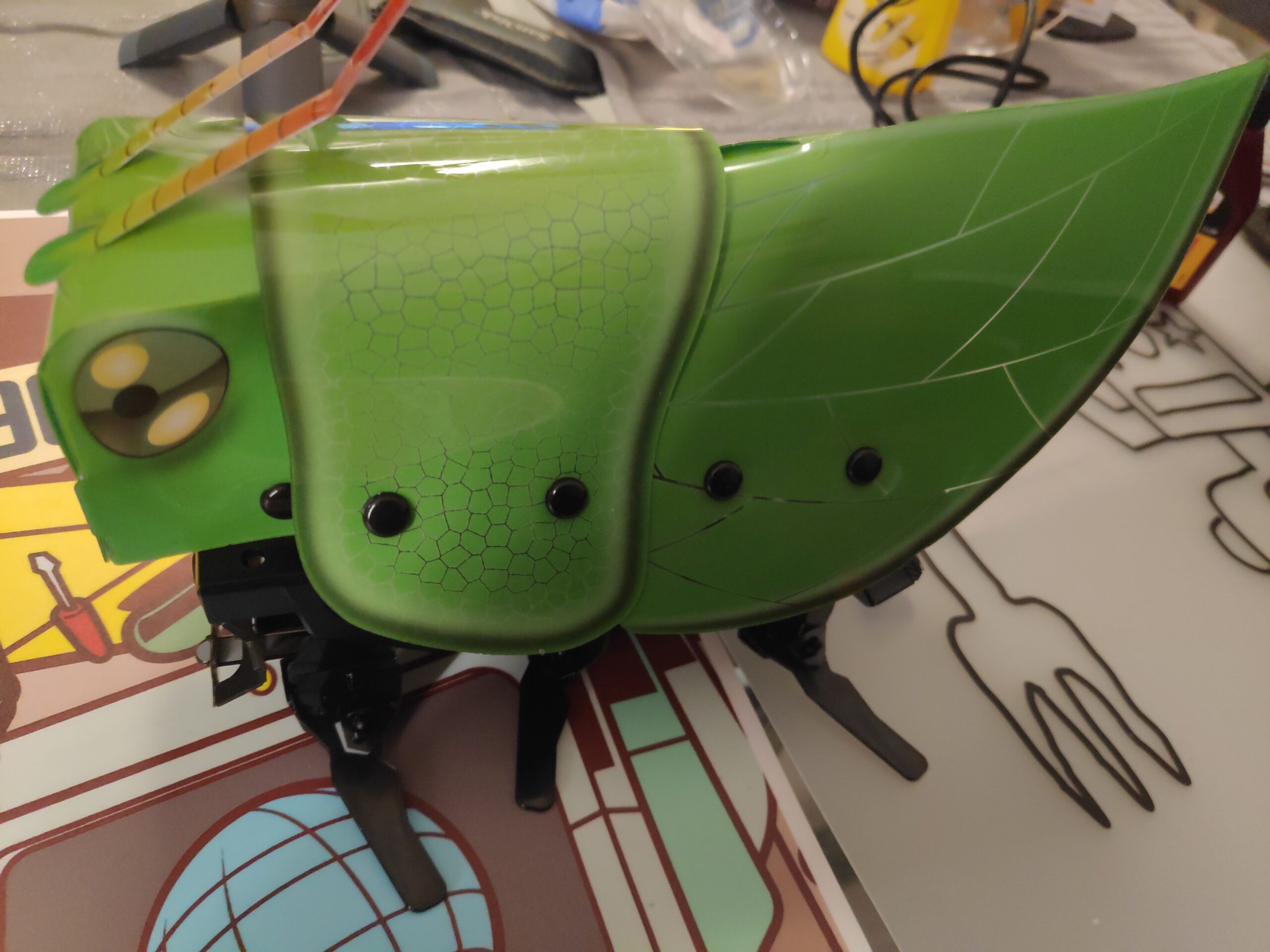
LITTLETON, Colo., 2022 /PRNewswire/ — Luxonis, a Colorado-based robotic vision platform, is thrilled to introduce rae, its first fully-formed and high-powered personal robot. Backed by a Kickstarter campaign to help support its development, rae sets itself apart by offering a multitude of features right out of the box, along with a unique degree of experimental programming potential that far exceeds other consumer robots on the market. The most recent of a long line of Luxonis innovations, rae is designed to make robotics accessible and simple for users of any experience level.

„rae is representative of our foremost goal at Luxonis: to make robotics accessible and simple for anyone, not just the tenured engineer with years of programming experience,“ said Brandon Gilles, CEO of Luxonis. „A longstanding truth about robotics is that the barrier to entry sometimes feels impossibly high, but it doesn’t have to be that way. By creating rae, we want to help demonstrate the kinds of positive impacts robotics can bring to all people’s lives, whether it’s as simple as helping you find your keys, talking with your friend who uses American Sign Language, or playing with your kids.“
At its core, rae is a world-class robot, and includes AI, computer vision and machine learning all on-device. Building upon the technology of the brand’s award-winning OAK cameras, rae offers stereo depth, object tracking, motion estimation, 9-axis IMU data, neural inference, corner detection, motion zooming, and is fully compatible with the DepthAI API. With next-generation simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM), rae can map out and navigate through unknown environments, and is preconfigured with ROS 2 for access to its robust collection of software and applications.
Featuring a full suite of standard applications, rae offers games like follow me and hide and seek, and useful tools like barcode/QR code scanning, license plate reading, fall detection, time-lapse recording, emotion recognition, object finding, sign language interpretation, and a security alert mode. All applications are controllable through rae’s mobile app, which users can use from anywhere around the world. They can also link with Luxonis‘ cloud platform, RobotHub, to manage customizations, download and install user-created applications, and collaborate with Luxonis‘ user community.
Crowdfunding campaigns and developing trailblazing products that roboticists love is something that is in Luxonis‘ DNA, which is made evident by its established track record of two previously successful campaigns. Luxonis‘ first Kickstarter for the OpenCV AI Kit in 2021 raised $1.3 million with 6,564 backers, and the second for the OAK-D Lite raised $1.02 million with 7,988 backers. With the support of robot hobbyists and brand loyalists, as well as new target backers such as educators, students, and parents, rae is en route to leave an impact as a revolutionary personal robot that isn’t limited to niche demographics.
Pricing for rae starts at $299 and international shipping is available.
Interested backers can learn more about the campaign here.
For more information about Luxonis, visit https://www.luxonis.com/
About Luxonis:
The mission at Luxonis is robotic vision, made simple. They are working to improve the engineering efficiency of the world through their industry leading and award winning camera systems, which embed AI, CV, and machine learning into a high performing, compact package. Luxonis offers full-stack solutions stretching from hardware, firmware, software, and a growing cloud-based management platform, and prioritizes customer success above all else through the continued development of their DepthAI ecosystem.