible Fünffinger-Hand. Musk hält Einsätze im Haushalt oder in der Kinderbetreuung bald für möglich und auch Goldman Sachs sieht für den weltweiten Markt für Humanoide hohes Potential. Demnach könnte dieser bis 2035 auf 38 Milliarden US-Dollar steigen. Neben US-amerikanischen Unternehmen verfolgt auch die Volksrepublik ambitionierte Ziele und will innerhalb der nächsten drei Jahre zum Weltmarktführer im Bereich humanoider Roboter aufsteigen. Mittelfristig sollen in China fünf Prozent aller Jobs von Humanoiden übernommen lassen. Das würde dem Einsatz von rund 35 Millionen Einheiten entsprechen. Bereits heute sind in Chinas Unternehmen Humanoide von Unitree, AgiBot, Engine AI, Fourier oder Ubtech in unterschiedlichen Applikationen und Branchen im Einsatz.
Branchenprimus Unitree bringt als einer der ersten Hersteller weltweit mit dem G1 einen kleinen Humanoiden zum spektakulär niedrigen Preis auf den Markt. So soll die Basisversion des 1,3 Meter großen und 35 kg leichten G1 in China nur 16.000 Euro kosten, hierzulande werden dann daraus wohl eher knapp 30.000 Euro. Und je nach Ausbaustufe kann sich dieser Preis schnell mehr als verdoppeln. Das Interesse am G1 ist groß, wie Unitree-Marketingmanagerin Qian Yuqi verrät: „Es gibt bereits Bestellungen aus dem In- und Ausland. Zunächst dürften vor allem wissenschaftliche Forschungseinrichtungen unseren Roboter einsetzen, aber auch Industriebetriebe können sich vorstellen, G1 für einfache Arbeiten zu nutzen.“
Die Entwicklung zeigt: Die Zeit für Humanoide und damit für eine neue Ära der Automation ist gekommen. Dank KI sind sie bereits jetzt in der Lage, einen Teil der Aufgaben zu übernehmen, die bislang Menschen vorbehalten waren. Die automatica verspricht spannenden Einblicke, was Humanoide zu leisten im Stande sind und wie ihr Einsatz die Arbeitswelt beeinflussen kann.
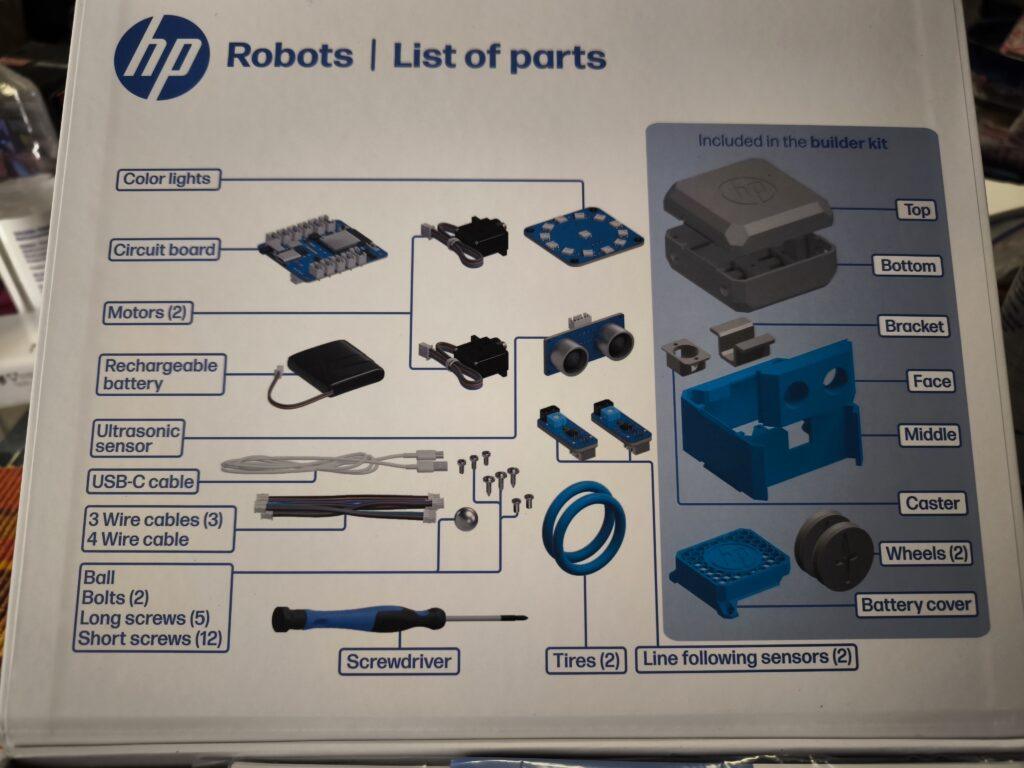
Creativity in motion: The modular robot Otto from HP Robots
The HP Robots Otto is a versatile, modular robot designed specifically for educational purposes. It offers students and teachers an exciting opportunity to immerse themselves in the world of robotics, 3D printing, electronics and programming. The robot was developed by HP as part of their robotics initiative and is particularly suitable for use in science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM) classes.
Key features of Otto:
- Modular design: Otto is a modular robot that allows students to build, program and customize it through extensions. This promotes an understanding of technology and creativity. The modular structure allows various components such as motors, sensors and LEDs to be added or replaced, which increases the learning curve for students.
- Programmability: The robot can be programmed with various programming languages, including block-based programming for beginners and Python and C++ for advanced programmers. This diversity allows students to continuously improve their coding skills and adapt to the complexity of the tasks.
- Sensors and functions: Equipped with ultrasonic sensors for obstacle detection, line tracking sensors and RGB LEDs, Otto offers numerous interactive possibilities. These features allow students to program complex tasks such as navigating courses or tracing lines. The sensors help to detect the environment and react accordingly.
- 3D printing and customizability: Students can design Otto’s outer parts themselves and produce them with a 3D printer. This allows for further personalization and customization of the robot. This creative freedom not only promotes technical understanding, but also artistic skills. Own parts can be designed and sensors can be attached to desired locations.

Educational approach:
Otto is ideal for use in schools and is aimed at students from the age of 8. Younger students can work under supervision, while older students from the age of 14 can also use and expand the robot independently. The kit contains all the necessary components to build a functioning robot, including motors, sensors, and a rechargeable battery.
Programming environments:
Otto is programmed via a web-based platform that runs on all operating systems. This platform offers different modes:
- Block-based programming: Similar to Scratch Jr., ideal for beginners. This visual programming makes it easier to get started in the world of programming and helps students understand basic concepts such as loops and conditions.
- Python: A Python editor is available for advanced users. Python is a popular language that works well for teaching because it is easy to read and write. Students can use Python to develop more complex algorithms and expand their programming skills.
- C++: Compatible with the Arduino IDE for users who have deeper programming knowledge. C++ offers a high degree of flexibility and allows students to access the hardware directly, allowing for their own advanced projects.
Expansion Kits:
In addition to the Starter Kit, there are several expansion kits. All expansion kits require the starter kit, as they are built on top of it.
Emote Expansion Kit:
- It includes components such as an LED matrix display, OLED display, and an MP3 player that allow the robot to display visual and acoustic responses.
- This kit is particularly suitable for creative projects where Otto should act as an interactive companion.
- The emote kit allows Otto to show emotions, mirror human interactions, and develop different personalities.
Sense Expansion Kit:
- With the Sense Kit, Otto can perceive its surroundings through various sensors.
- Included are sensors for temperature, humidity, light and noise as well as an inclination sensor. These enable a wide range of interactions with the environment.
- The kit is ideal for projects that focus on environmental detection and data analysis.
Interact Expansion Kit:
- The Interact kit expands Otto’s tactile interaction capability through modules such as push buttons, rotary knobs and accelerometers.
- It enables precise inputs and reactions, as well as measurement of acceleration.
- This kit is great for playful activities and interactive games.
Invent Expansion Kit:
- The Invent kit is specifically designed to encourage users‘ creativity. It allows the individual adaptation of Otto’s functionalities and design through 3D printing and additional modules as well as compatible clamping blocks.
- Users can design and print new accessories to make the robot unique.
- Equip Otto with legs and teach him to walk or make him fit for outdoor use off-road with chains.

Use in the classroom:
Otto comes with extensive resources developed by teachers. These materials help teachers design effective STEM lessons without the need for prior knowledge. The robot can be used both in the classroom and at home. The didactic materials include:
- Curricula: Structured lesson plans that help teachers plan and execute lessons.
- Project ideas and worksheets: A variety of projects that encourage students to think creatively and expand their skills.
- Tutorials and videos: Additional learning materials to help students better understand complex concepts.
Conclusion:
The HP Robots Otto is an excellent tool for fostering technical understanding and creativity in students. Thanks to its modular design and diverse programming options, it offers a hands-on learning experience in the field of robotics and electronics. Ideal for use in schools, Otto provides teachers with a comprehensive platform to accompany students on an exciting journey into the world of technology. In particular, Otto’s versatility through the 3D-printed parts and expansion packs offers the opportunity to build the personal learning robot.
Robots-Blog showing all the robots at Spielwarenmesse Nuremberg 2025
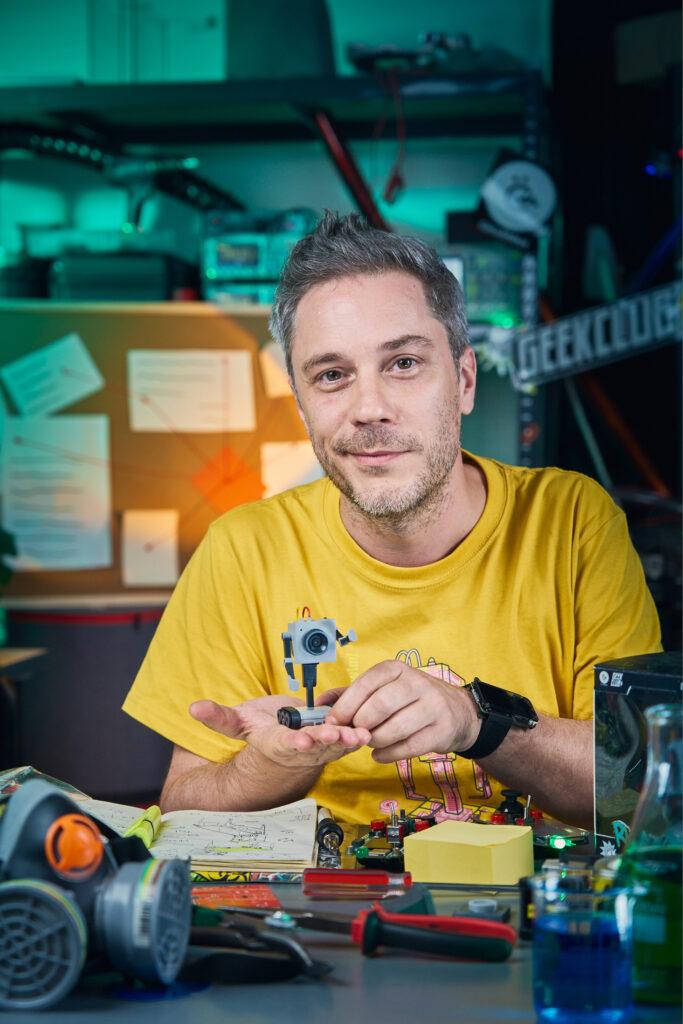
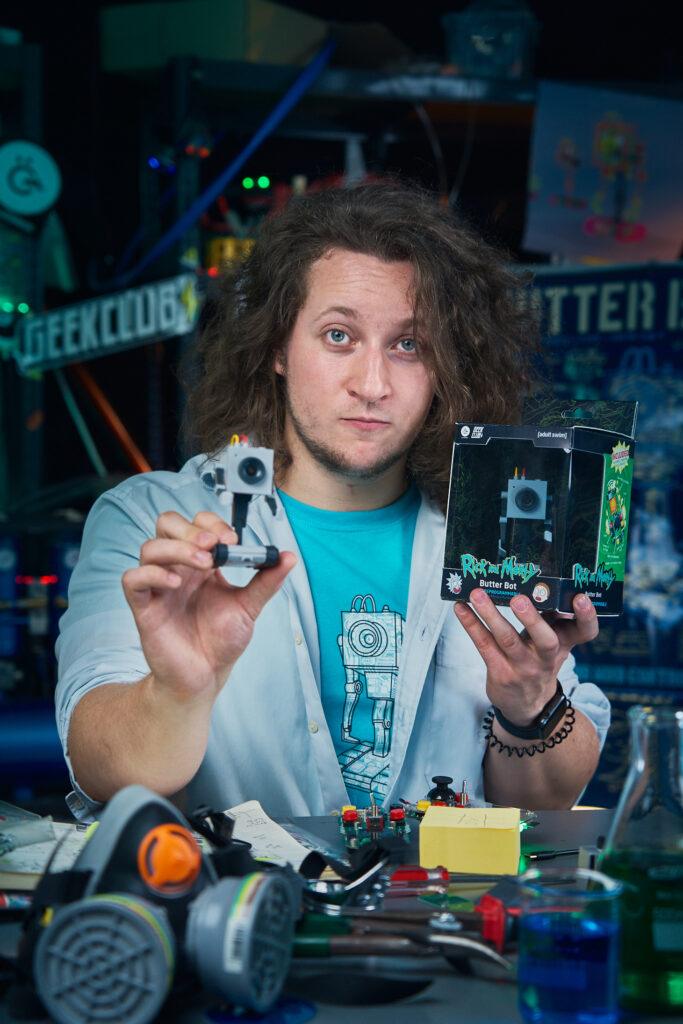
Geek Club and CircuitMess in Partnership with Warner Bros. Discovery Global Consumer Product Launch Rick and Morty™ Butter Bot
After a string of successful Kickstarter campaigns, Geek Club and CircuitMess have teamed up once again to launch an exciting new project: an AI-powered desk robot designed especially for Rick and Morty fans.
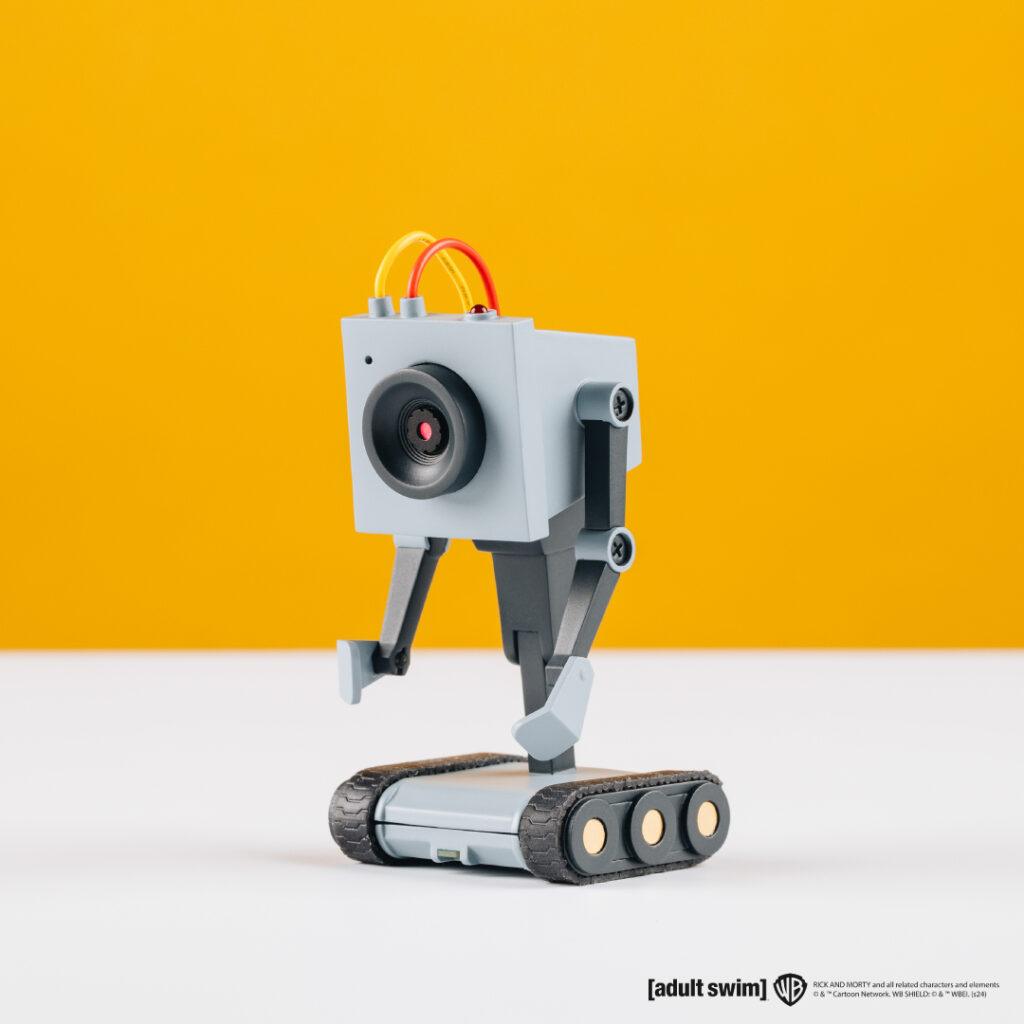
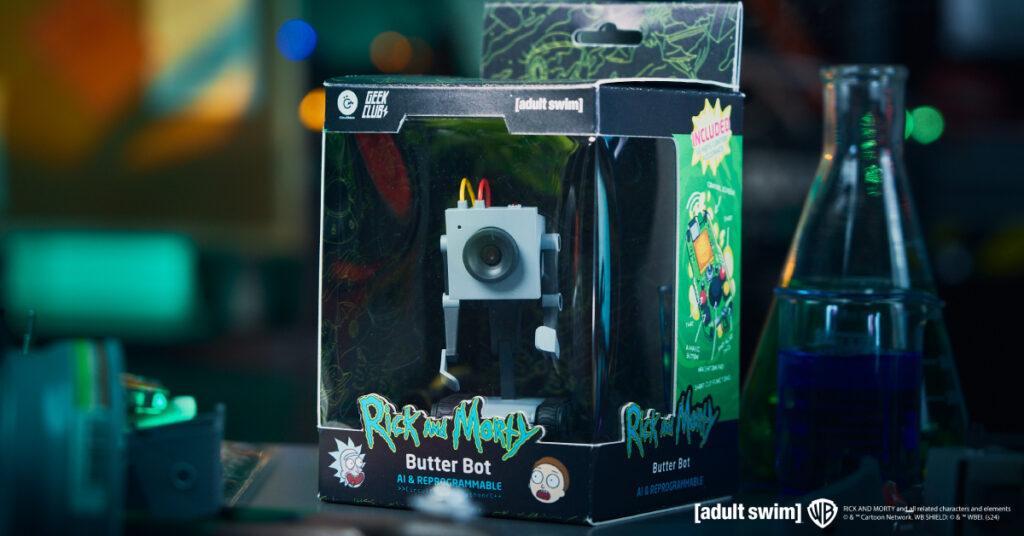
Zagreb, Croatia – November 2024 – Geek Club and CircuitMess are thrilled to announce the official launch of their Kickstarter campaign for the Butter Bot, a revolutionary AI-powered robot inspired by the one made famous in the popular Adult Swim series, Rick and Morty, and first seen in season 1 episode 9. This innovative product is officially licensed by Warner Bros. Discovery Global Consumer Products (WBDGCP), bringing the iconic Butter Bot to life in a way fans have never seen before.

From Screen to Reality: A Partnership That Is Bringing Butter Bot to Life
A shared love of Rick and Morty show between CircuitMess and Geek Club teams led to this project. Both companies saw an opportunity to bring a beloved character to life in a way that was both true to the show and technologically innovative. They chose the Butter Bot because of its iconic status and potential for interactive, educational, and entertaining applications. By turning a simple butter-passing robot into a multifunctional AI companion, they aimed to create a product that would resonate with fans and tech enthusiasts alike, merging humor and functionality seamlessly.

From Mars to Multiverse: The Next Chapter for CircuitMess and Geek Club
The collaboration was a logical union of the two companies after the massive success of the previous Kickstarter – NASA Perseverance AI-powered Mars Rover. Both companies create educational STEM DIY kits for kids and adults in order to make learning STEM skills easy and fun. While CircuitMess is focused primarily on toys, Geek Club’s products are always robot and space-themed.
„Partnering with WBDGCP on this project has been an exciting next step in our collaboration with Circtuit Mess, says Nico, co-founder of Geek Club, sharing his enthusiasm: “The Butter Bot is a testament to what happens when creativity, technology, and fandom collide. We’re excited to see the support and engagement from the community as we launch our Kickstarter campaign.“
Geek Club is an American company that specializes in designing and producing DIY robotics kits that educate their users on soldering and electronics. They focus primarily on space exploration and robotics, all to make learning engineering skills easy and fun for their young and adult audience.
Beyond Butter: Introducing the AI-Powered Butter Bot
The Butter Bot is not just a simple robot with the sole purpose of passing the butter, as originally in the show. It comes with a unique remote controller that allows for precise maneuvering of its movement while also providing a live feed from the bot’s camera. The interactive robot has advanced AI capabilities, making it a versatile companion in any setting.
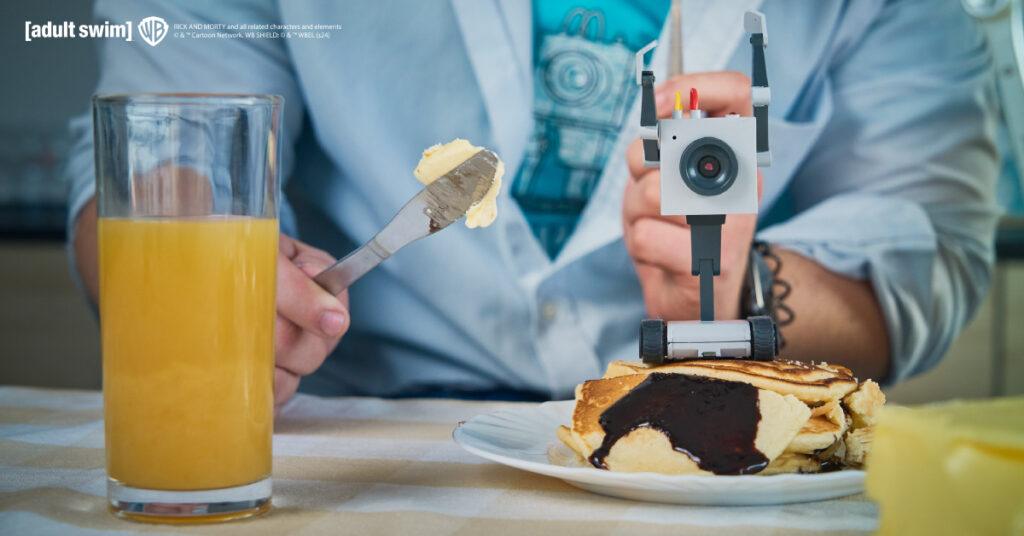

„Bringing the Butter Bot from Rick and Morty into the real world has been an incredible journey,” says Albert Gajšak, CEO of CircuitMess, expressing his excitement about the launch: “We’ve poured our hearts into creating a product that not only honors the original character but also adds a whole new level of interactivity and functionality. We can’t wait to see how fans will use and enjoy it.“
To this day, CircuitMess has developed numerous educational products that encourage kids and adults to create rather than just consume. They successfully delivered 7 Kickstarter campaigns and made thousands of geeks worldwide extremely happy. CircuitMess‘ kits are a unique blend of resources for learning about hardware and software in a fun and exciting way.
The Butter Bot Kickstarter campaign offers backers exclusive early-bird pricing and special rewards.
For more information and to back the project, visit the Butter Bot Kickstarter page here (https://www.kickstarter.com/projects/albertgajsak/rick-and-mortytm-butter-bot-an-ai-powered-desk-robot), or check out the Geek Club and CircuitMess websites to see all their other kits.
About Geek Club
Geek Club is a crew of designers and engineers led by co-founders Nicolas Deladerrière and Nikita Potrashilin. Their mission is to build electronic construction kits for curious minds in over 70 countries worldwide. They are most often inspired by NASA and other Space Agencies of the world and hope to push their fans’ minds further, strengthen their skills, and advance their knowledge of electronics and Space.
Their vision is to create a world of inventors for the next generation of technology with their space-themed STEM kits. Find out more at www.geekclub.com.
Nicolas Deladerrière, co-founder of Geek Club
Mail: [email protected]

About CircuitMess
CircuitMess is a technology startup founded in 2017 by Albert Gajšak and Tomislav Car after a successful Kickstarter campaign for MAKERbuino.
CircuitMess employs young, ambitious people and has recently moved to a new office in Croatia’s capital, Zagreb, searching for talented individuals who will help them create unique electronic products and bring technology to the crowd in a fun and exciting way. Find out more at www.circuitmess.com.
Albert Gajšak, co-founder and CEO of CircuitMess
Mail: [email protected]

About Rick and Morty
Rick and Morty is the Emmy® award-winning half-hour animated hit comedy series on Adult Swim that follows a sociopathic genius scientist who drags his inherently timid grandson on insanely dangerous adventures across the universe. Rick Sanchez is living with his daughter Beth’s family and constantly bringing her, his son-in-law Jerry, granddaughter Summer, and grandson Morty into intergalactic escapades.
Rick and Morty stars Ian Cardoni, Harry Belden, Sarah Chalke, Chris Parnell, and Spencer Grammer.
About Warner Bros. Discovery Global Consumer Products
Warner Bros. Discovery Global Consumer Products (WBDGCP), part of Warner Bros. Discovery’s Revenue & Strategy division, extends the company’s powerful portfolio of entertainment brands and franchises into the lives of fans around the world. WBDGCP partners with best-in-class licensees globally on award-winning toy, fashion, home décor and publishing programs inspired by the biggest franchises from Warner Bros.’ film, television, animation, and games studios, HBO, Discovery, DC, Cartoon Network, HGTV, Eurosport, Adult Swim, and more. With innovative global licensing and merchandising programs, retail initiatives, and promotional partnerships, WBDGCP is one of the leading licensing and retail merchandising organizations in the world.
Wandelbots presents NOVA: The world’s first agnostic operating system for robots
Dresden, November 6th, 2024 – Last night at its exclusive launch event in Dresden, Wandelbots unveiled the world’s first agnostic operating system specifically developed for industrial robotic automation. With NOVA, a new era of automation begins, setting new standards in efficiency, accessibility, and innovation.
„With NOVA, we are witnessing a new dawn in industrial automation,“ said Christian Piechnick, CEO of Wandelbots. „Just as Android revolutionized smartphones and Windows transformed the PC world, NOVA will make industrial robotics accessible to everyone and create new ways for software developers to commercialize.“
Carl Doeksen, Global Robotics / Automation Director for Abrasive Systems at 3M states: „At 3M, we collaborate with startups, to augment our innovation model. We’re proud to be part of Wandelbots‘ journey to democratize robotics. Today, the vast majority of the abrasive applications are still done manually. Wandelbots NOVA will lower the barrier for companies to automate these types of processes. With NOVA, users are empowered with the process know-how they need to select the right abrasive materials; they can easily input the parameters for their workpiece and specify the desired final state using a simple UI. For 3M, NOVA provides an opportunity—not only to equip end-users with the tools they need, but to make our extensive expertise in process technology more accessible.“
Modern Programming Languages and Vendor Independence
Wandelbots NOVA is the world’s first agnostic operating system for robots, designed to make robotics accessible to everyone. By supporting modern development tools like Python and JavaScript, NOVA empowers millions of developers to create and scale robotic applications with ease, reducing the complexity of automation. Following a Plan, Build, and Operate approach, NOVA simplifies the entire automation lifecycle with AI technologies at its core—from planning and simulation to deployment and scaling—ensuring continuous support throughout each phase. Its seamless integration with existing hardware allows businesses to leverage past investments while scaling across multiple robots and brands, without costly retooling—accelerating projects, lowering costs, and increasing flexibility. Wandelbots’ close collaboration with Microsoft and OpenAI ensures scalability and that the latest and greatest AI capabilities enhance NOVA’s feature set.

As a vendor-independent operating system, NOVA simplifies and optimizes the complex world of industrial robotics by integrating hardware components from various manufacturers and making them accessible to everyone using through a modern interface. Complex programming and inflexible automation landscapes are now things of the past. NOVA’s open API concept, unique user experience, and seamless integration of externally developed apps make it a versatile platform for both robot users and millions of software developers.
Proprietary and outdated programming languages, high operating costs, a lack of skilled labor, and closed ecosystems have so far prevented the full realization of robotics‘ enormous potential—especially in small- and medium-sized enterprises, where robotics is still a niche topic. NOVA, as a unified operating system, will significantly advance robotics by enabling easy programming and control of robots from different manufacturers without the need for specialized expertise. This reduces operating costs, speeds up innovation processes, and eliminates the dependence on hard-to-find skilled personnel. Especially for SMEs, where the current level of automation is still in the single digits, NOVA opens up entirely new perspectives.
An Open Ecosystem for Software Developers
Wandelbots NOVA is much more than just an operating system. It offers a unified user interface for all robot manufacturers and models. Software developers can access development tools, UI elements, standardized libraries, and sample applications through the dedicated developer portal. Using the Python-based programming language „Wandelscript,“ they can create innovative solutions for interacting with robots and share their experiences within the community specifically created for this purpose.
A New Era of Automation
The launch of NOVA marks a turning point. It opens up new opportunities for companies to leverage automation. In addition, software developers, who currently create apps or websites, can now unleash their creativity in a completely new industry.
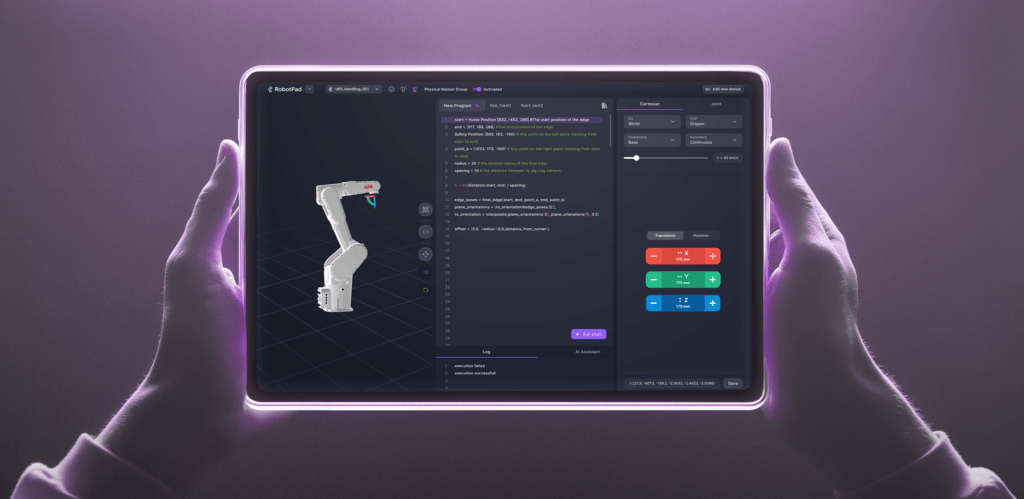
How NOVA Supports Companies
Wandelbots NOVA was developed with four key objectives to support companies:
- Support revenue growth: Automate processes faster and more reliably.
- Optimize Operations: Manage the entire robotics automation process through a single platform and reduce the complexity of shop floor IT.
- Reduce costs and risks: Virtual planning, commissioning, and support of automation systems lower the barrier to entry and the risk of unnecessary investments.
- Improved Usability: Automation projects with user-friendly frontend applications enable easy interaction between employees and robots.
Addressing the Labor Shortage and Simplifying Robotics
One major advantage of NOVA is its ability to counter the growing shortage of skilled robot programmers and production workers. Through intuitive frontend applications and a unified user interface, NOVA makes it easier than ever for employees to interact with robots without requiring technical knowledge. A modern and unified programming language also opens up a completely new field of activity for millions of software developers, thus strengthening the industry’s innovative capacity.
Investment Protection Thanks to Realistic Simulation with Digital Twins
Future automation systems can be tested for functionality before costly hardware equipment is purchased. The integration of Wandelbots NOVA with the NVIDIA Omniverse platform empowers developers and operators to create physically accurate digital twins of robots, factories, and movable workpieces for simulation before real-world deployment. This seamless integration delivers consistency between the digital twin and the physical automation cell throughout their entire lifecycle, which can enhance efficiency and reduce potential errors.
Wandelbots NOVA – Beta Phase Starts Now
Since June, the first approximately 50 customers have been able to experience the advantages of Wandelbots NOVA in the closed beta phase. Now, Wandelbots is making its operating system available to more users in the open beta phase. Interested users can register at https://www.wandelbots.com/developers-beta
Learn More at the SPS Trade Fair
We warmly invite you to see NOVA yourself and test it live at the SPS from November 12th to 14th: https://www.wandelbots.com/sps You can find us in Hall 6, Stand 248. Feel free to contact us at [email protected] to schedule an appointment. We are also happy to be available for interviews on-site.
In short:
- NOVA enables programming and controlling robots independent of the vendor
- NOVA brings robotics out of the niche and makes it accessible to the masses
- Software developers can easily create their own robotics applications
- NOVA, in combination with NVIDIA Omniverse, enables simulation and planning with digital twins
- Strong collaboration with Microsoft ensures scalability and cutting-edge AI features
- Interested companies and developers can sign up for the beta phase
Vention stellt KI-fähigen Automatisierungscontroller für Robotik- und Industrieanwendungen auf Demo Day vor
Montreal/Berlin, 18. September 2024 – Vention, das Unternehmen hinter der cloud-basierten Manufacturing Automation Platform (MAP), stellt auf seinem heutigen Demo Day in Berlin eine neue KI-Anwendung vor. MachineMotion AI ist der erste KI fähige Automatisierungscontroller mit beschleunigter Computertechnologie von NVIDIA.
Als Herzstück des Hardware- und Software-Ökosystems von Vention schließt MachineMotion AI die Lücke zwischen herkömmlichen speicherprogrammierbaren Steuerungen (SPS) und modernen Roboterprogrammierumgebungen. Der Controller der dritten Generation wurde entwickelt, um die Konzeption und Bereitstellung von Roboteranwendungen für produzierende Unternehmen jeder Größe erheblich zu vereinfachen.
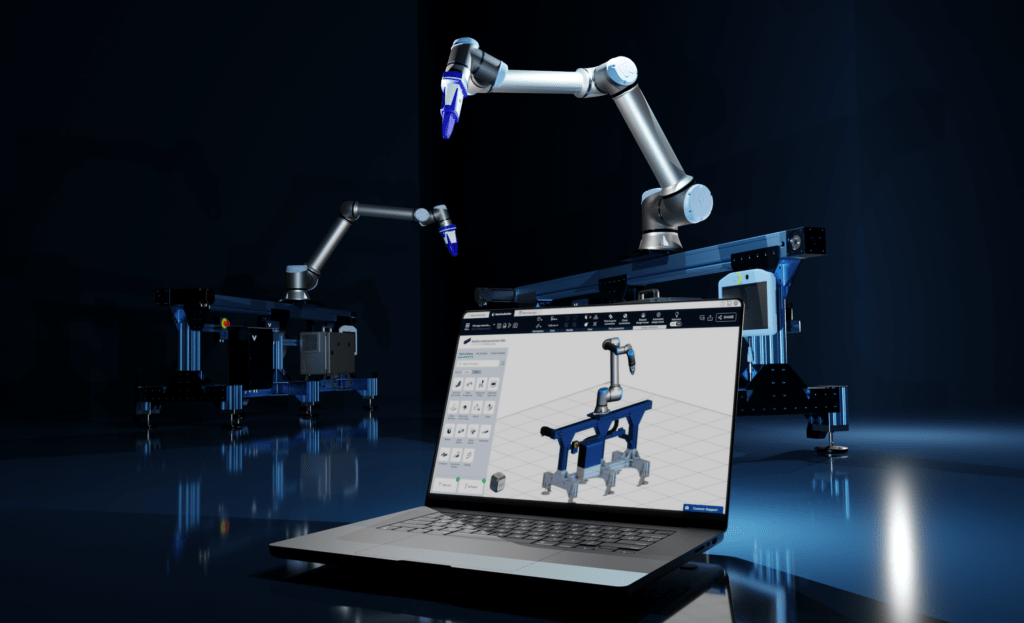
MachineMotion AI basiert auf der NVIDIA Jetson-Plattform für Edge-KI und -Robotik. Der Controller entwickelt KI-fähige Roboter mit NVIDIA GPU-beschleunigter Pfadplanung weiter und bietet die Möglichkeit, 2D-/3D-Wahrnehmungsmodelle auszuführen, die in synthetischen und physischen Umgebungen trainiert wurden.
MachineMotion AI ist mit führenden Robotermarken (z.B. Universal Robots, FANUC und ABB) kompatibel und lässt sich per Plug-and-Play mit Hunderten von Bewegungsgeräten und Sensoren verbinden – von Förderbändern und Aktuatoren bis hin zu Sicherheitsgeräten, Computer-Vision-Systemen, Telepräsenzkameras und mehr.
„Wir sind auf dem Weg, die industrielle Automatisierung zu demokratisieren und bauen dabei das umfassendste Unternehmen für industrielle Automatisierung und Robotik auf. Die heutigen Ankündigungen festigen Ventions Position als intuitivste Plattform für Automatisierung und Robotik und zeigen gleichzeitig die fortschrittlichen Funktionen, die Experten in der Branche benötigen“, sagt Etienne Lacroix, Gründer und CEO von Vention.
Weitere Informationen zu der Zusammenarbeit mit NVIDIA finden Sie hier. Demo Day in Berlin (18.9.)
Der diesjährige europäische Demo Day findet am 18.9. ab 14 Uhr in der Vention Europazentrale in Berlin statt. Etienne Lacroix, Gründer und CEO von Vention, wird vor Ort sein und für Pressegespräch zur Verfügung stehen. Mehr Informationen zum Event in Berlin finden Sie hier.
Über Vention
Vention hilft Unternehmen, ihre Produktionsbereiche durch eine demokratisierte Benutzererfahrung in nur wenigen Tagen zu automatisieren. Mit der digitalen Fertigungsautomatisierungsplattform MAP von Vention können Kunden automatisierte Geräte direkt über ihren Webbrowser entwerfen, bestellen und bereitstellen. Vention hat seinen Hauptsitz in Montreal und Niederlassungen in Berlin und Boston. Die über 300 Mitarbeiter betreuen mehr als 4.000 Kunden auf fünf Kontinenten und in 25 Fertigungsindustrien.
Successful Kickstarter campaign: MD Robot Kit promotes creativity and education in robotics
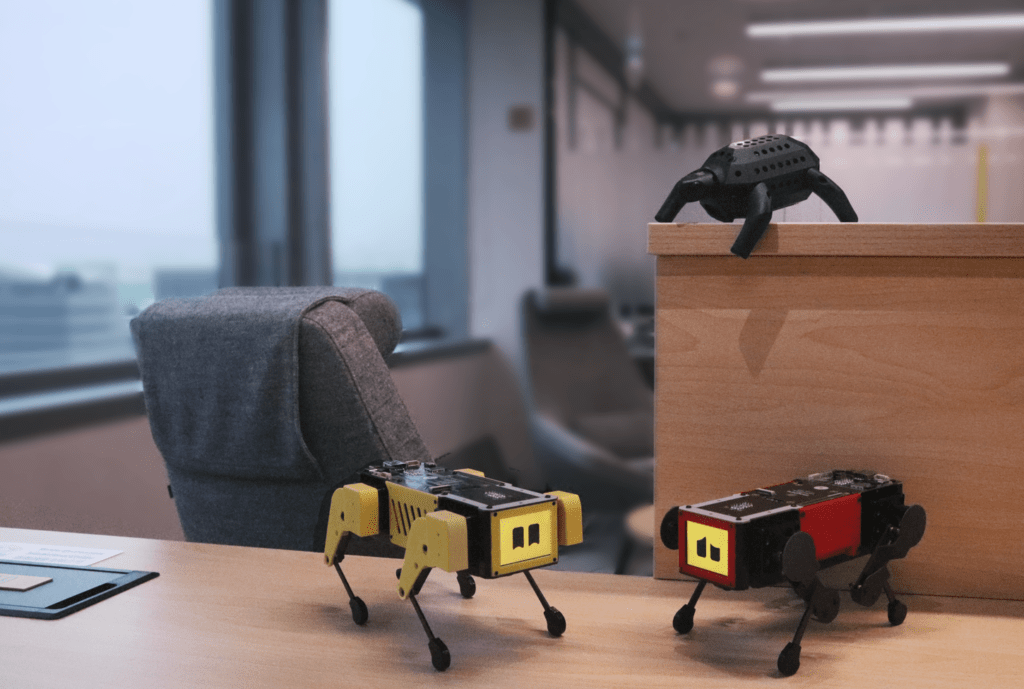
MangDang’s Kickstarter project „MD Robot Kit: Unlock your AI Robot Engineering Dream Job“ aims to promote the creativity and technical know-how of robotics enthusiasts. It offers two main robots, each addressing different needs and interests.
The first robot, the Mini Pupper, is available in several versions, including Mini Pupper 1, Mini Pupper 2, and the 2G and 2GA models. This robot is a low-cost, personal quadruped kit that comes with open-source software. The Mini Pupper supports multimodal generative AI platforms such as OpenAI’s ChatGPT, Google’s Gemini, and AWS’s Claude. It is also compatible with ROS1 and ROS2, which expands its capabilities in the areas of SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) and navigation. The integration of OpenCV allows the robot to perform deep learning with cameras. Thanks to the use of Raspberry Pi and Arduino, the Mini Pupper offers high adaptability and expandability, making it ideal for developers who want to realize their own projects.

The second robot presented is the Turtle Robot, which will be available soon. This robot is specifically aimed at schools, homeschooling families, and robot enthusiasts. While detailed specifications have not yet been fully released, it is clear that the Turtle Robot also aims to support learning and creativity in the field of robotics.
The campaign itself has set a funding goal of 9000€ and has clearly exceeded it with a sum of just under 19000€, which corresponds to over 200% of the original goal. The campaign runs from September 5, 2024 to October 5, 2024 and has attracted 80 supporters so far. A standout feature of the MD Robot Kits is their open-source nature, which allows users to assemble the robots in less than an hour. This makes them particularly accessible to a wide range of audiences, ranging from educational institutions to DIY enthusiasts. The project is designed not only to impart technical knowledge, but also to promote the joy of creating and customizing robots.
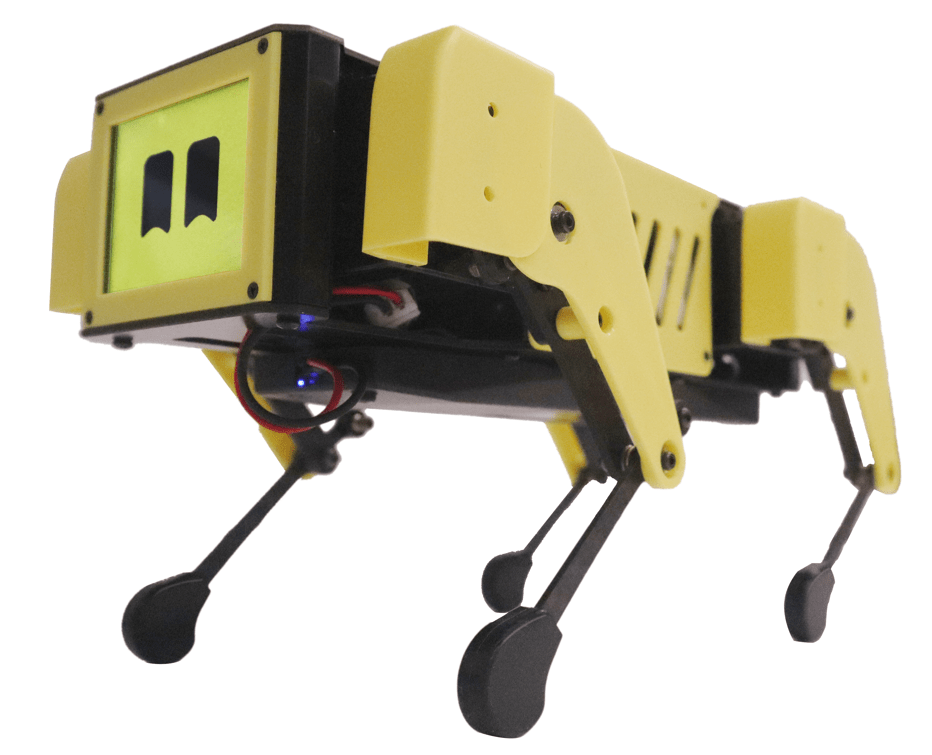
1. Mini Pupper:
- Versions: Mini Pupper 1 (2021), Mini Pupper 2 (2022), Mini Pupper 2G & 2GA.
- Design: A low-cost, personal quadruped kit with open-source software.
- Features: Supports multimodal generative AI such as OpenAI’s ChatGPT, Google’s Gemini, and AWS’s Claude. It is compatible with ROS1 and ROS2 for SLAM & navigation and is based on OpenCV for deep learning with cameras.
- Extensibility: Uses Raspberry Pi and Arduino, which allows for high adaptability.
- Open-source platform: The Mini Pupper supports the Robot Operating System (ROS) and offers features such as SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) and navigation. It is equipped with lidar and camera sensors that allow it to map its surroundings and move autonomously
- Technical specifications: The robot has 12 degrees of freedom, made possible by advanced servo motors. These motors provide feedback on acceleration and force, which allows precise control.
- Hardware and expandability: The Mini Pupper uses the Raspberry Pi 4B or the Raspberry Pi Compute Module 4 as the central processing unit and is equipped with an ESP32 as a microcontroller. It has an IPS display with a resolution of 240 x 320 pixels, a microphone, speakers and a touch sensor.
- Adaptability: Thanks to its open-source nature, the Mini Pupper can be modified deeply. Users can add their own modules and customize the robot for different projects, such as tracking objects in space.
- Education and community: The Mini Pupper is ideal for schools and homeschooling families. It comes with comprehensive guidance and resources to help you get started with robotics. Users can become part of a global community to share ideas and get support.
- Price and availability: As part of the Kickstarter campaign, the Mini Pupper will be offered in different versions, with the base model costing around 479 euros. Delivery is scheduled to begin in February, with supporters aware of the financial risk of crowdfunding campaigns.

2. Turtle Robot:
- Open-source project: The Turtle Robot is based on Arduino and is an open-source project that supports the integration of generative AI. This allows users to customize and expand the robot.
- Affordability: The Turtle Robot is a low-cost learning platform for multimodal generative AI and comes at an introductory price of 60% off $99. This makes it particularly attractive to educational institutions and DIY enthusiasts.
- Ease of use: The robot is designed to be set up and put into operation within a week. This makes it easier for beginners to start learning and experimenting quickly.
- Support and resources: MangDang offers comprehensive support across multiple channels, as well as access to all code and design files via a GitHub repository. Users can print the STL design files and contribute their own ideas.
- Multimodal Generative AI: The Turtle Robot uses advanced AI technologies that enable continuous voice interactions. The AI can remember previous conversations and give personalized answers based on them.
- Application examples: There are two Arduino projects that can be used with the Turtle Robot: one for testing individual functions and another that performs all functions via voice control.
- Availability: The Turtle Robot was available as part of the Kickstarter campaign until October 2024 and will be available in an online store after that.

Vention and ABB collaborate to make cobot automation accessible to SMBs
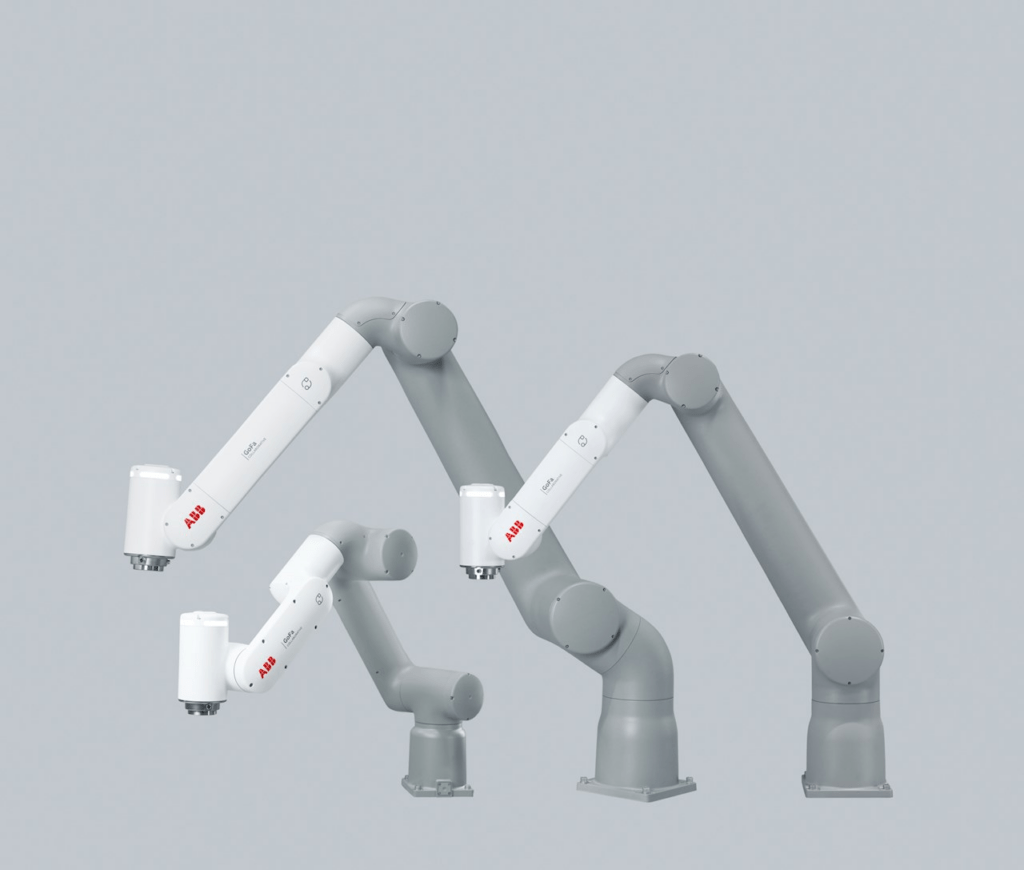
Montreal/Berlin, September 10, 2024 – Vention, the company behind the cloud-based Manufacturing Automation Platform (MAP), announces its collaboration with ABB Robotics, confirming the compatibility between the Vention platform and the ABB GoFa™ family of cobots. Vention and ABB customers benefit from a seamless integration of both companies‘ technologies, from the design phase of the robot cells to the processes on the factory floor.
As part of the Vention ecosystem, ABB will gain access to a wider range of do-it-yourself automation customers, while Vention will expand its offering with ABB’s robotic solutions. The mutually beneficial relationship will expand market reach and innovation for both companies.

Enhanced automation capabilities with the ABB GoFa™ CRB15000 Series
The ABB GoFa™ robots, now available on the Vention marketplace, offer manufacturers proven cobots with a payload of 5 kg, 10 kg and 12 kg. Known for their safety, ease of use and performance, ABB GoFa™ robots are designed to work side-by-side with humans in various applications, from assembly and welding to material handling and inspection.
ABB GoFa™ robots, enhanced by the power of the Vention Manufacturing Automation Platform
ABB GoFa™ robots are now compatible with the entire Vention platform, including MachineBuilder (design), MachineLogic (robot programming), MachineAnalytics (operational monitoring and data) and Remote Support (on-demand support). This compatibility provides ABB customers with an intuitive user experience, from the design to the operation of robot cells. In addition, ABB GoFa™ robots will be available for Vention’s innovative Rapid Series application line during 2025.
„We are very pleased to welcome ABB to the Vention ecosystem. This collaboration enhances our ability to deliver democratized and powerful automation solutions“ says Etienne Lacroix, Founder and CEO of Vention.
„The partnership with Vention represents a significant step forward for both companies. This collaboration combines ABB’s advanced cobot portfolio with Vention’s expertise in application design and delivery. By bringing together our hardware and software capabilities, we’re making robot automation more accessible and easier to integrate for businesses of all sizes. „Our joint efforts will address key industry trends and help companies improve their operations and make workplaces safer and more efficient,“ said Andrea Cassoni, Head of Collaborative Robotics at ABB Robotics.
About Vention
Vention helps companies automate their production areas in just a few days through a democratized user experience. Vention’s digital manufacturing automation platform allows customers to design, automate, order, and deploy automated equipment directly from their web browser. Vention is headquartered in Montreal, Canada, with offices in Berlin and Boston. Its more than 300 employees serve more than 4,000 customers on five continents and in 25 manufacturing industries. For more information, see vention.com or follow us on LinkedIn. *MachineMotion, MachineLogic, MachineCloud and Vention are trademarks of Vention Inc.
About ABB Robotics
ABB (ABBN: SIX Swiss Ex) ABB is a technology leader in electrification and automation, enabling a more sustainable and resource-efficient future. The company’s solutions combine technical expertise and software to optimize the manufacturing, movement, power, and operation of things. Building on more than 140 years of excellence, ABB’s more than 105,000 employees are committed to driving innovation that accelerates industrial transformation. www.abb.com
ABB Robotics & Discrete Automation, as one of the world’s leading providers of robotics and machine automation, is the only company with a comprehensive and integrated portfolio that includes robots, autonomous mobile robots and machine automation solutions developed and orchestrated by our value-added software. We help companies of all sizes and industries – from automotive to electronics to logistics – to become more resilient, flexible and efficient. ABB Robotics & Discrete Automation is helping customers transition to the connected and collaborative factory of the future. The business unit employs around 11,000 people at over 100 locations in around 53 countries. go.abb/robotics
Go-to-Automationsanwendungen für einen schnellen ROI
Wie Sie Kosten senken und die Vorteile der Automationsklassiker Pick & Place, Prüfen und Dosieren am besten für sich nutzen
Autor: Alexander Mühlens, Geschäftsbereichsleiter Low Cost Automation bei der igus GmbHAus der Industrie sind Roboter schon lange nicht mehr wegzudenken – ob als Maschinenbestücker, Qualitätsprüfer oder Montagehelfer. Doch viele kleinere und mittelständischen Unternehmen (KMU) drohen ins Hintertreffen zu geraten. Denn oft wissen Sie garnicht, wo sie anfangen sollen. Welche Anwendungen lassen sich überhaupt automatisieren? Und häufig scheinen die Investitionskosten zu hoch und die Integration und Bedienung zu komplex.
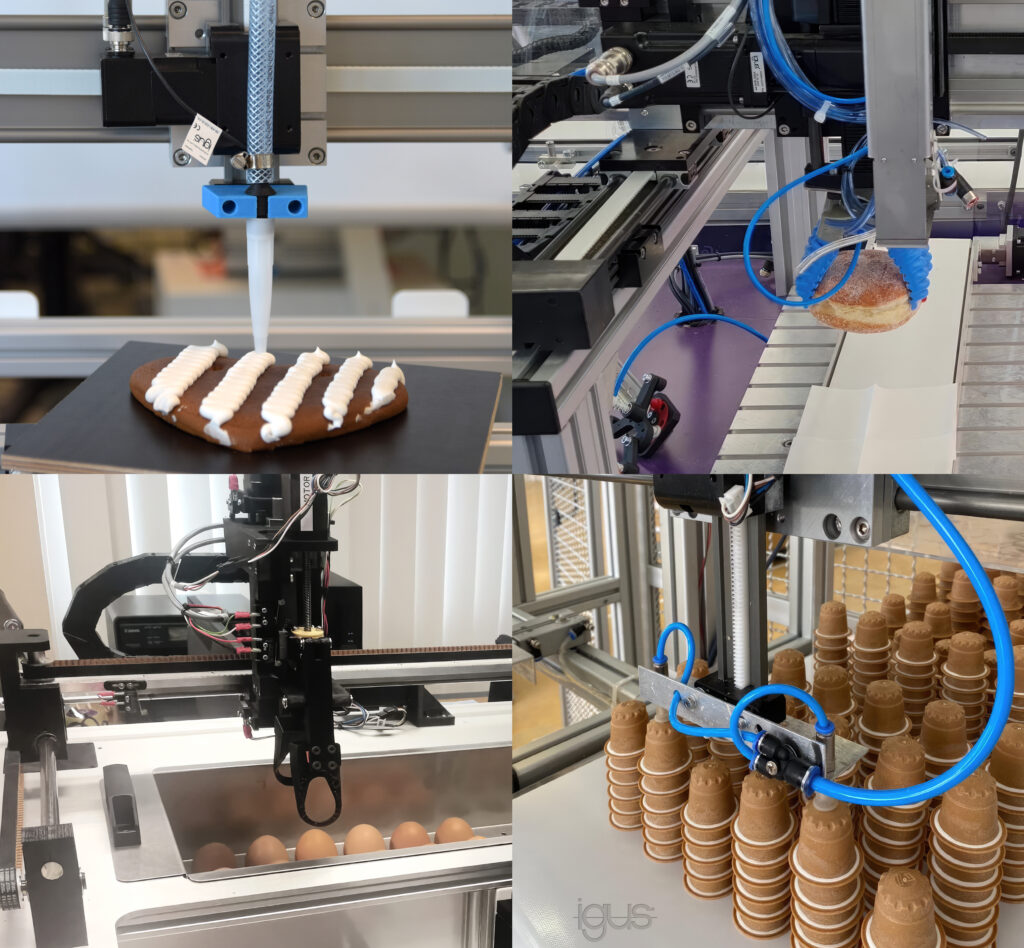

Picken, dosieren, schleifen oder prüfen: Es gibt eine Vielzahl an monotonen, repetitiven und anstrengenden Arbeiten, die sich einfach automatisieren lassen. Doch sich nur einen Roboter anzuschaffen, führt am Ende leider zu keiner Lösung. Am Ende muss das gesamte System aus Roboter und Komponenten wie Vision-Systeme, Greifer und Sensoren funktionieren. Doch insbesondere KMU wissen häufig nicht, wo sie nach einer Lösung suchen sollen und wie die passende Lösung überhaupt aussieht. Außerdem ist es wichtig, nicht zu komplex anzufangen. Der herstellerneutraler Robotik-Marktplatz RBTX hilft Automatisierungswilligen dabei, die einfachste und kostengünstigste, funktionierende Lösung zu finden.
Über 400 Komplettlösungen aus der Praxis
Das Besondere: Interessierte finden auf dem Marktplatz nicht nur Roboter und Einzelkomponenten, sondern Einblick wie es andere machen. Als Inspirationsquelle zum sofortigen Nachmachen finden sich online über 400 sofort adaptierbare Automatisierungsprojekte aus der Praxis. Von der automatisierten Regenwurmfarm über einen Berliner-Picker bis hin zum Agrarroboter, der Unkraut erkennt und vernichtet. Mehrere tausend KMU aus aller Welt haben auf RBTX.com bereits ohne konstruktionstechnische Vorkenntnisse Automationslösungen realisiert. 95 Prozent dieser Komplettlösungen sind für unter 12.000 Euro erhältlich. Die Low-Cost-Lösungen amortisieren sich nachweislich bereits ab 3-12 Monaten. Zu den Hauptanwendungsbereichen zählen unter anderem Pick & Place-Aufgaben, die Qualitätsprüfung sowie Klebe- und Dosieranwendungen.
Effizientes Handling von Produkten mit Pick & Place-Robotern
Ein Pick & Place-Roboter befördert ein Objekt zuverlässig von A nach B. Häufig handelt es sich dabei um wiederholende und zeitfressende Tätigkeiten, die viel Optimierungspotenzial innerhalb einer Produktion bieten. Ob bei der Maschinenbestückung, Palettierung, Sortierung oder Vormontage. Die Vorteile von Low Cost-Roboterlösungen haben einen Automatisierungstrend in Branchen wie Landwirtschaft, Lebensmittelindustrie, Medizintechnik bis hin zum Handwerk ausgelöst. Pick & Place-Systeme finden sich vor allem zunehmend in alltäglichen Endkunden-Anwendungen, zum Beispiel in Verkaufsautomaten.
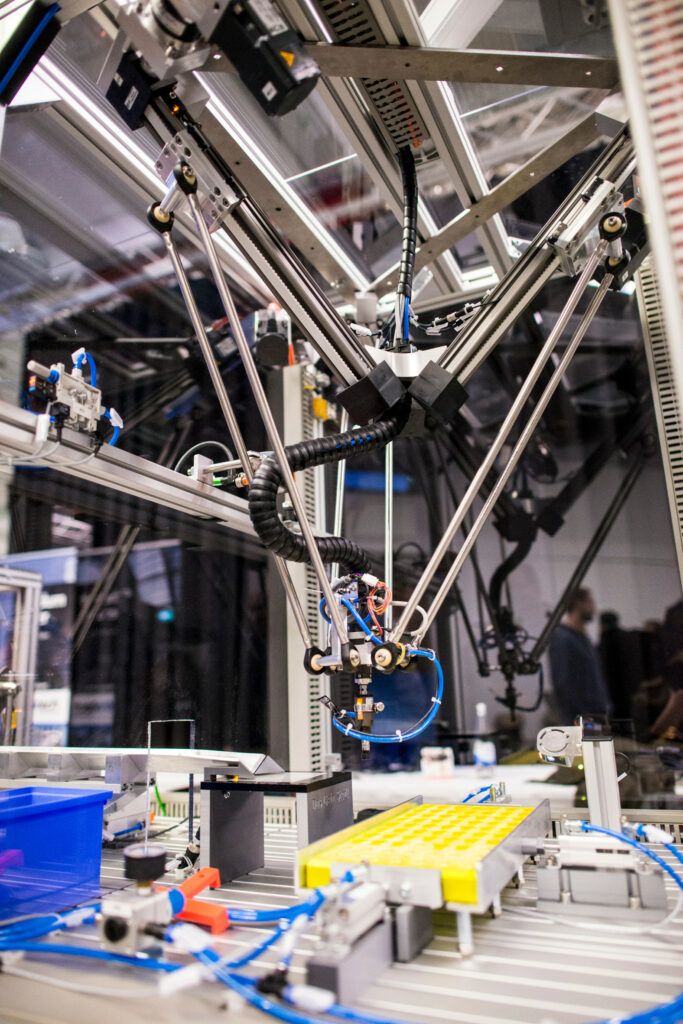
Verschiedene Robotertypen wie Gelenkarm-, Delta- oder Portalroboter können die unterschiedlichsten Anwendungsszenarios realisieren. So kommen Portalroboter zum Beispiel für das Greifen von Medikamenten zum Einsatz, um sie zur Ausgabe zu befördern, während ein SCARA Roboter als „Labor-Assistent“ das sichere Aufnehmen und Ablegen von Reagenzgläsern übernimmt – und das bereits für 7.820 Euro. Der Vorteil der Roboter-Systeme: Sie nehmen Bauteile präzise und mit konstanter Qualität auf und setzen sie am gewünschten Ablageort ab. Die Vorgänge sind exakt wiederholbar.
Automatisierte Qualitätsprüfung für mehr Präzision und Planbarkeit
Mit einer automatisierten Qualitätskontrolle lassen sich repetitive Prüfvorgänge effizient und präzise durchführen. Die Einsatzszenarien von Prüfrobotern sind so unterschiedlich und individuell wie die zu automatisierenden Arbeitsvorgänge. Ob Oberflächenprüfung, Maßprüfung oder Funktionsprüfung – Prüfprozesse und -merkmale unterscheiden sich in der Praxis stark. Mithilfe von RBTX wurde beispielsweise ein Robotersystem für das automatisierte Be- und Entladen einer Prüfstation für Leiterplatinen konfiguriert.

Ebenso ein Flächenportal, das mithilfe einer Kamera einzelne Uhren ansteuert, um visuell zu prüfen, ob sich Minuten- und Sekundenzeiger bewegen. Ein Roboterarm kommt unter anderem auch bei der End-of-Line-Prüfung von Ladegeräten für Elektrofahrzeuge zum Einsatz. Prüfprozesse lassen sich durch den Einsatz von Robotern effizient verschlanken und besser planen. Darüber hinaus arbeiten Roboter rund um die Uhr ohne Qualitätseinbußen. Es werden identische Vorgänge und eine präzise, gleichbleibende Messung des Prüfmerkmals sichergestellt.
Sicher kleben und dosieren – ohne Materialverschwendung
Neben Prüf- und Pick & Place-Aufgaben kann auch das Auftragen von Klebe-, Versiegelungs-, Lackiermitteln und Isolierschäumen effizient automatisiert werden. Meistens geht es darum Materialverschwendung zu vermeiden und präziser zu kleben bzw. zu dispensieren. Und dafür benötigt man keinen Roboter mit Investitionskosten im 6-stelligen Bereich. Mit Low Cost-Robotern kann fast alles verklebt werden. Sie erreichen eine Präzision von ca. 0,5 mm. Ein weiterer Grund ist die Arbeitsplatzsicherheit. Denn der Roboter kann problemlos mit Chemikalien in Berührung kommen und unterstützt bei unergonomischen Arbeiten. Vor allem Klebeprozesse an kleinen Werkstücken, erfordern ein hohes Maß an Konzentration und Präzision. Dabei ist es häufig wichtig, dass der Kleber das Bauteil exakt abdichtet. Dort liegt die Automation durch Roboter nah. Mithilfe von RBTX konnte zum Beispiel ein Kunde durch den Einsatz eines automatischen Dosierroboters die Geschwindigkeit beim Auftragen von Dichtungsmasse auf ein Metallteil, einem wichtigen Arbeitsschritt in seiner Produktion, vervierfachen. Die einfache Handhabung der Maschine ermöglicht es selbst ungeschulten Mitarbeitern, den Roboter sofort zu nutzen.
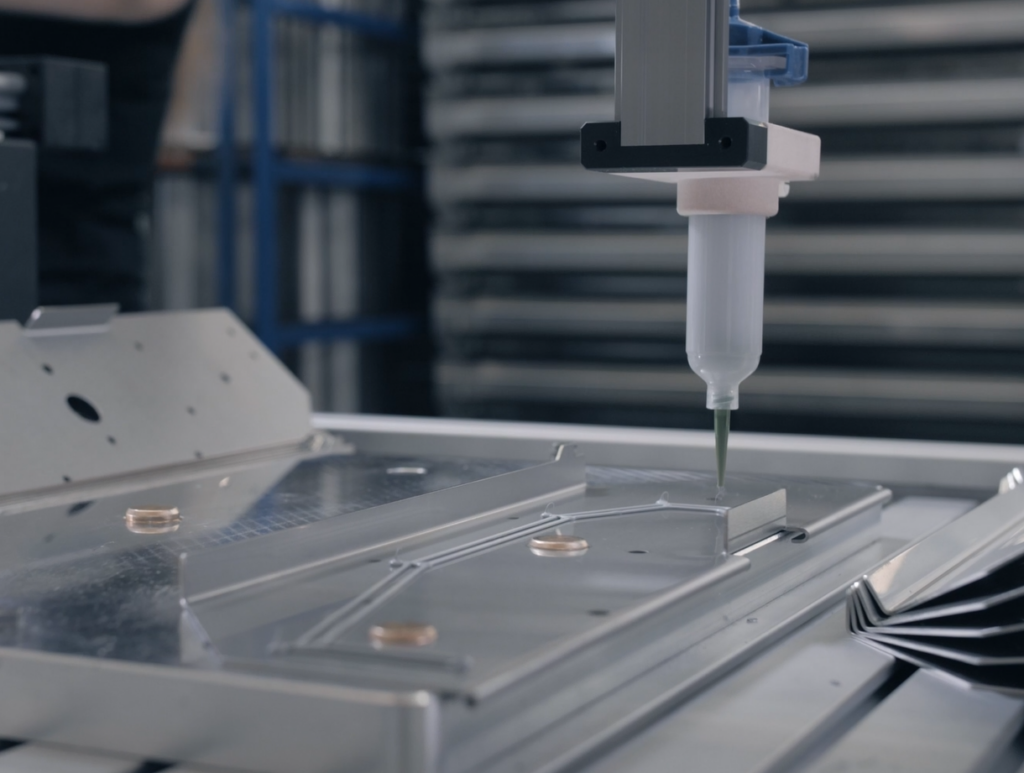

Für das Kleben und Dosieren lassen sich je nach Anwendung verschiedenste Robotersysteme einsetzen. Mithilfe eines eigenen Dosierroboter-Konfigurators können Anwender in nur wenigen Klicks eine individuelle Roboterlösung zusammenstellen, die präzise Klebe- und Dosiervorgänge automatisiert.
Wer noch nach Inspiration sucht, findet auf RBTX.com alle Anwendungsbeispiele aus der Praxis: https://rbtx.com/de-DE/solutions
RBTX ist eine eingetragene Marke der igus GmbH.
