Today I built the base model with a gripper and sent my feedback to the developers. It’s already really great product but there are always things to tweak or make better. Do not miss to support it on Kickstarter!
WeiterlesenRotrics DexArm knows how to visit its favourite website
RBTXpert von igus: Remote Integration für kostengünstige Automatisierung zum Festpreis
Neuer Service hilft Kunden bei der schnellen Umsetzung ihres Automatisierungsprojektes und sorgt für schnellen ROI
Köln, 20. Mai 2021 – Günstig automatisieren und von einem schnellen Return of Invest profitieren – aber wie? Vor dieser Frage stehen häufig nicht nur Automatisierungs-Einsteiger. Der RBTXpert unterstützt ab sofort dabei, das geplante Projekt zum Erfolg zu bringen. Der neue Service hilft, die richtigen Low-Cost-Komponenten auszuwählen, prüft die Machbarkeit und steht bei der Inbetriebnahme zur Seite.
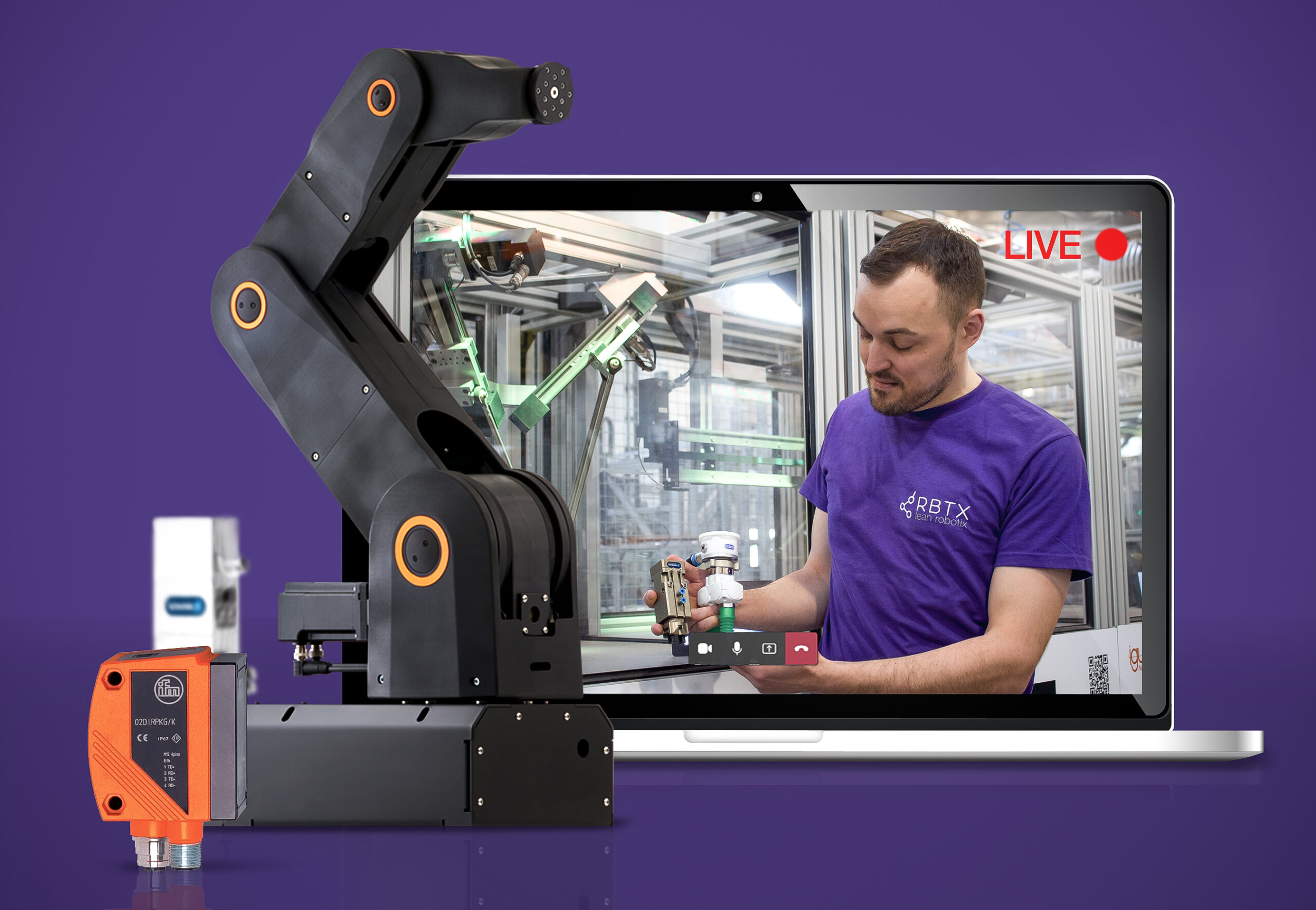

Alle Möglichkeiten der Low-Cost-Robotik auf einer Plattform zu bündeln, transparent und einfach zu bedienen: Das ist das Ziel von RBTX.com. Auf der Online-Plattform haben Nutzer die Möglichkeit, sich mit nur wenigen Klicks eine eigene kostengünstige Roboterlösung zusammenzustellen. Doch nicht alle Anwender wissen von Anfang an, was sie genau für ihr Automatisierungsprojekt benötigen. „Für den Kunden steht erst einmal seine individuelle Anwendung im Mittelpunkt. Und er weiß, welche Aufgaben automatisiert werden sollen“, sagt Jens Klärner, Product Owner RBTX. „Der neue RBTXpert hilft ihm jetzt, die richtigen Komponenten dafür zu finden und die preisgünstigste Lösung, die sicher funktioniert.“
Automatisierung leicht gemacht mit dem RBTXpert
Am Anfang einer jeden Beratung steht die Frage „Was will ich automatisieren?“. Dazu wählt der Interessent einfach seinen kostenlosen Wunschtermin mit dem RBTXpert und beschreibt schließlich im Video-Call sein Vorhaben. Der Experte kümmert sich anschließend um das „Wie“. Im Remote-Termin wird gemeinsam die Machbarkeit geprüft, indem live die Vorteile unterschiedlicher Roboterkinematiken und Zubehör getestet werden. Anschließend erstellt der RBTXpert ein verbindliches Festpreisangebot. Dafür hat igus auf 400 Quadratmetern eine „Customer Testing Area“ aufgebaut. Hier lässt sich die Umsetzung der geplanten Automatisierung testen und optimieren. Per Video kann der Kunde daran mitwirken. Noch besser wird es, wenn der er das zu bewegende Teil danach für weitere Versuche zu igus schickt. Am Ende der kostenlosen Beratung steht die Gewissheit über die Machbarkeit des Automatisierungsprojektes und ein Angebot mit Festpreis. Entscheidet sich der Kunde für eine Realisierung werden im Anschluss die Komponenten geliefert. Bei der Inbetriebnahme hilft der RBTXpert Service erneut als Teil des Projektumfangs. „Unsere typischen Projekte haben 8.000 Euro Hardwarekosten und circa 20 Stunden Integrationsaufwand“, erklärt Alexander Mühlens, Leiter Geschäftsbereich Low Cost Automation bei igus. „Mit dem Service zielen wir auf Anwendungen mit Hardwarekosten zwischen 3.000 bis 25.000 Euro und einem Integrationsaufwand von unter 100 Stunden. Komplexere Projekte, die sich mit Low Cost Automation und dem RBTXpert heute noch nicht umsetzen lassen, nehmen wir in unserenEntwicklungsplan auf“, so Alexander Mühlens weiter.
Online-Marktplatz bietet große Low-Cost-Robotik-Auswahl
Zur Auswahl steht dafür auf RBTX.com eine breite Auswahl an Low-Cost-Automation-Produkten. Das elektro-mechanische Grundgerüst bilden dabei unter anderem Gelenkarmroboter, Deltaroboter und kartesische Roboter von igus, aber auch Roboter von anderen Anbietern. Diese Basis erweitern dann Einzelkomponenten verschiedener Hersteller, etwa Greifer, Kameras und Steuerungen. Das Produktangebot wird kontinuierlich erweitert: Zum Beispiel mit igus Neuheiten wie dem vollintegrierten ReBeL Tribo-Wellgetriebe mit Motor, Absolutwert-Encoder, Kraftregelung und Controller. Mit den drylin Scara-Robotern steht ab Sommer ein modular aufgebauter Roboter mit vier Freiheitsgraden zur Verfügung. „Das zeigt: RBTX wird immer größer und attraktiver für Kunden ebenso wie Anbieter von Low-Cost-Automation und bringt beide Seiten zusammen“, unterstreicht Jens Klärner. „Der Kunde hat dabei immer die Sicherheit, dass alle unterschiedlichen Komponenten auch problemlos miteinander funktionieren. Der RBTXpert erweitert dieses Angebot und unterstützt dabei, dass es die individuell richtige Auswahl ist. Damit wird der Einstieg in eine kostengünstige Automatisierung mit einem schnellen Return on Investment für Viele jetzt noch einfacher.“
flatcat, der gruseligste Roboter aller Zeiten, ist nur noch sieben Tage auf Kickstarter
Entweder haben Sie schon eins, oder Sie haben bald eins. Roboterhaustiere erobern die Verbrauchermärkte weltweit in Form von Babyrobben, Hundewelpen oder einem schwanzwedelnden Kissen. Jetzt bekommen sie Gesellschaft von einer überfahrenen Katze.
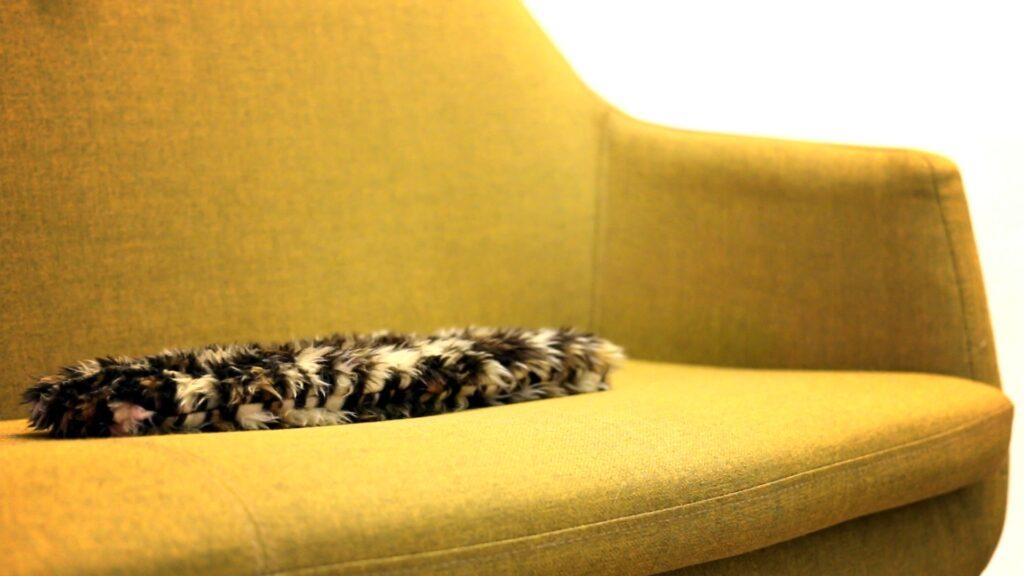

(lifePR) (Berlin, 14.05.21) flatcat wurde von Gizmodo ((https://gizmodo.com/…)) als “der gruseligste Roboter, den man je gesehen hat” betitelt, und das mag für einige tatsächlich so sein. Für viele andere ist es ein zugegebenermaßen seltsames, aber niedliches Roboter-Haustier, das sie umarmen und mit dem sie spielen wollen.
Die ersten paar Flatcats sind ab sofort und nur noch sieben Tage lang auf Kickstarter ((https://www.kickstarter.com/…), der beliebtesten Crowdfunding-Website, erhältlich. Die Kampagne steht kurz vor der Vollfinanzierung, braucht aber noch ein paar entscheidende Zusagen von Roboter-Enthusiasten aus nah und fern, die etwas bewegen wollen.
Der Roboter, der von Jetpack Cognition Lab , einem in Berlin ansässigen Unternehmen mit Grazer Wurzeln entwickelt und hergestellt wird, ist ein Roboter der neuen Art. Er ist völlig anders als alle anderen vergleichbaren Produkte auf dem Markt. Was ihn einzigartig macht, ist seine sensomotorische Kompetenz, die Kräfte seiner eigenen Bewegung und die von außen durch Menschen oder einfach durch die Schwerkraft erzeugten Kräfte zu spüren und darauf zu reagieren.
Die Fähigkeit, Kräfte direkt in den Gelenken zu spüren, erlaubt es Flatcat, neugierig zu sein und seinen eigenen Körper und die Welt auf die sicherste Art und Weise zu erkunden. Die Technologie dafür kommt aus dem Forschungsfeld der Entwicklungsrobotik, bei dem Teile der Entwicklung von Tieren und Menschen in Software und Algorithmen umgesetzt werden.
Mögliche Verwendungszwecke von flatcat sind als Haustier im Wohnzimmer, um einfach zu spielen und gemeinsam die Welt der sensomotorischen Erfahrung und Bewegung zu erkunden; als therapeutischer Roboter, um sanft einfache Bewegungen zu stimulieren, Gesellschaft und Trost zu spenden; oder als Desktop-Forschungs-Roboter für Wissenschaftler und Hacker:innen gleichermaßen, da er neben seiner hochmodernen sensomotorischen Sensibilität auch Open Source, erweiterbar und modifizierbar ist.
Jetpack Cognition Lab, Inc
Seit seinen Anfängen im Jahr 2019 bringt Jetpack Cognition Lab radikale Innovationen aus der wissenschaftlichen Forschung auf den Konsumentenmarkt. Die Gründer des Labs sind Dr. Oswald Berthold und Matthias Kubisch. Sie lernten sich während ihres Studiums an der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin kennen und taten sich zusammen, um die schrägsten und lustigsten Roboter der Welt zu entwickeln.
Berthold ist ein in österreichischer Künstler-Technologe, geboren in Graz, der schon mit dem Kollektiv farmersmanual Musikgeschichte geschrieben hat, indem er neuartige Stile und innovative Ansätze zur digitalen Musikproduktion und -veröffentlichung im Internetzeitalter einführte. Spätestens seit er 2018 seine Promotion in Robotik innerhalb der Adaptive Systems Group der HU Berlin abgeschlossen hat, ist er damit beschäftigt, Grundlagenforschung in Kundennutzen zu verwandeln.
Kubisch ist ein deutscher Informatiker, Kreativer und Aktivist. Er hat als wesentliches Mitglied des Teams gearbeitet, das den modularen humanoiden Roboter Myon im ALEAR-Projekt unter der Leitung von Dr. Manfred Hild entwickelt hat. Außerdem hat er die Industrie von innen gesehen und Algorithmen zur Steuerung von elektrischen Kraftwerken entwickelt. Er ist nicht nur ein Experte für adaptive Echtzeitalgorithmen und maschinelles Lernen, sondern auch ein genialer Elektronikdesigner und Produktvisionär.
World’s Largest Robotics Competition Returns: Robotics Education & Competition (REC) Foundation to Host Live Remote VEX Robotics World Championship 2021
The Robotics Education & Competition (REC) Foundation, a 501c3 nonprofit and VEX Robotics, is back to showcase the incredible talent and skill of a range of student competitors by hosting the first-ever Live Remote VEX Robotics World Championship May 17-29, 2021. Leveraging the REC Foundation’s Live Remote Tournament interface, teams from around the world will be able to compete in real-time tournaments or live skills matches to be crowned champions.
During the live remote event, students in grades three through college will compete in timed, heart-pounding robotics competition matches with their custom-built robots. Like at past world championships, competitors will have the opportunity to see familiar faces, activities, and share the excitement of the event.

To ensure the safety of its robotics community due to the pandemic, this unique event will adapt to a virtual format. Typically, the annual VEX Robotics World Championship attracts more than 30,000 attendees from all 50 states and more than 70 nations.
The Many Uses of Drone Videography For Event Marketing
This article was written by Anthony Jamison, a representative at Drones Services Phoenix. Anthony Jamison is the head of the Outreach Department of Drone Services Phoenix, Arizona’s premier aerial photography and videography company
There is no question about the impact unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) or aerial drones are making across industries these days.
Whether you’re a general contractor, a miner, a roofer, farmer, or a filmmaker, you will surely find suitable uses for an aerial drone, which can reach places and spaces you never imagined would be accessible a decade or so ago.

And today’s drones are not just about physically reaching hard-to-access spots. The fact that most, if not all of them are fitted with high-definition cameras also makes them capable of taking stunning photographs and videos while in flight.
The beauty of aerial drone videography also makes UAVs perfect for marketing activities, specifically event marketing.
If you’re part of a corporate marketing team and you’re organizing a music festival, a trade show, or any event, you might want to make good use of drones in the following ways:
Finding The Perfect Location
You need an open-air venue for your event, and you have already set your sights on a piece of land a few miles from the city.
The place may look good on the ground, but you want a complete idea of what it can offer and what you can do to the area for the event.
The solution? Get a drone in the air and shoot photos and videos of the whole property. With aerial photos and videos on hand, you can make a full assessment of the venue’s event-worthiness and start your planning for the event itself.
Billboards In The Sky
Billboards have always been a staple in marketing and advertising, and they still work, especially those huge ones that nobody can ever miss.
However, you can take things a step further by using flying billboards to market your event. Get a couple of drones, attach banners or tarpaulins to them, and have them fly over certain areas where your billboards in the sky can get the most eyes on them.
Enhanced Security
Your event can always use more security, and drones are more than capable of providing that.
With drones flying overhead during an event, you and your team can easily spot disturbances and possible trouble areas and alert security personnel to them right away.
Live Streaming
Event marketers can use live streaming with drones not only to hype up an event before it takes place but also broadcast the whole thing live to a massive audience while it’s unfolding.
Live streaming drone videos of the venue and the various preparations can help create buzz for the event itself and make people look forward to being there. Your brand’s followers would love to see behind-the-scenes footage of members of your team doing whatever they can to help make the event a success.
Once the event is taking place, a drone with live streaming capabilities can give the people who can’t make it to the venue a chance to see the goings-on while they are going on, making them feel like they’re there with you.
Creating Videos For Social Media
If live-streaming is not possible, you can always have your drone shoot all the necessary shots just the same, then create a video that you can post on all your social media channels.
As much as possible, post your drone videos for your event on YouTube and Facebook. After all, the former is the world’s top video streaming channel, while the latter has close to three billion active users worldwide.
While you’re at it, post your drone videos on your company website, too, since they can also help attract more traffic.
Giving Sponsors Due Credit
More often than not, major events are made possible with the help of corporate and individual sponsors.
You can show your appreciation for their involvement in your event by playing all over the venue videos shot by your drones featuring sponsors’ banners, signage, booths, or any indicator of the help they extended to you.
Celebratory Drone Light Shows
If your budget allows it, putting up a drone light show can serve as a high point for the event itself.
Unlike expensive fireworks, drone light shows don’t disperse toxic pollutants into the air, litter the venue with spent casings, and, more importantly, don’t scare birds, wildlife, and pets to death.
The creative possibilities are also endless, as drones can be used to create every imaginable pattern and shape in every possible color hundreds of feet in the air.
The crowd at your event and the people watching the live stream will indeed find themselves immensely entertained if you close the proceedings with a drone light show.
There are many other possible uses of drones for your event marketing efforts, but the ones listed above should be a good enough place to start.
You can always get a drone or two yourself to use in event marketing, but keep in mind that operating a drone requires a license.
If having your own drone is out of the question, you can always opt to partner with a drone services provider who has the license and the expertise to fly drones safely.
GinoBot, Inspiring Inventors of the Future with STEM Disciplines, Launches on Kickstarter
The all-in-one smart toy incorporates science, technology, engineering and mathematics disciplines with playtime, in a hands-on way.
Astoria, New York – (May 3, 2021) Keeping children entertained and engaged in today’s tech-driven world is now easier with GinoBot. The tool that implements a fun, hands-on experiencewith unlimited expansion potential for learning STEM disciplines, computational thinking, and digital literacy is launching on Kickstarter today.
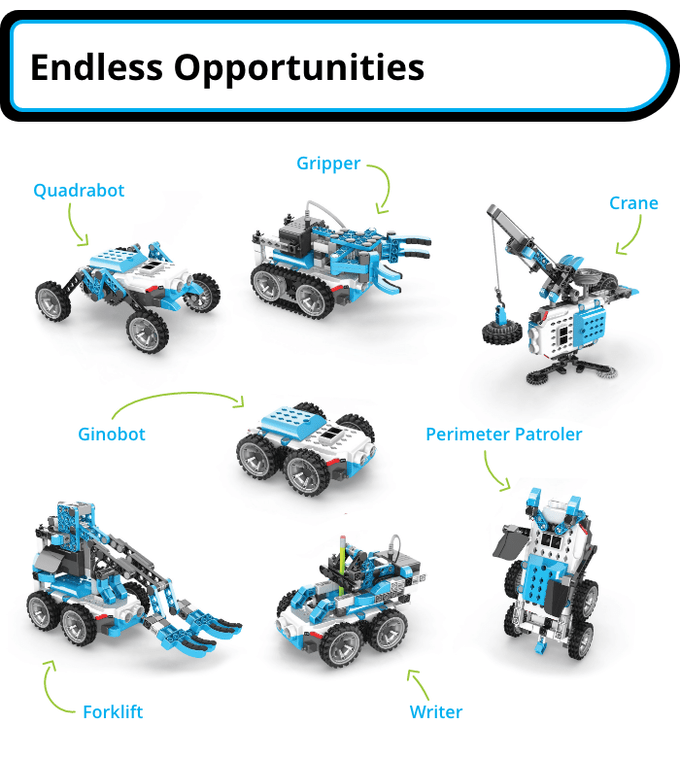
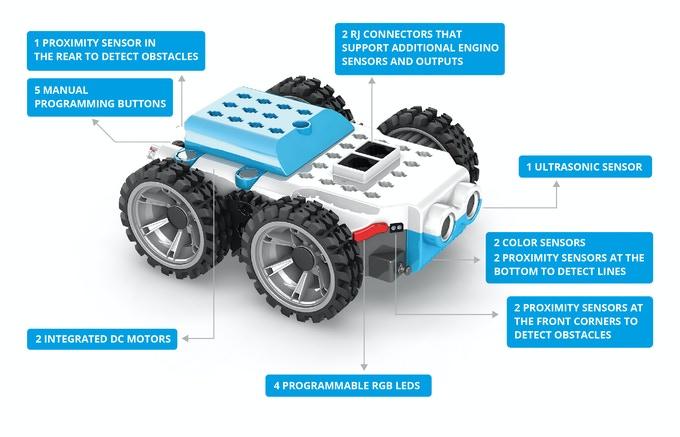
GinoBot seamlessly blends playtime with advanced learning to sharpen a child’s mind for the future. From plug-and-play robot to high-end coding and electronics, the progression of skills with GinoBot is unlimited. Children ages 6+ can build simple or complex models with GinoBot’s scalable, and compatible design.
It features KEIRO software for block-based programming, which is compatible with a PC (Windows, Linux, MAC OS) and smart devices (Google Play, Apple Store). GinoBot has Bluetooth and WiFi connectivity, as well as a micro USB connector. It can also connect with 3rd party hardware like Arduino, Microbit and Raspberry Pi, among others.
Science, technology, engineering and math, or STEM toys are the future. GinoBot is a solution for children to learn 21st century skills that lets them playfully learn how to code, design, build, and rebuild models quickly, no matter their age or learning style.
“Children are our future and we believe they are all gifted with the power to perform astonishing technological feats,” said Costas Sisamos, founder and CEO of Engino. “As STEM learning principles become more prominent in our children’s curriculum, GinoBot is a great learning tool that will keep young minds hungry to explore, design and create enabling them to experience the limitless thrill of scientific discovery.”
GinoBot is a great way to invest in your child’s imagination and expand their creativity. To pre-order, visit pr.go2.fund/ginobot.
About Engino
Engino is a toy manufacturer that specializes in construction toys and smart educational toys, and have been at the vanguard of the STEM education movement for the past 15 years. A few years ago, Engino joined the robotics market and started developing programmable robots. These robots are supported with an extensive curriculum so children can learn the digital-side of thinking and how to do programming, coding, and more. For more information, visit https://www.engino.com/.
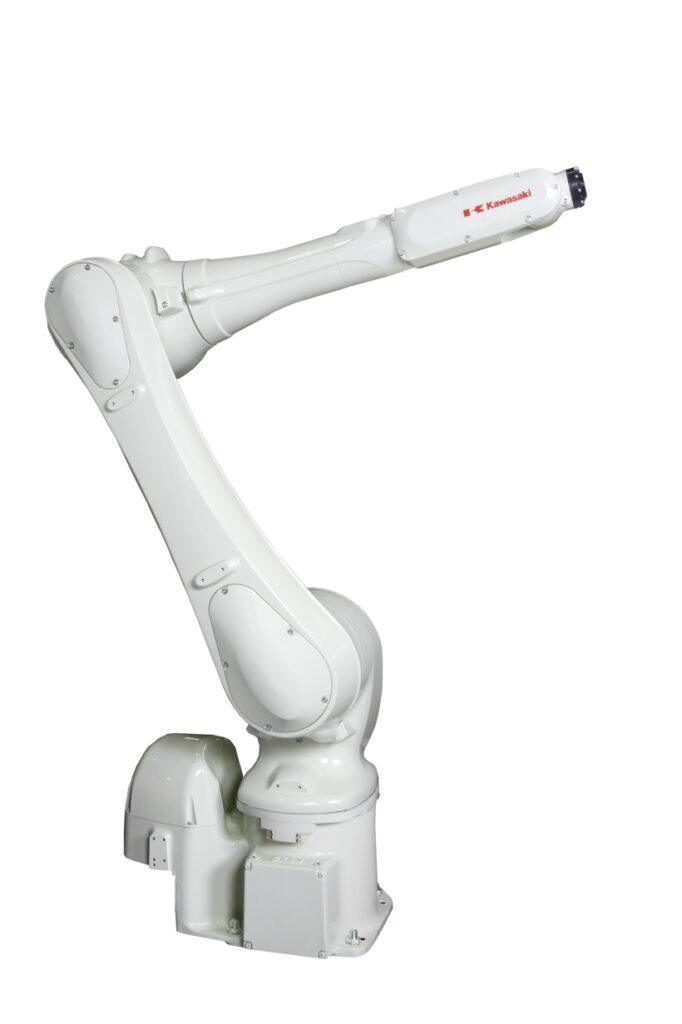
Kawasaki Introduces RS013N Medium Payload Robot to North American Market
WIXOM, MI, USA — Kawasaki Robotics’ dedication to continuous improvement is evident in their technically advanced general purpose robot line: the R series. With a history dating back to the mid-1980s, Kawasaki has continued to refine their general purpose robot arms over time, routinely producing robots with wider working ranges, faster cycle times, longer reach, and increased torque. The release of the RS007N/L models in 2017 marked the beginning of a new generation of Kawasaki R series and the latest model, the RS013N, is no exception. By offering a 13 kg payload capacity, a wide working range, small footprint and IP67-classi ed design, the NEW RS013N sets the industry benchmark for small-to-medium payload robots.
Industry Leading Speed & Flexibility
The new robot’s design includes a new arm structure, drive system and lighter main unit, which enables high speeds and a large working area. Its 1,460 mm reach is the largest in its class, allowing for installation flexibility and use in a wider variety of applications. The RS013N robot also leads its class in speed, resulting in reduced cycle times and increased productivity.

Kids learn coding with the new Sparklekits

What is Sparklekits?
Sparklekits is a STEM kit with a set of modular magnetic blocks & puzzles that promotes educational discovery through open-ended play and hands-on experience using advanced technology. It is extremely easy to assemble and super intuitive to use. It is a better and more fun STEM education tool that integrates building, learning, coding and play.

Advanced Design
Sparklekits breaks down complicated engineering into easy-to-assemble, functional magnetic modular blocks that children can use without using any cables, screws or tools. Kids can’t get it wrong, creating an environment that invites experimentation and creativity while building confidence.
These building blocks are infused with magical, seamless technology that allows kids to code, build, and explore at their own pace. Built-in games and challenges let kids between 5-12 learn through play, and it’s fully LEGO-compatible!
https://www.kickstarter.com/projects/sparkleteam/sparkle-kits
Tombot, creator of the first affordable, FDA-regulated medical robotic animal, is now accepting investors
SANTA CLARITA, CALIF. (PRWEB) MAY 03, 2021
Tombot, creator of Jennie, the World’s first affordable, FDA-regulated medical grade robotic animal designed to stimulate emotional attachment, just launched their equity crowdfunding campaign and is looking to raise up to the maximum permissible funding goal of $5M via a Regulation Crowdfunding (Reg CF) offering on StartEngine!
Millions of people facing health adversities cannot safely or practically care for a live animal companion. Jennie, selected as one of TIME’s 2020 Best Inventions, was designed to significantly reduce the behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia, and reduce the need for psychotropic medications, for the 90M+ seniors with dementia and pre-dementia mild cognitive impairment worldwide.

