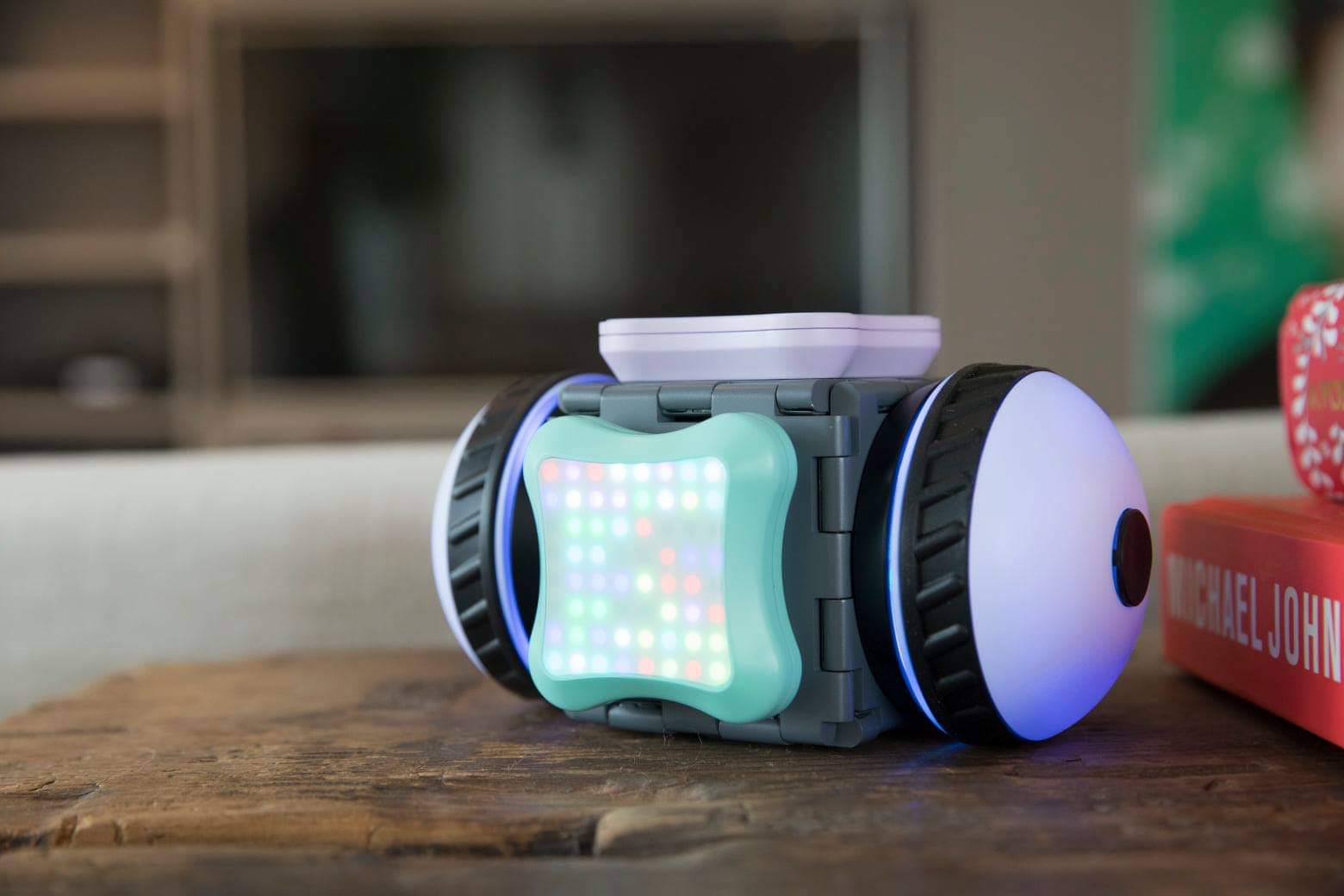
Entweder haben Sie schon eins, oder Sie haben bald eins. Roboterhaustiere erobern die Verbrauchermärkte weltweit in Form von Babyrobben, Hundewelpen oder einem schwanzwedelnden Kissen. Jetzt bekommen sie Gesellschaft von einer überfahrenen Katze.
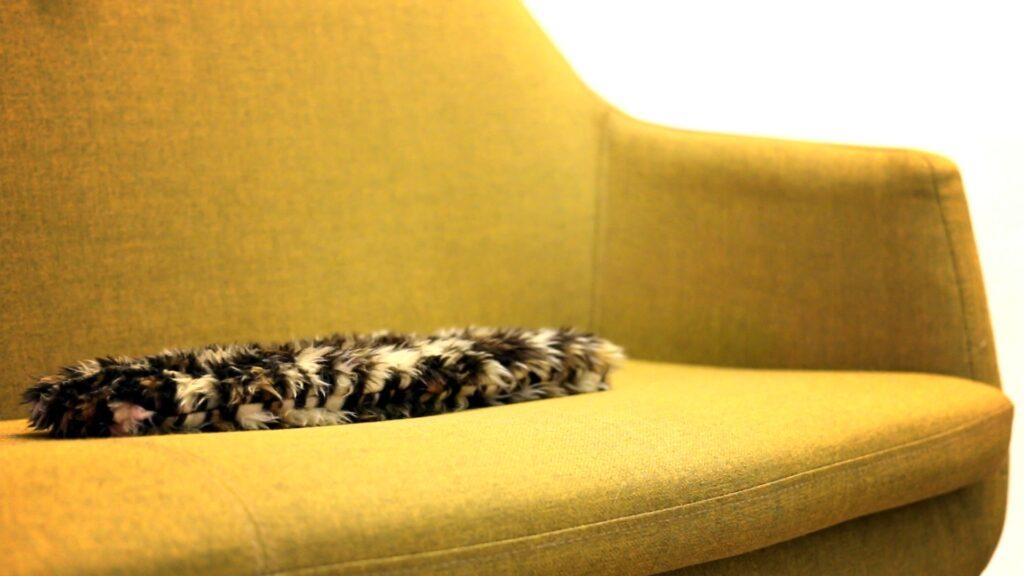

(lifePR) (Berlin, 14.05.21) flatcat wurde von Gizmodo ((https://gizmodo.com/…)) als “der gruseligste Roboter, den man je gesehen hat” betitelt, und das mag für einige tatsächlich so sein. Für viele andere ist es ein zugegebenermaßen seltsames, aber niedliches Roboter-Haustier, das sie umarmen und mit dem sie spielen wollen.
Die ersten paar Flatcats sind ab sofort und nur noch sieben Tage lang auf Kickstarter ((https://www.kickstarter.com/…), der beliebtesten Crowdfunding-Website, erhältlich. Die Kampagne steht kurz vor der Vollfinanzierung, braucht aber noch ein paar entscheidende Zusagen von Roboter-Enthusiasten aus nah und fern, die etwas bewegen wollen.
Der Roboter, der von Jetpack Cognition Lab , einem in Berlin ansässigen Unternehmen mit Grazer Wurzeln entwickelt und hergestellt wird, ist ein Roboter der neuen Art. Er ist völlig anders als alle anderen vergleichbaren Produkte auf dem Markt. Was ihn einzigartig macht, ist seine sensomotorische Kompetenz, die Kräfte seiner eigenen Bewegung und die von außen durch Menschen oder einfach durch die Schwerkraft erzeugten Kräfte zu spüren und darauf zu reagieren.
Die Fähigkeit, Kräfte direkt in den Gelenken zu spüren, erlaubt es Flatcat, neugierig zu sein und seinen eigenen Körper und die Welt auf die sicherste Art und Weise zu erkunden. Die Technologie dafür kommt aus dem Forschungsfeld der Entwicklungsrobotik, bei dem Teile der Entwicklung von Tieren und Menschen in Software und Algorithmen umgesetzt werden.
Mögliche Verwendungszwecke von flatcat sind als Haustier im Wohnzimmer, um einfach zu spielen und gemeinsam die Welt der sensomotorischen Erfahrung und Bewegung zu erkunden; als therapeutischer Roboter, um sanft einfache Bewegungen zu stimulieren, Gesellschaft und Trost zu spenden; oder als Desktop-Forschungs-Roboter für Wissenschaftler und Hacker:innen gleichermaßen, da er neben seiner hochmodernen sensomotorischen Sensibilität auch Open Source, erweiterbar und modifizierbar ist.
Jetpack Cognition Lab, Inc
Seit seinen Anfängen im Jahr 2019 bringt Jetpack Cognition Lab radikale Innovationen aus der wissenschaftlichen Forschung auf den Konsumentenmarkt. Die Gründer des Labs sind Dr. Oswald Berthold und Matthias Kubisch. Sie lernten sich während ihres Studiums an der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin kennen und taten sich zusammen, um die schrägsten und lustigsten Roboter der Welt zu entwickeln.
Berthold ist ein in österreichischer Künstler-Technologe, geboren in Graz, der schon mit dem Kollektiv farmersmanual Musikgeschichte geschrieben hat, indem er neuartige Stile und innovative Ansätze zur digitalen Musikproduktion und -veröffentlichung im Internetzeitalter einführte. Spätestens seit er 2018 seine Promotion in Robotik innerhalb der Adaptive Systems Group der HU Berlin abgeschlossen hat, ist er damit beschäftigt, Grundlagenforschung in Kundennutzen zu verwandeln.
Kubisch ist ein deutscher Informatiker, Kreativer und Aktivist. Er hat als wesentliches Mitglied des Teams gearbeitet, das den modularen humanoiden Roboter Myon im ALEAR-Projekt unter der Leitung von Dr. Manfred Hild entwickelt hat. Außerdem hat er die Industrie von innen gesehen und Algorithmen zur Steuerung von elektrischen Kraftwerken entwickelt. Er ist nicht nur ein Experte für adaptive Echtzeitalgorithmen und maschinelles Lernen, sondern auch ein genialer Elektronikdesigner und Produktvisionär.